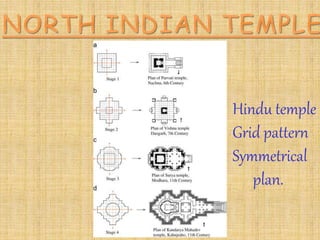
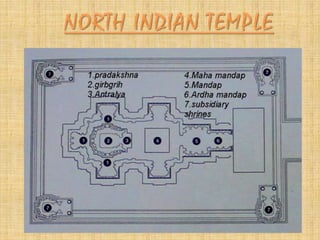
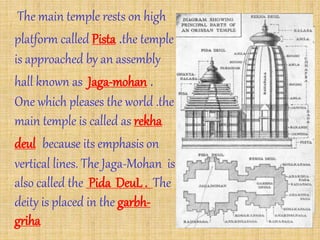
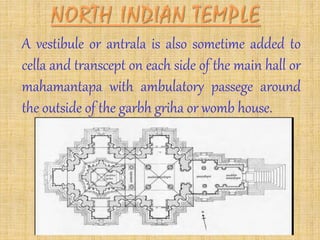
The document summarizes different styles of Hindu temple architecture across India from 600 AD to the present. It discusses the key features of seven regional styles:
1) Orissa style temples from 800-1250 AD known for curved shikhara towers and profusely ornamented exteriors. Examples given are Jagannath Temple and Konark Sun Temple.
2) Kashmir style temples from the 8th century featuring Graeco-Roman style columns like at Martand Temple.
3) Khajuraho style temples from 950-1050 AD with a basic latin cross plan and intricate carvings, like Kandariya Mahadev Temple.
4) Rajputana