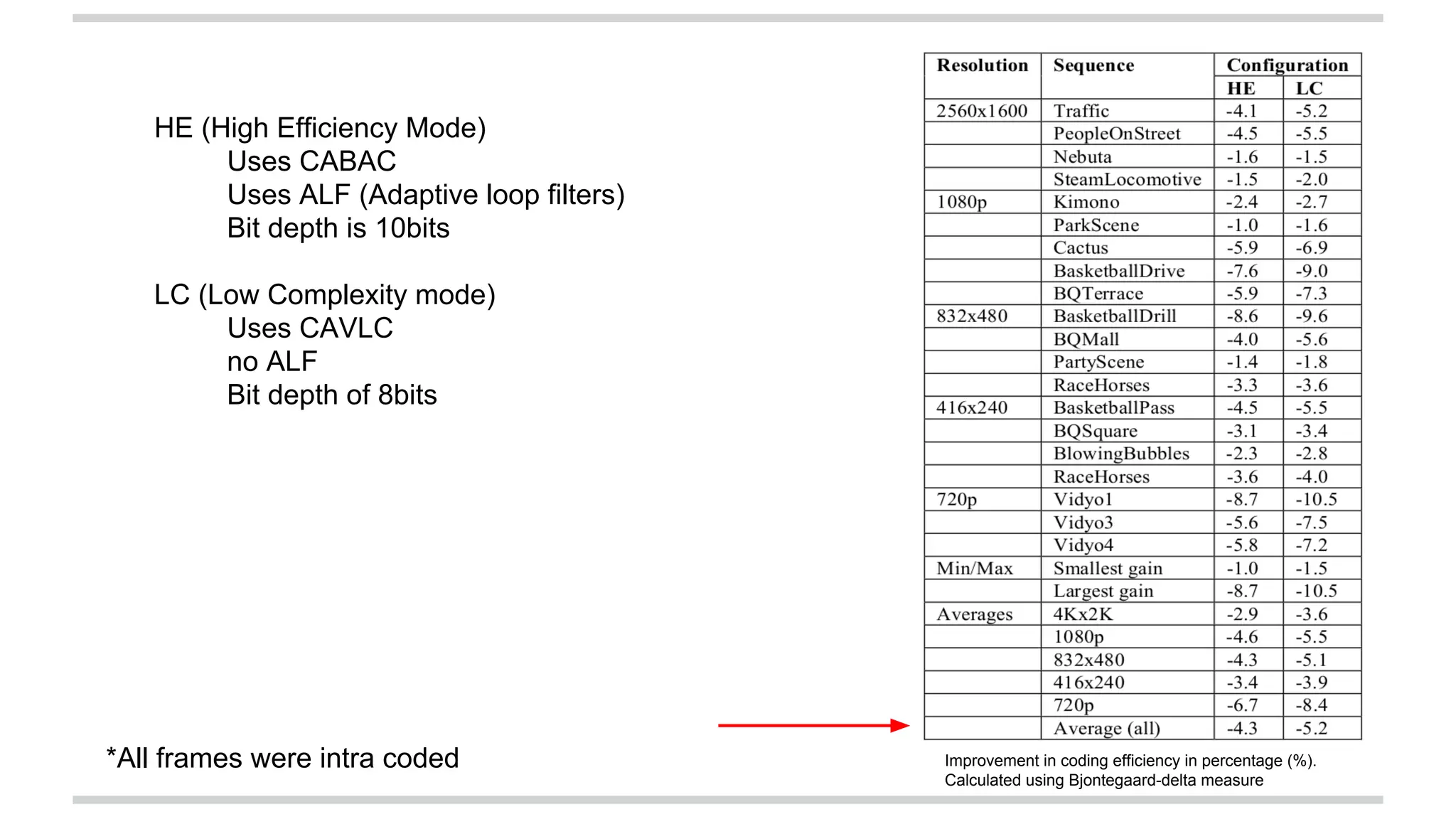
