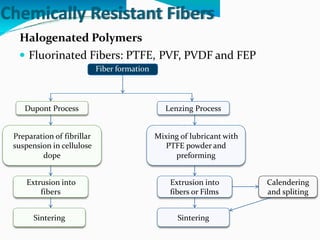
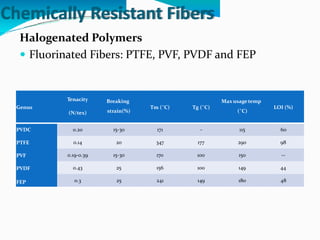
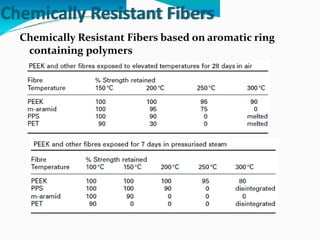
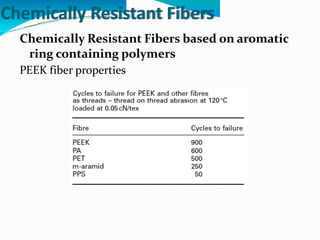
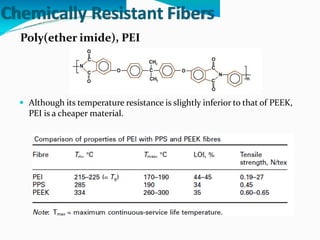
Chemically resistant fibers are essential for environments requiring high resistance to chemicals and heat, utilized in applications like filtration, protective textiles, and geotextiles. These fibers are characterized by their stable chemical bonds and structural integrity, often made from halogenated or aromatic polymers, and feature properties such as strong thermal resistance and low flammability. Notable examples include poly(vinylidene chloride), PTFE, and poly(etheretherketone), each providing specific advantages in chemical exposure and durability.