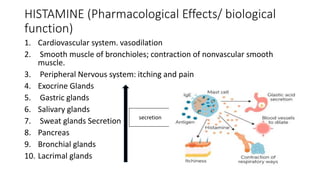
Histamine is an important chemical messenger that mediates allergic and inflammatory responses. It is synthesized from the amino acid histidine and stored in mast cells. Upon release, histamine binds to four types of histamine receptors (H1-H4) to produce various effects throughout the body, such as gastric acid secretion and smooth muscle contraction. Antihistamines are commonly used to treat allergic reactions by blocking H1 receptors, while H2 receptor antagonists inhibit gastric acid production. Histamine plays a key role in many physiological processes and understanding its receptors has led to treatments for conditions like ulcers, allergies, and inflammation.