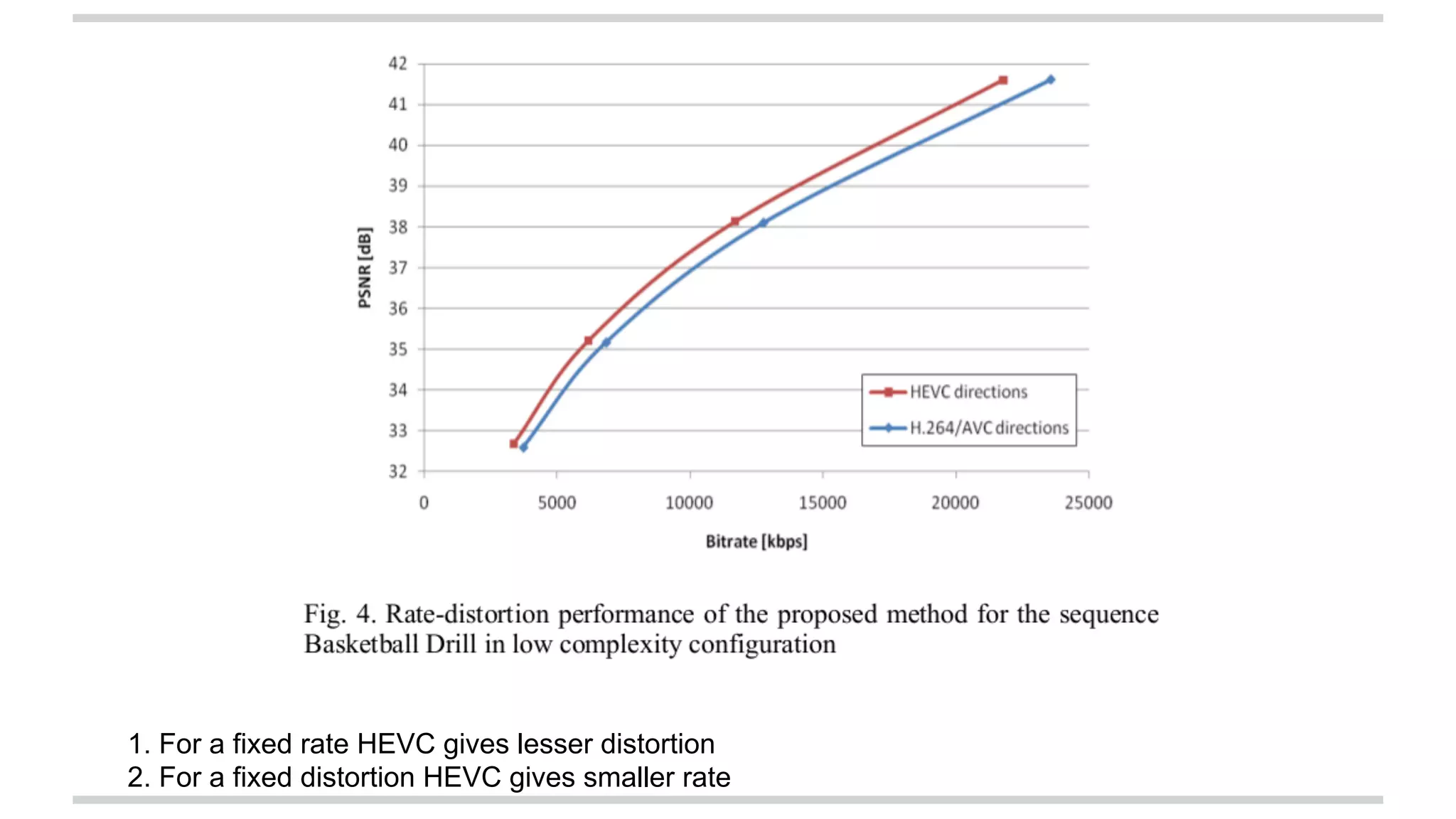
