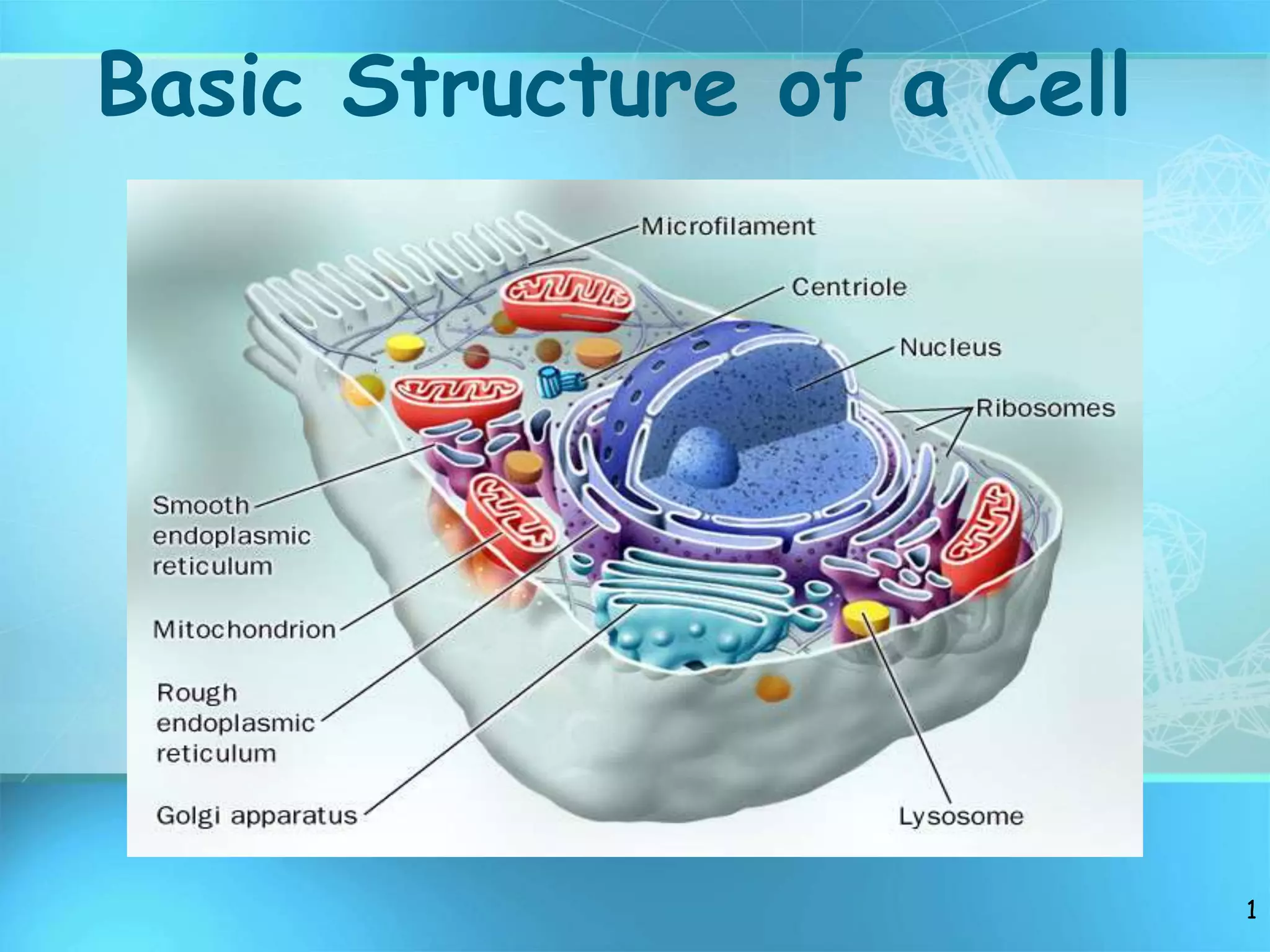
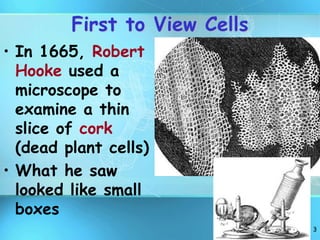
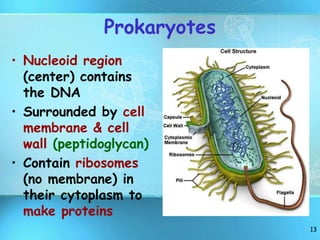
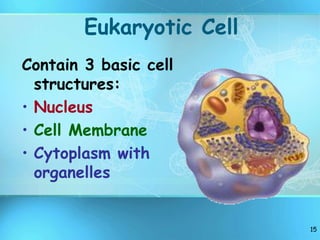
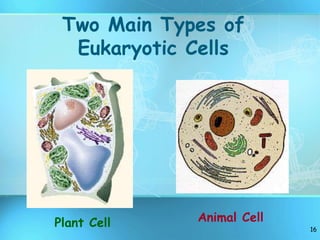
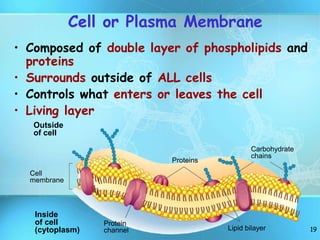
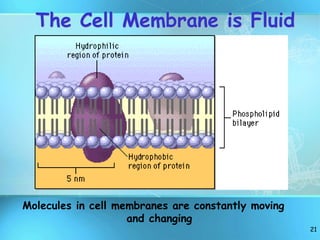
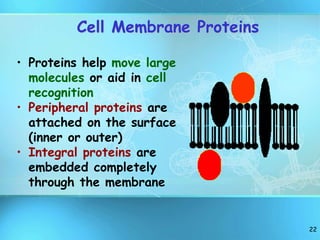
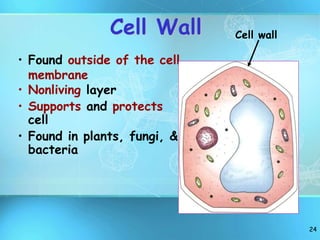
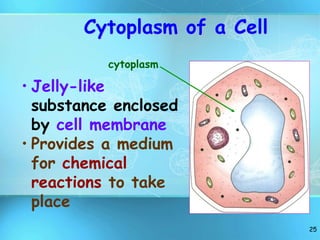
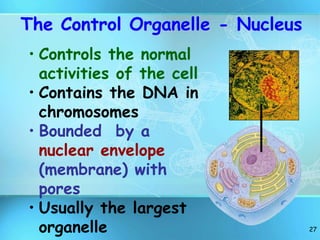
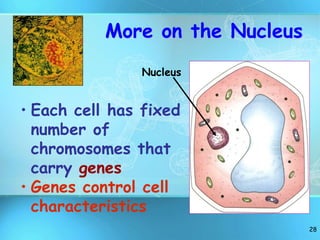
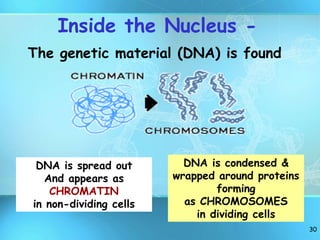
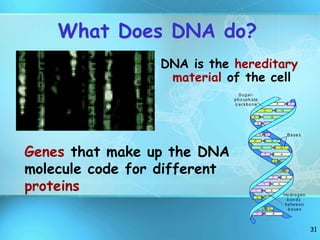
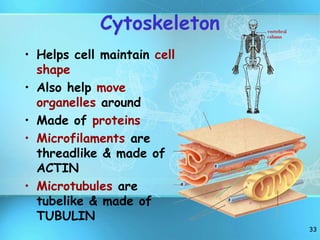
