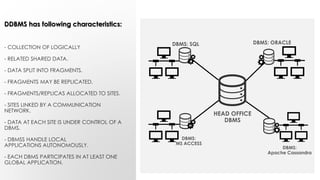
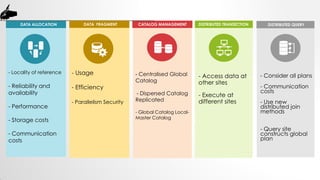
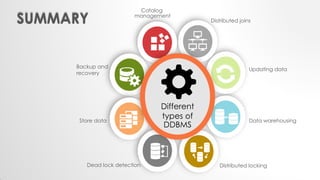
The document discusses distributed database management systems (DDBMS), highlighting their architecture, characteristics, and benefits such as improved processing power and local autonomy. It addresses the challenges facing DDBMS, including complexity in design and security concerns. Additionally, the document outlines fundamental rules and concepts related to distributed transactions and query processing.

![DISTRIBUTED DATABASE
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
MALAYSIA
INDONESIA
CHINA
KOREA
JAPAN
INDIA
PHILIPPINE
AUSTRALIA
HONGKONG
Separate DBMS
CONCEPT
DDMS
THAILAND](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hofferpptxddbms-150314025858-conversion-gate01/85/Distributed-Database-2-320.jpg)