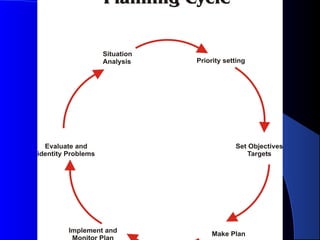
This document outlines the essential components of a Health Management Information System (HMIS). It discusses the inputs, processes, and outputs of an HMIS and how it provides decision support. Key aspects covered include data collection, standardization, indicators, uses for planning, management, and assessment, and sources of health information such as vital events, infectious diseases reporting, and health facilities records. The document also defines health institutions and care providers and discusses data collection instruments and transmission of reports from facilities to higher levels.