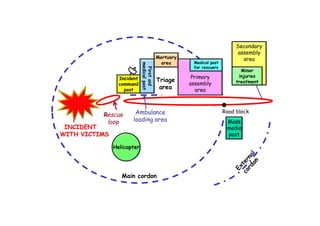
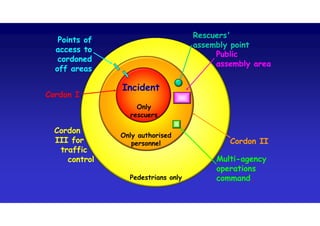
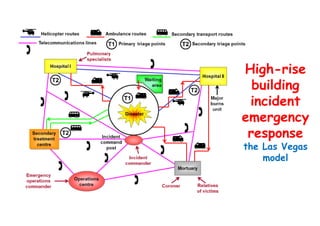
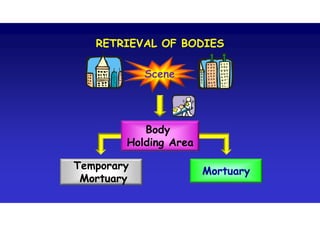
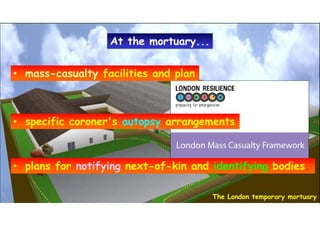
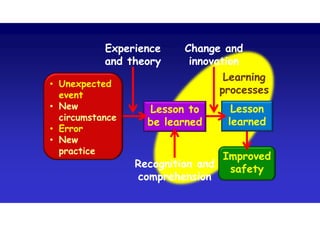
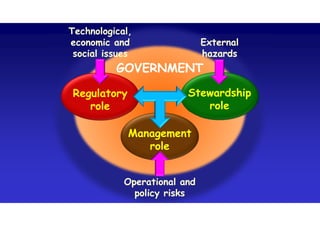
The document discusses the vulnerabilities of high-rise buildings during disasters, citing historical incidents such as the Grenfell Tower fire and the World Trade Center attack. It highlights the importance of fire safety measures, emergency response protocols, and the need for regulatory reforms to improve building safety. The overarching themes include the challenges in evacuation, the impact of design flaws, and the necessity for a cultural shift towards prioritizing safety in building regulations.