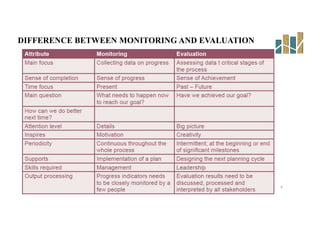
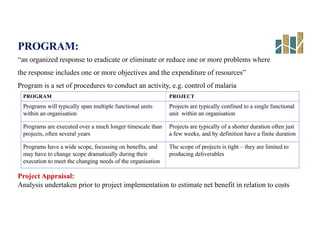
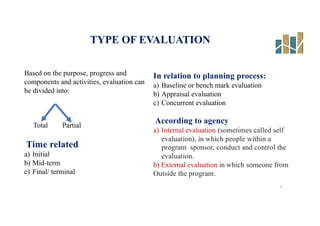
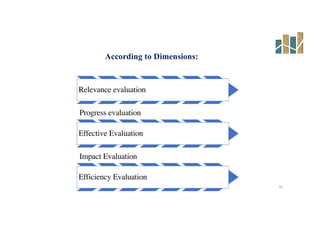
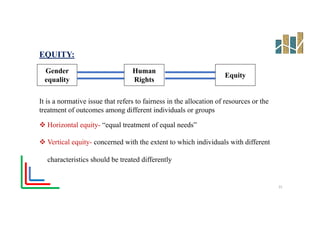
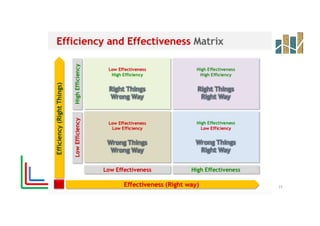
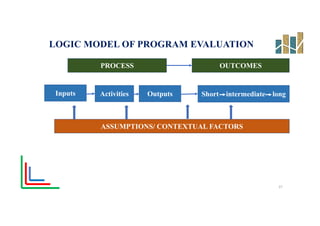
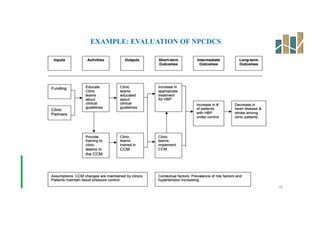
This document provides an evaluation of a health program. It discusses the purpose and types of program evaluation, including formative vs summative and internal vs external evaluations. Key aspects of programs that can be evaluated are outlined, such as accessibility, equity, quality, effectiveness, efficiency, and sustainability. A variety of tools for evaluation are mentioned, including surveys, case studies, and root cause analysis. The document also provides an example of evaluating India's National Program for the Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases and Stroke.