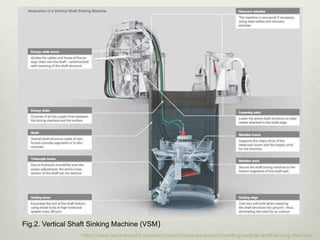
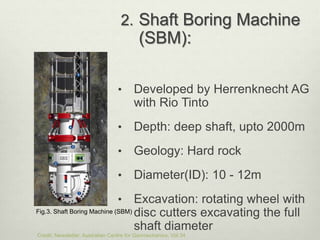
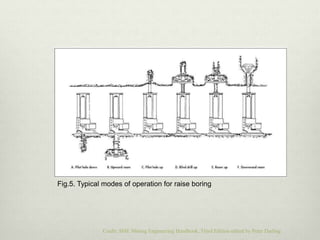
Mechanized shaft sinking methods such as shaft drilling, shaft boring, raise boring, and box-hole drilling have advantages over conventional drill-and-blast methods including higher sinking rates, improved safety, and reduced costs. Shaft boring machines excavate the full shaft diameter simultaneously while shaft drilling reams the shaft from an initial pilot hole. Recent developments include the vertical shaft sinking machine for shallow depths and soft rocks, and the shaft boring machine paired with pilot hole drilling for deep shafts in hard rock. Mechanized methods allow for simultaneous excavation, mucking, and ground support.
















![References
[1] Auld, A. Shafts and Raises in Rock Masses. Edited by Bell, F.G. (1994).Chapter
24.,Sec.24.3. In,Engineering in Rock Masses, paperback edition, pp.480-502. ISBN: 0-7506-
1965-1.
[2] Neye,E., Burger,W.,…& Kunstle,B. Future Trends in Shaft Development Edited by
Kicki,J., Sobczyk,E.J. & Kaminski,P. (2015). In,Vertical and Decline Shaft Snking: Good
Practices in Techniques and Technology. International Mining Forum 2015.ISBN: 978-1-138-
02820-3.
[3] Herrenknecht AG. Products Brochure. Available at www.herrenknecht.com
[4] Tuck,M.A. Underground Horizontal and Inclined Developments. Edited by Darling,P.
(2011). Chapter 12.4.In SME Mining Engineering Handbook, 3d ed.,pp.1195-1196. ISBN:
978-0-87335-264-2.
[5] Frenzel,C., Burger,W., Delabbio,F. Shaft Boring Systems for Mechanical Excavation of
Deep Shafts. In, Newsletter,Australian Center for Geomechanics, vol.34, May 2010, pp.2-4.
[6] Australian Mining (2014), Herrenknecht’s New Shaft Boring Enlargement Technology,
Available at www.australianmining.com.au](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/highspeedmechanisedshaftsinking-180314184131/85/High-speed-mechanised-shaft-sinking-20-320.jpg)