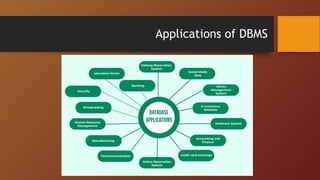
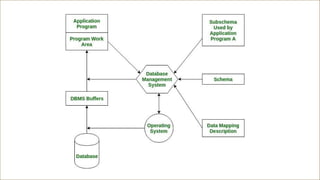
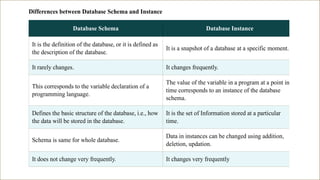
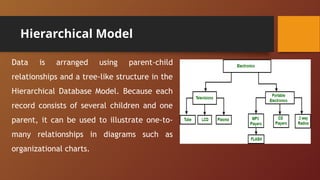
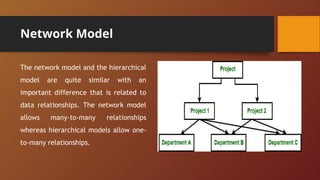
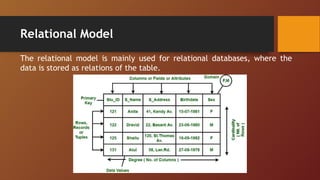
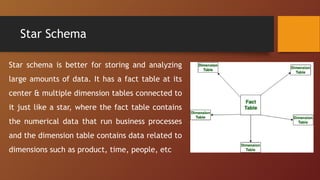
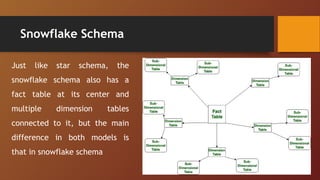
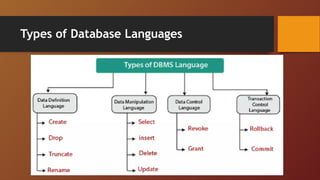
A Database Management System (DBMS) is software designed to manage and organize data efficiently, allowing users to create, modify, and query databases while ensuring security and access control. It includes features such as data modeling, storage and retrieval, concurrency control, data integrity, and backup mechanisms, with two main types being Relational (RDBMS) and Non-relational (NoSQL) systems. DBMS also facilitates collaboration, data sharing, and provides strong security measures to protect sensitive information.