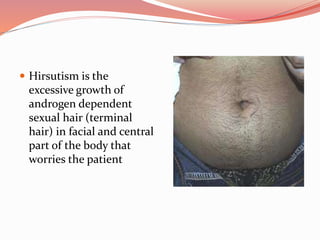
This document discusses the clinical approach and management of hirsutism and virilism. It defines hirsutism as excessive hair growth in androgen-dependent areas, while virilism is a more severe form involving additional masculine features. The clinical approach involves assessing a patient's history and examination findings to determine the severity and underlying cause. Management aims to remove excess hair, suppress androgens, and remove their source. Treatment options depend on the site of androgen overproduction and may include oral contraceptives, antiandrogens, cosmetic treatments like bleaching or laser, and surgery to remove tumors.