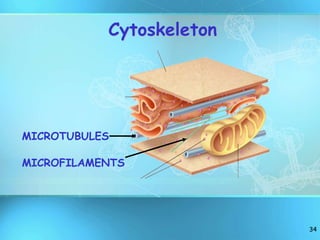
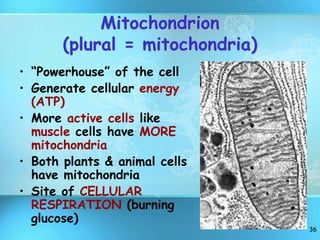
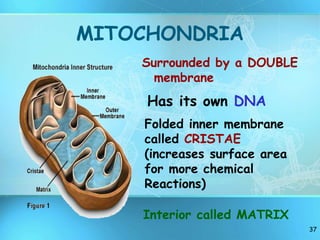
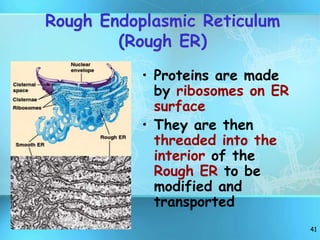
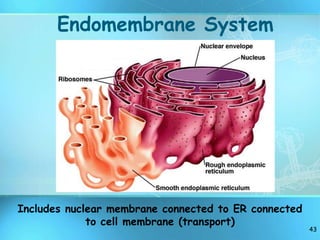
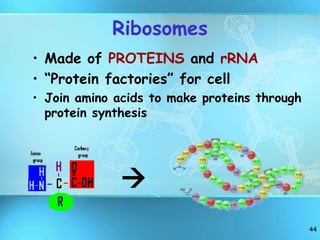
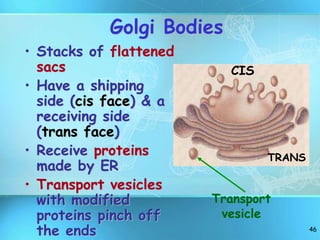
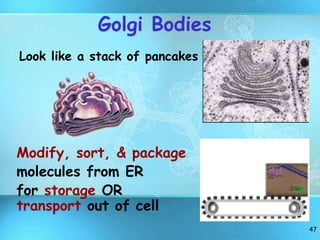
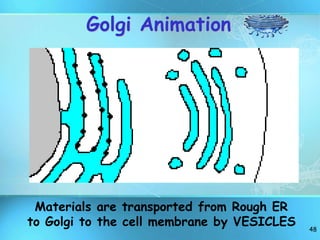
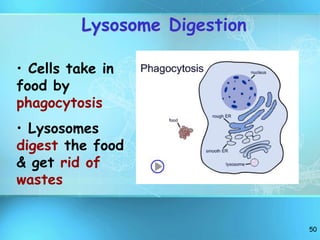
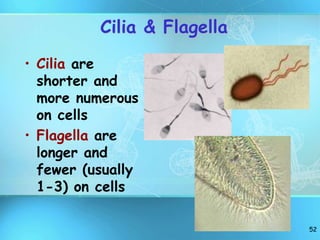
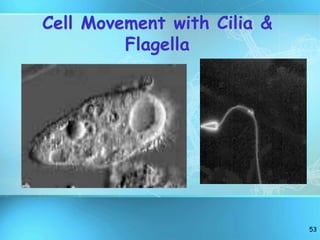
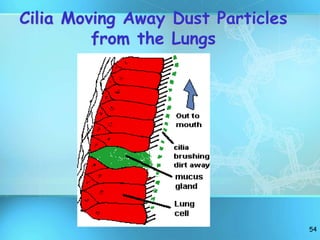
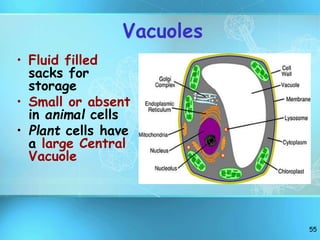
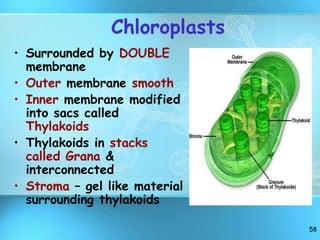
The document summarizes key discoveries and concepts regarding cell structure and function. It describes how Hooke and Leeuwenhoek first observed cells under microscopes in the 1600s. In the 1830s, Schleiden and Schwann developed the cell theory which states that all living things are made of cells, cells are the basic unit of structure and function, and cells come from preexisting cells. The document then discusses the basic structures of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, and various organelles like mitochondria, chloroplasts, the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, lysosomes, and vacuoles.