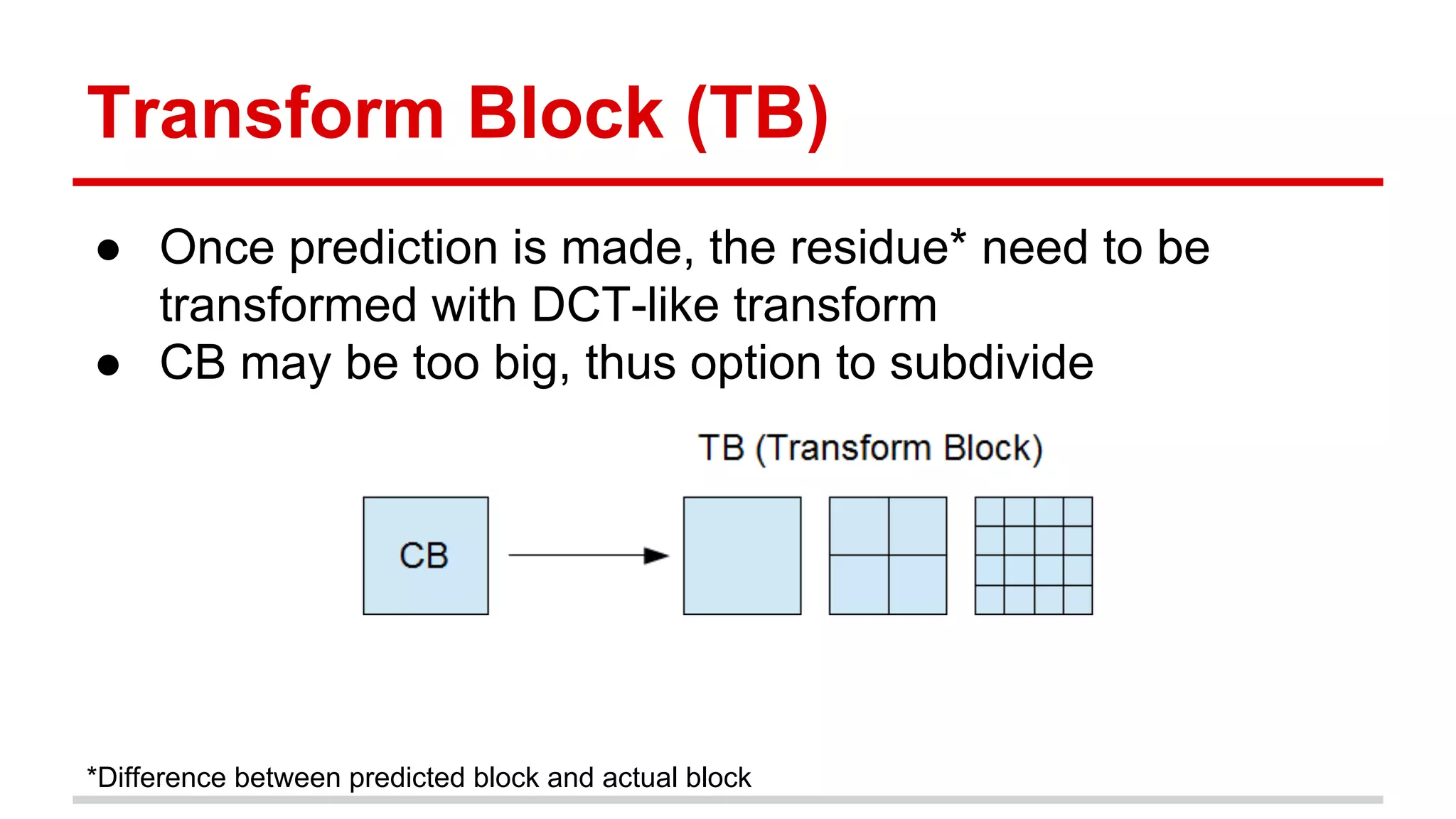
