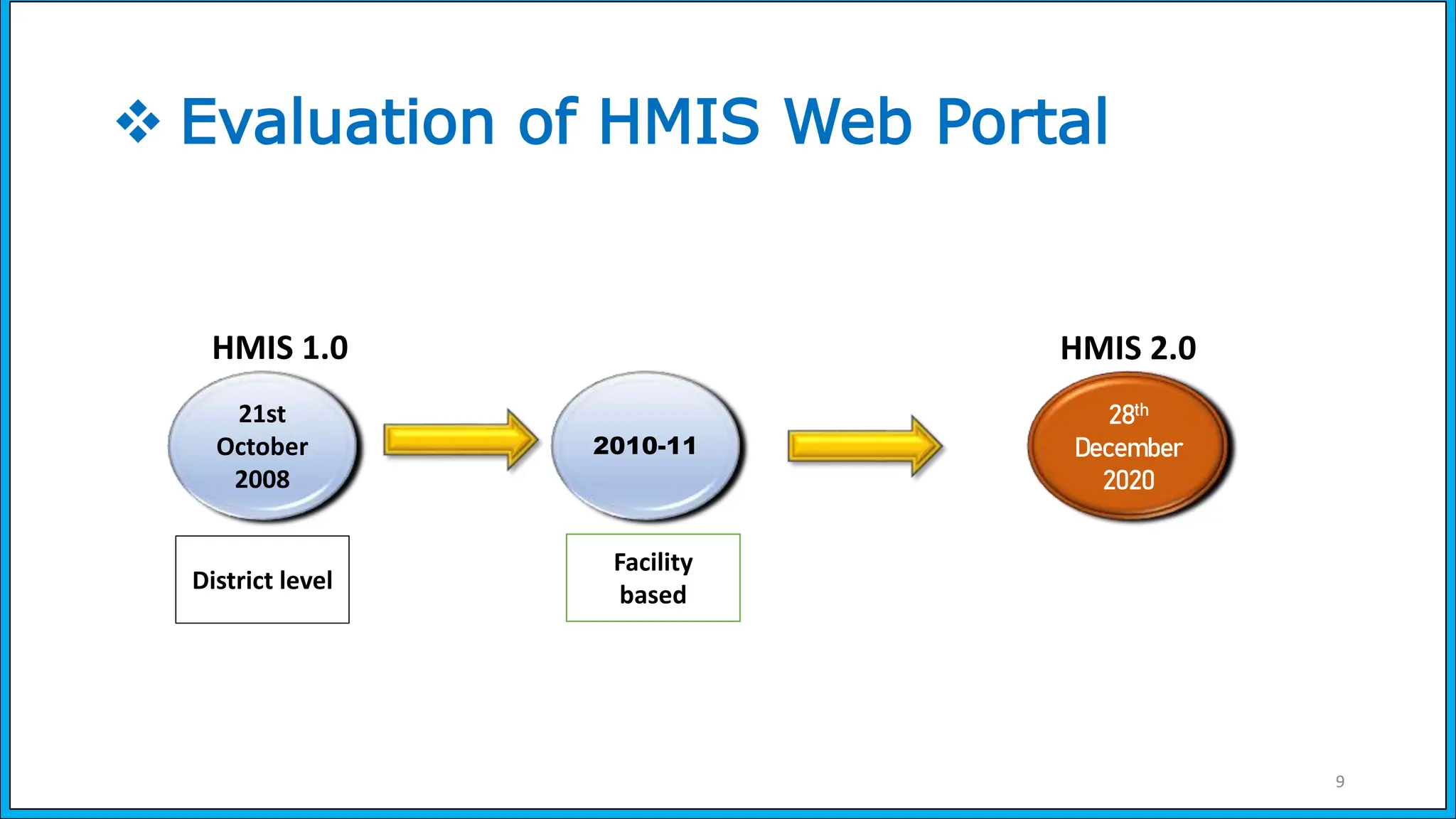
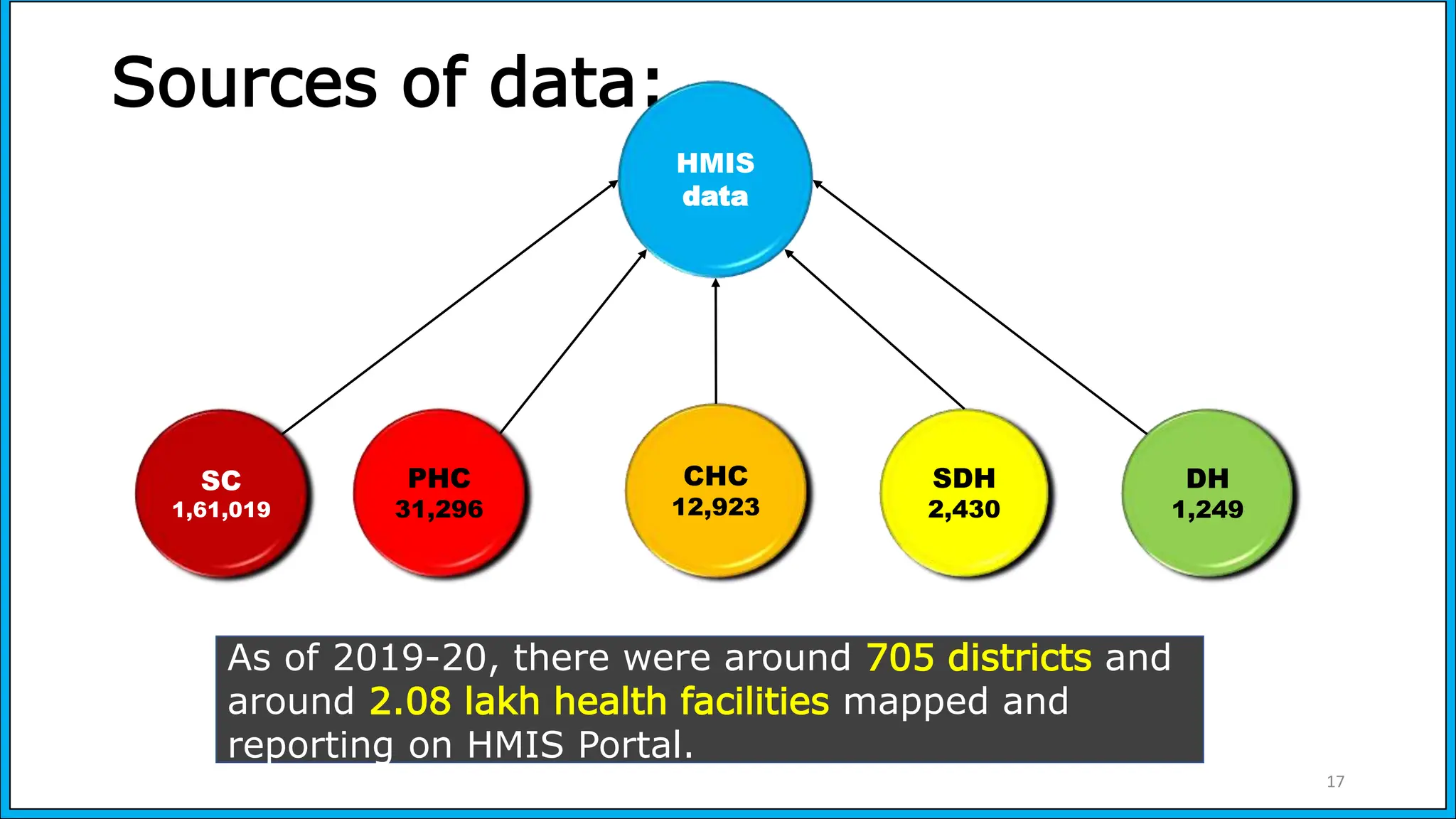
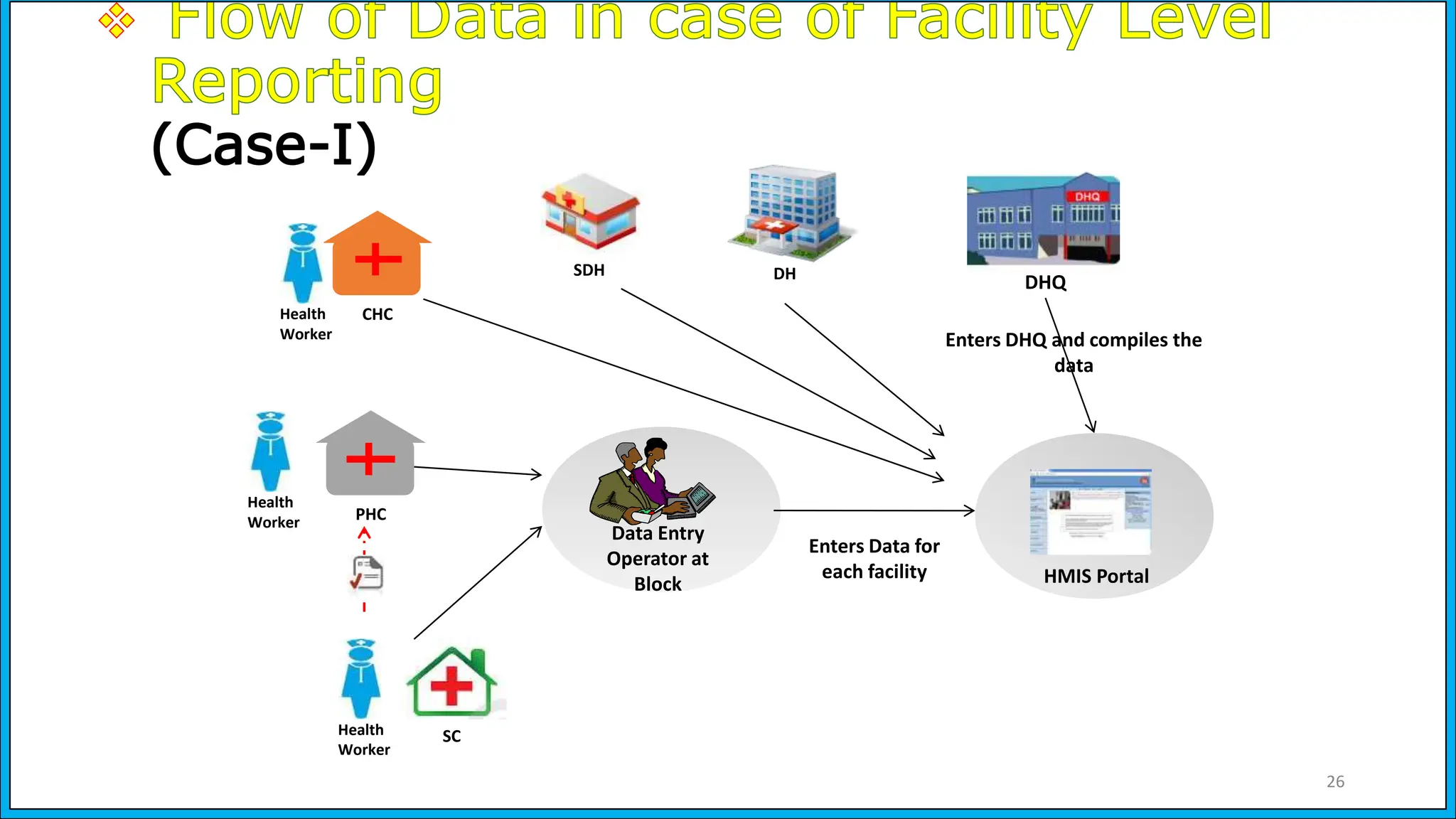
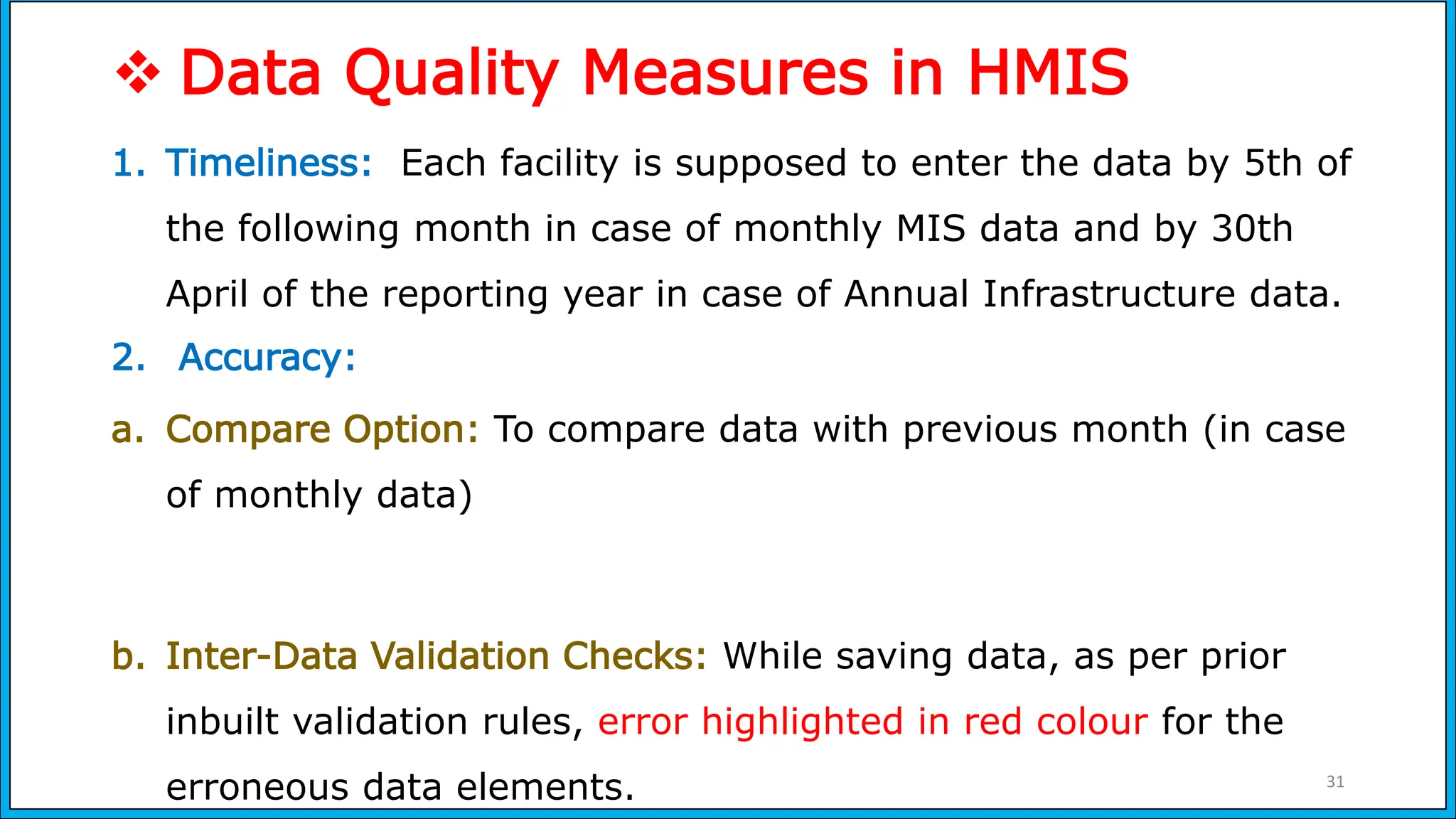
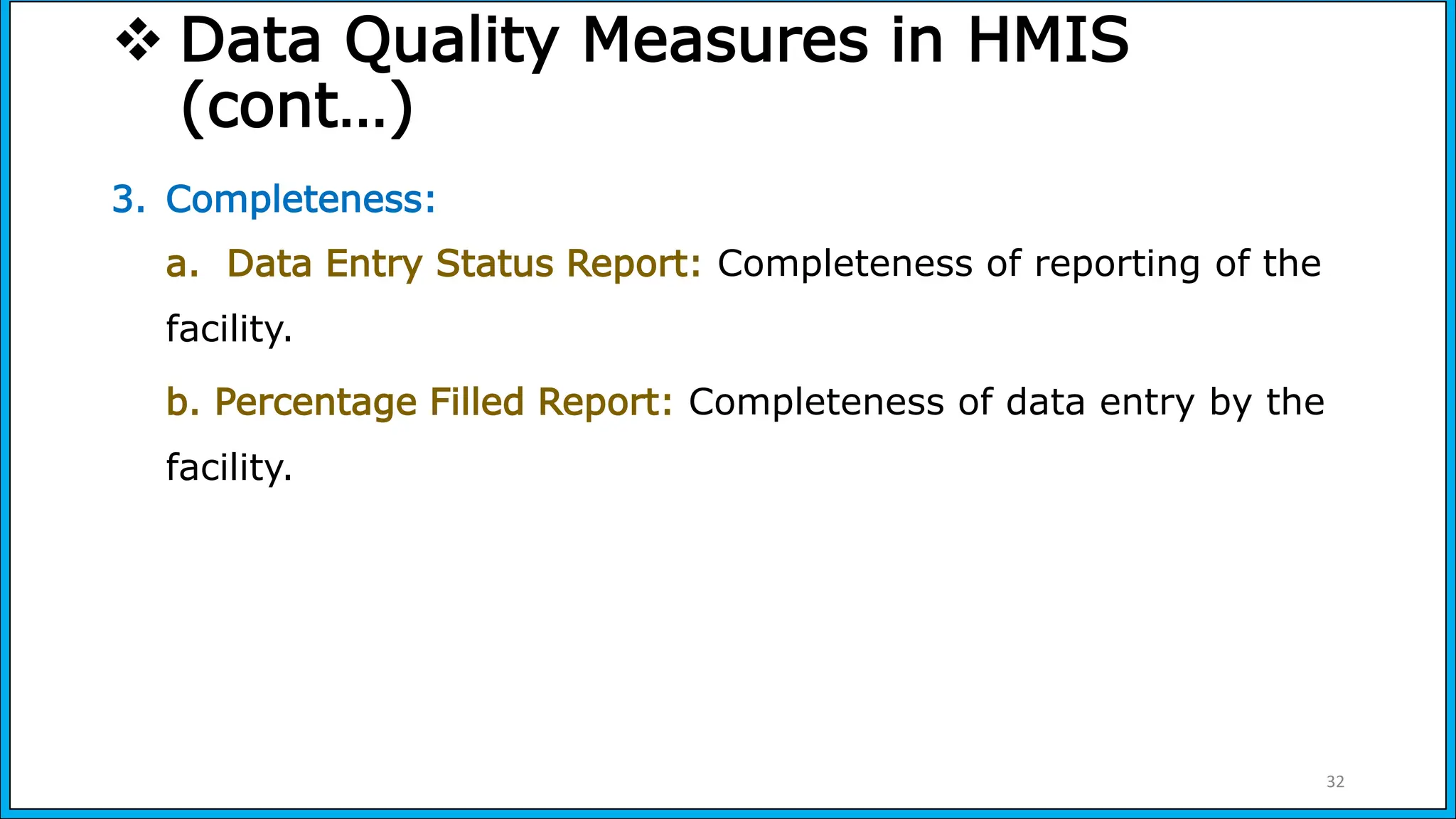
