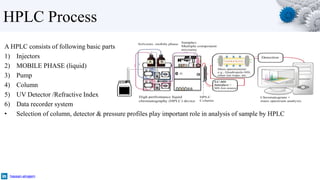
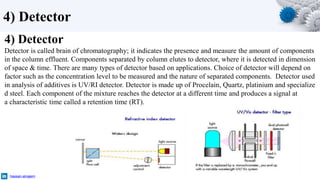
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is a technique in analytical chemistry used to separate, identify, and quantify each component in a mixture. HPLC works by passing a pressurized liquid solvent containing the sample mixture through a long column packed with a stationary solid phase. The components within the mixture interact differently with the two phases at varying rates during passage through the column, allowing separation. A detector then measures the separated components as they exit the column, allowing for identification and quantification.