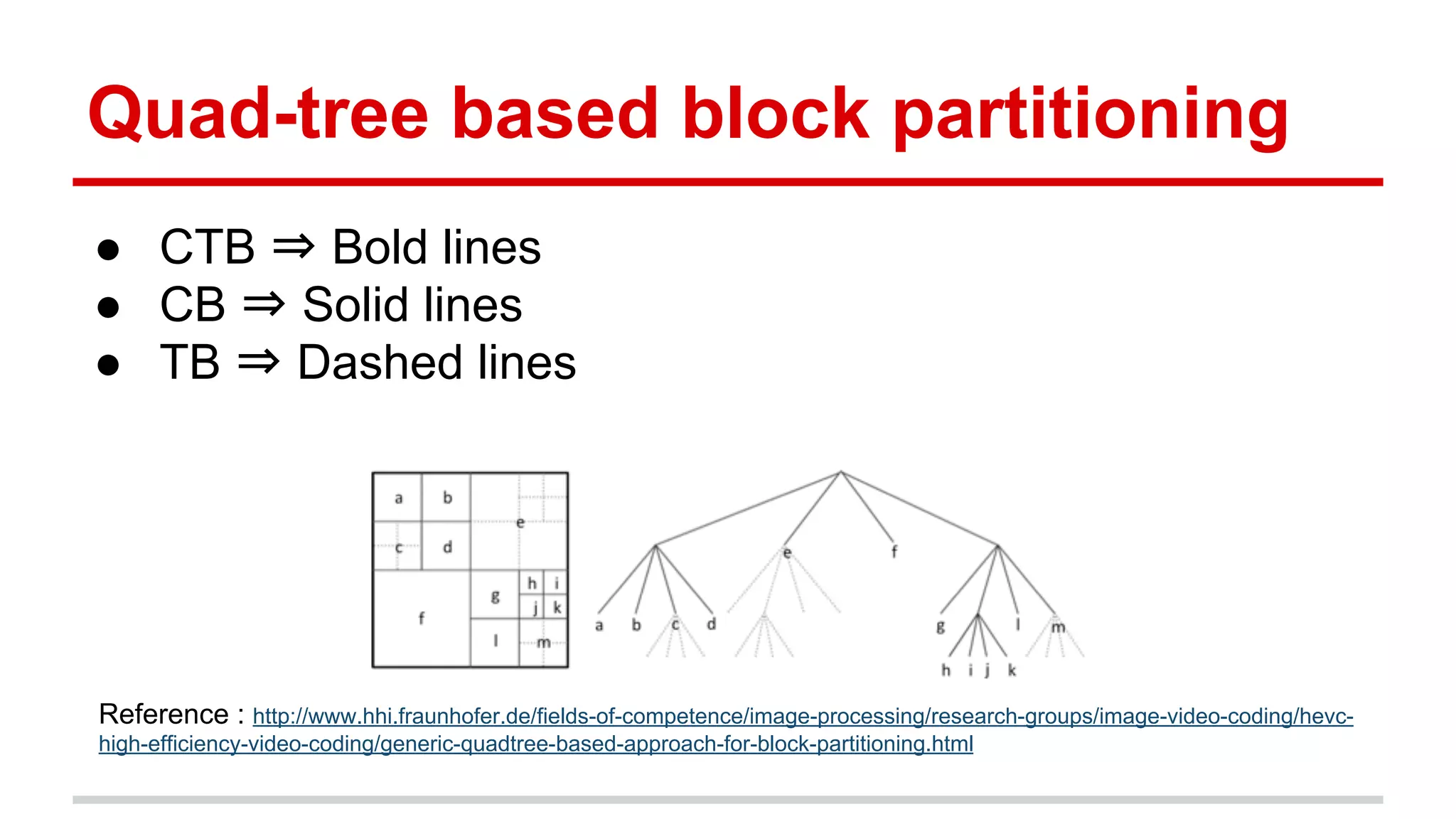