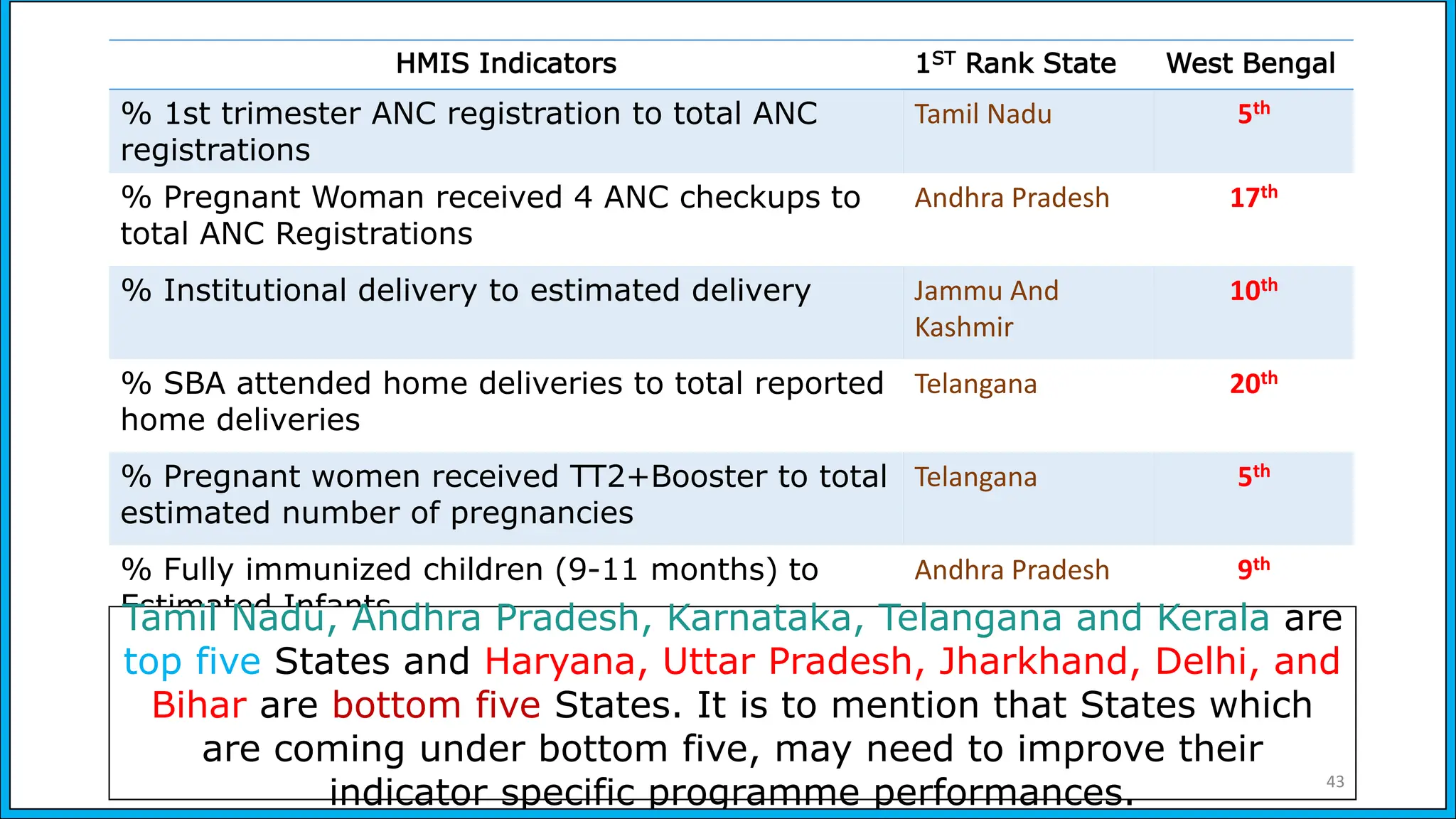
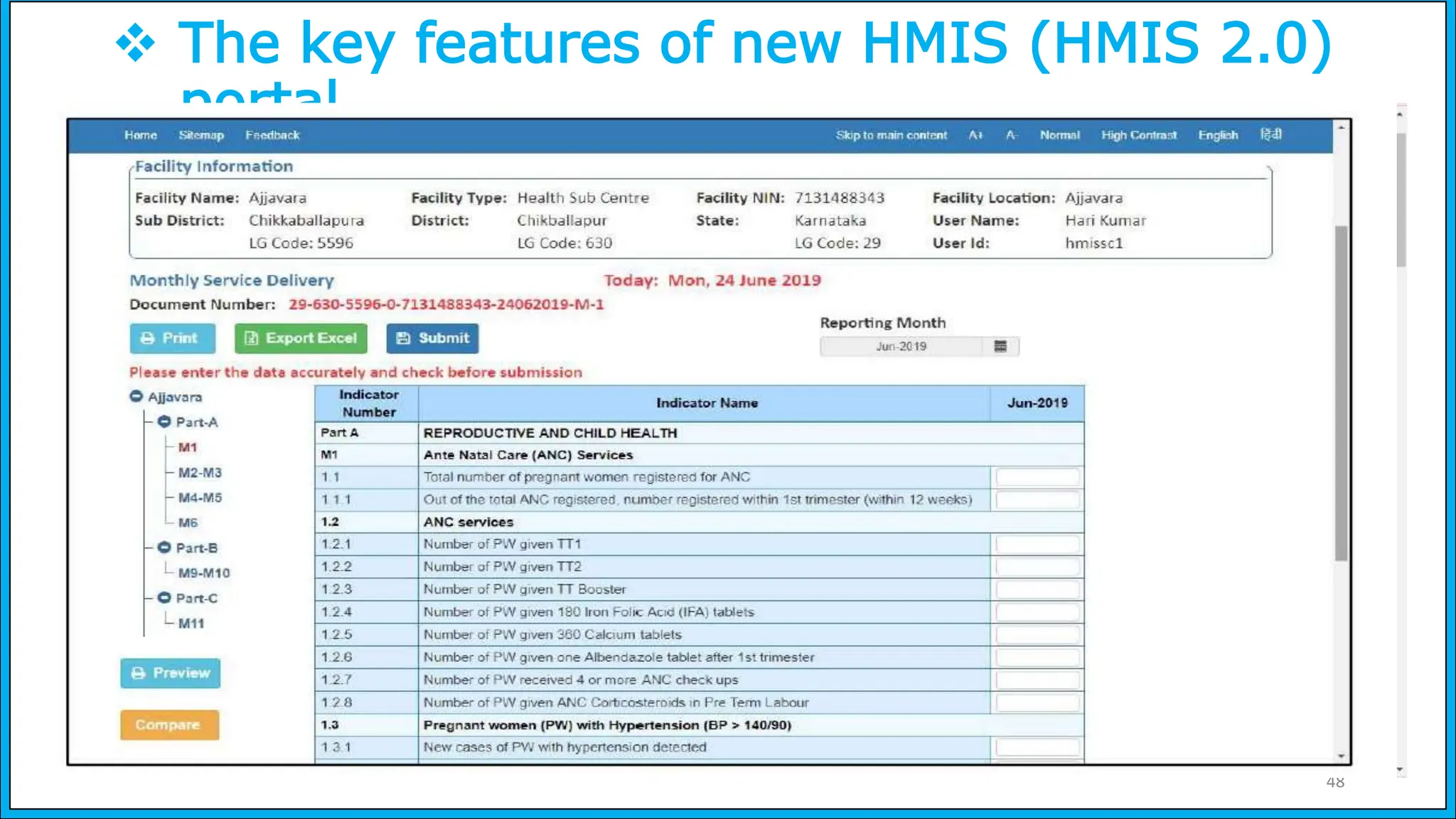
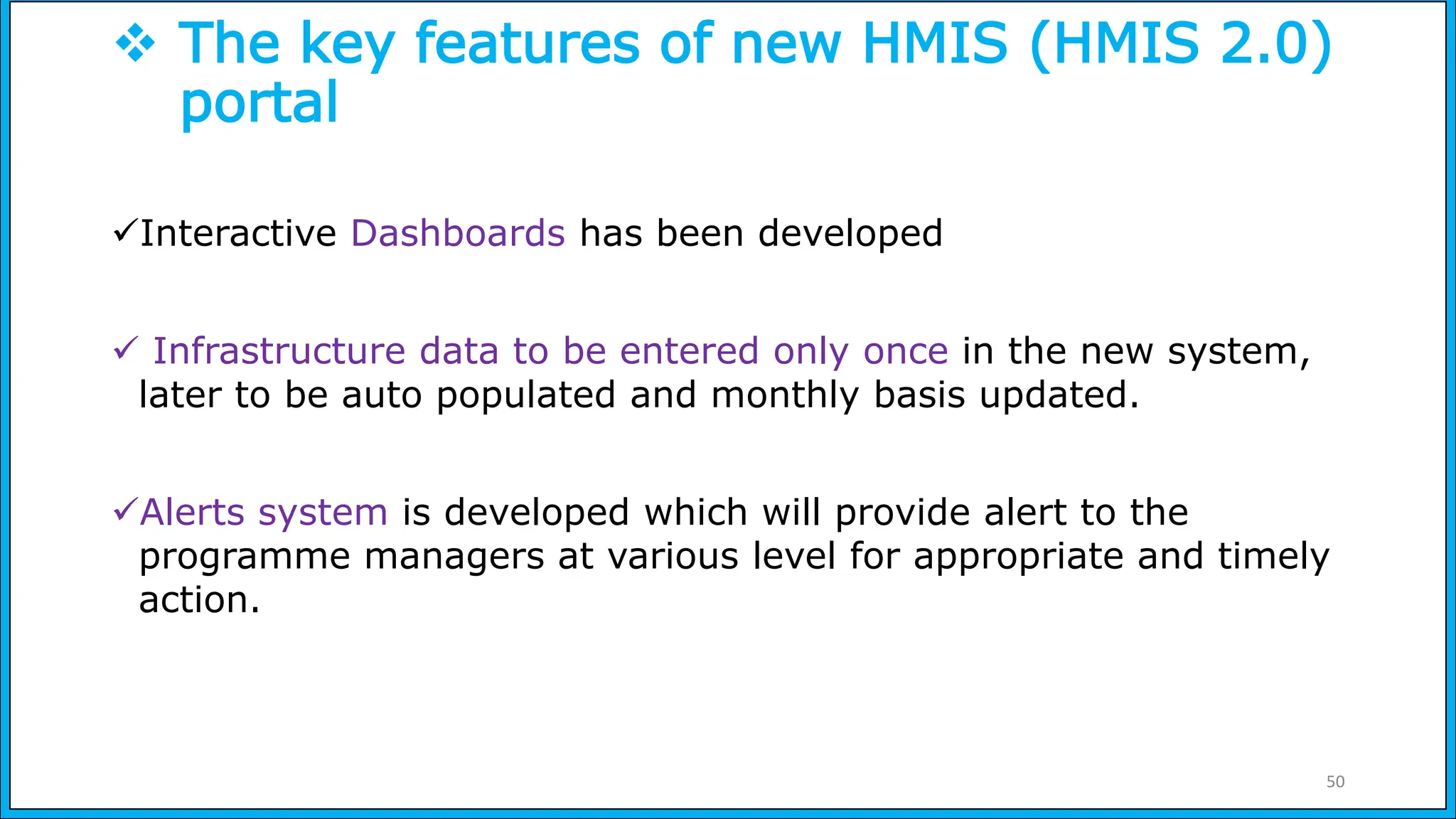
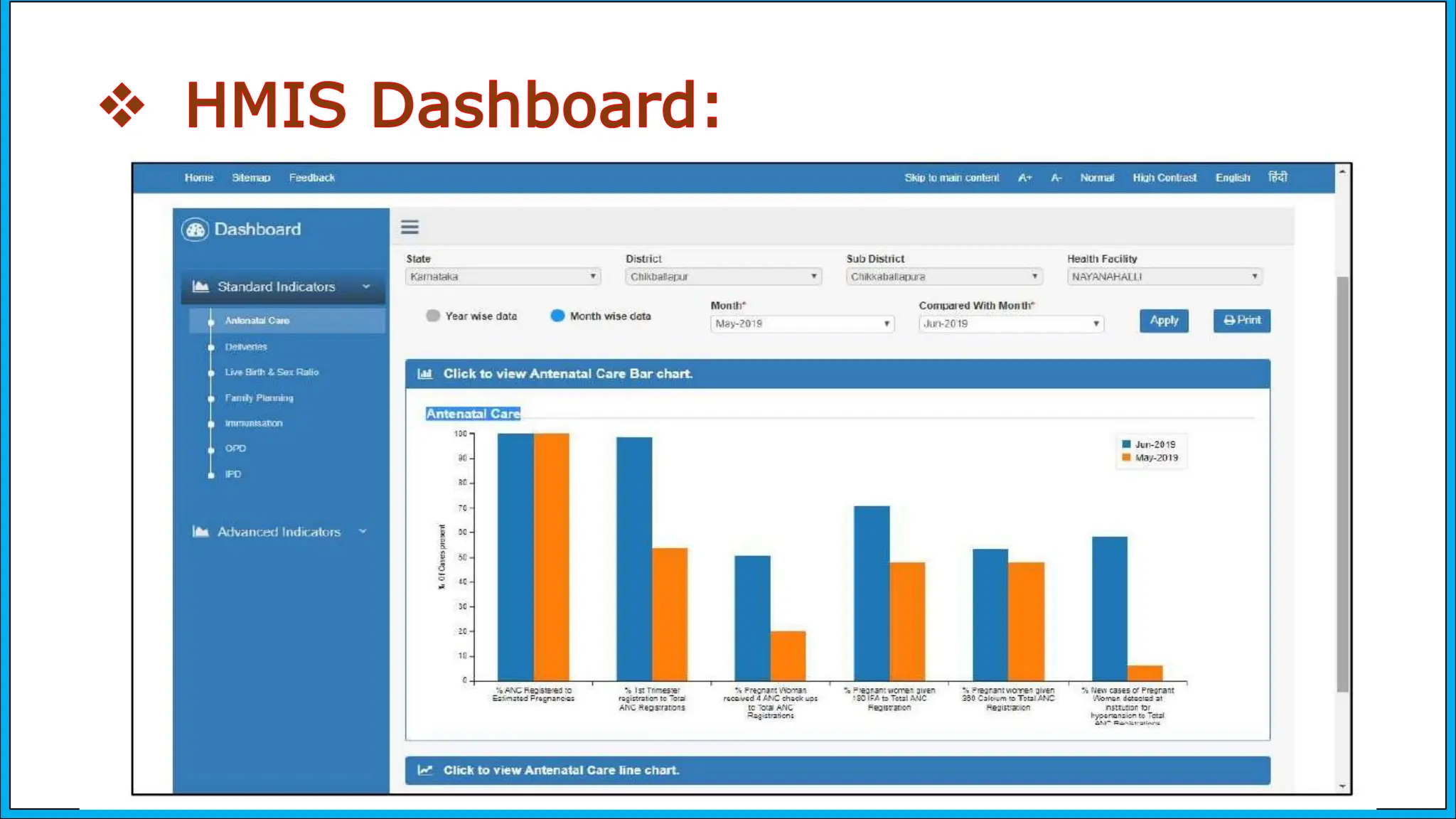
The document discusses the Health Management Information System (HMIS) in India, highlighting its role in monitoring health programs and facilitating evidence-based decision-making. It outlines the objectives, data collection processes, and recent upgrades like HMIS 2.0, which enhances data accessibility and quality. The HMIS is crucial for health policy formulation, program evaluation, and improving healthcare delivery efficiency.


































![1. HMIS-Health Management Information System [Internet]. [cited 2022 Jan 7]. Available from:
https://hmis.nhp.gov.in/#!/aboutus
2. Dehury RK. The progress and impact of Health Management Information System (HMIS) in monitoring and
evaluation of health programs in India. 3(4):7.
3. Pacific WHORO for the W. Developing health management information systems : a practical guide for
developing countries [Internet]. Manila : WHO Regional Office for the Western Pacific; 2004 [cited 2022
Mar 20]. Available from: http://iris.wpro.who.int/handle/10665.1/5498
57](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/healthmanagementinformationsystemshmis-240429143214-4acc13e5/75/Health-Management-Information-Systems-HMIS-pptx-46-2048.jpg)