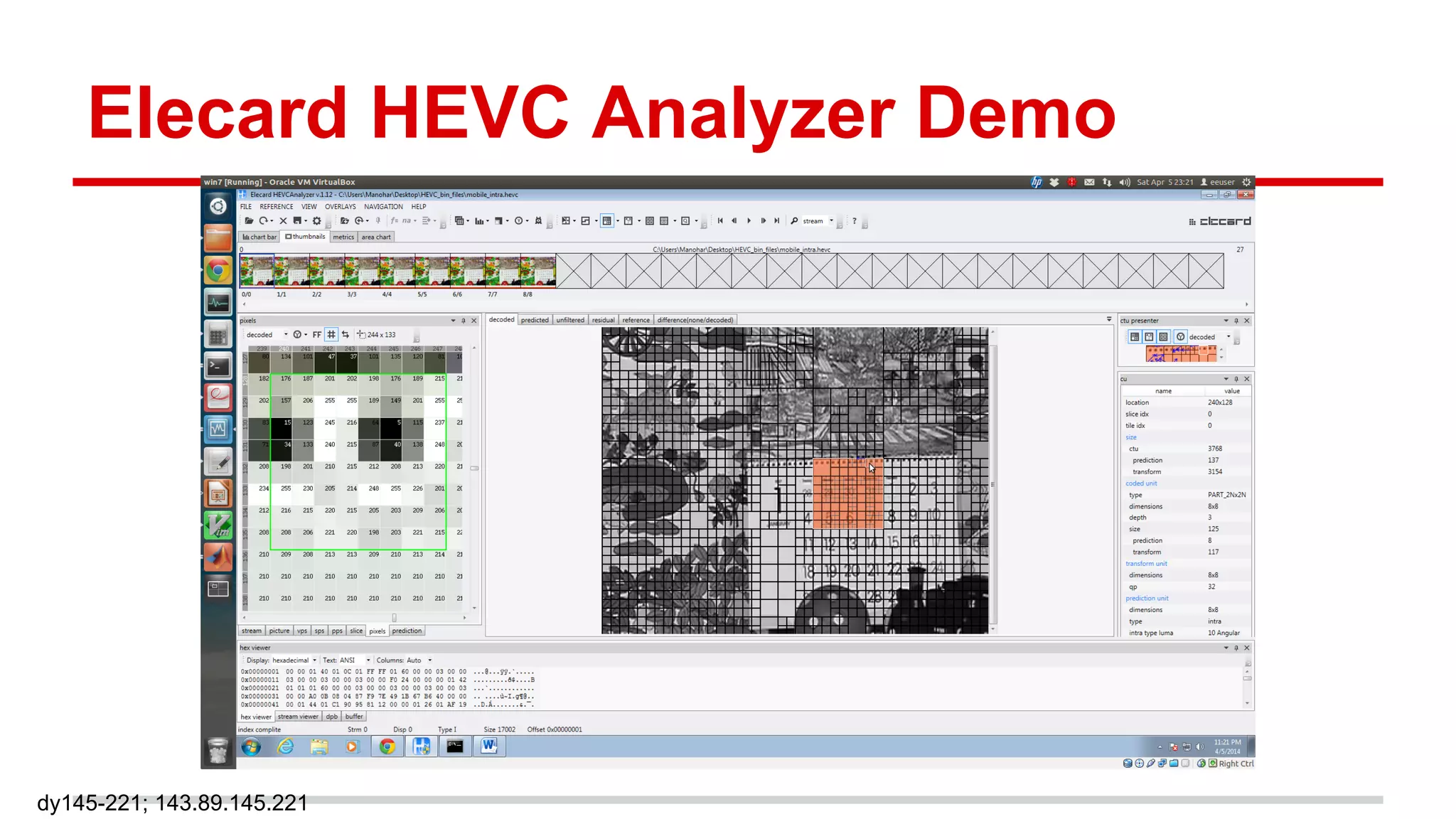
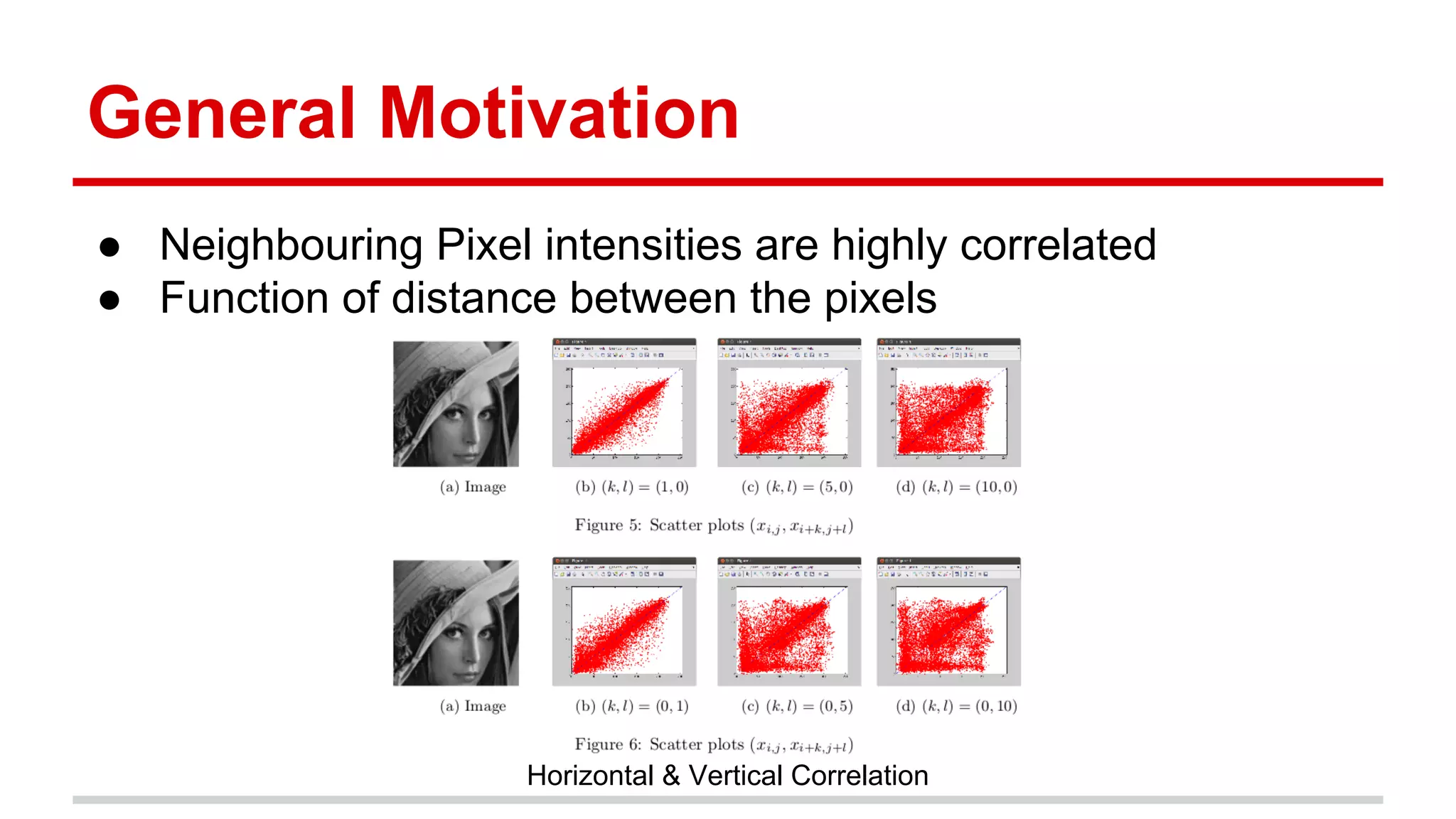
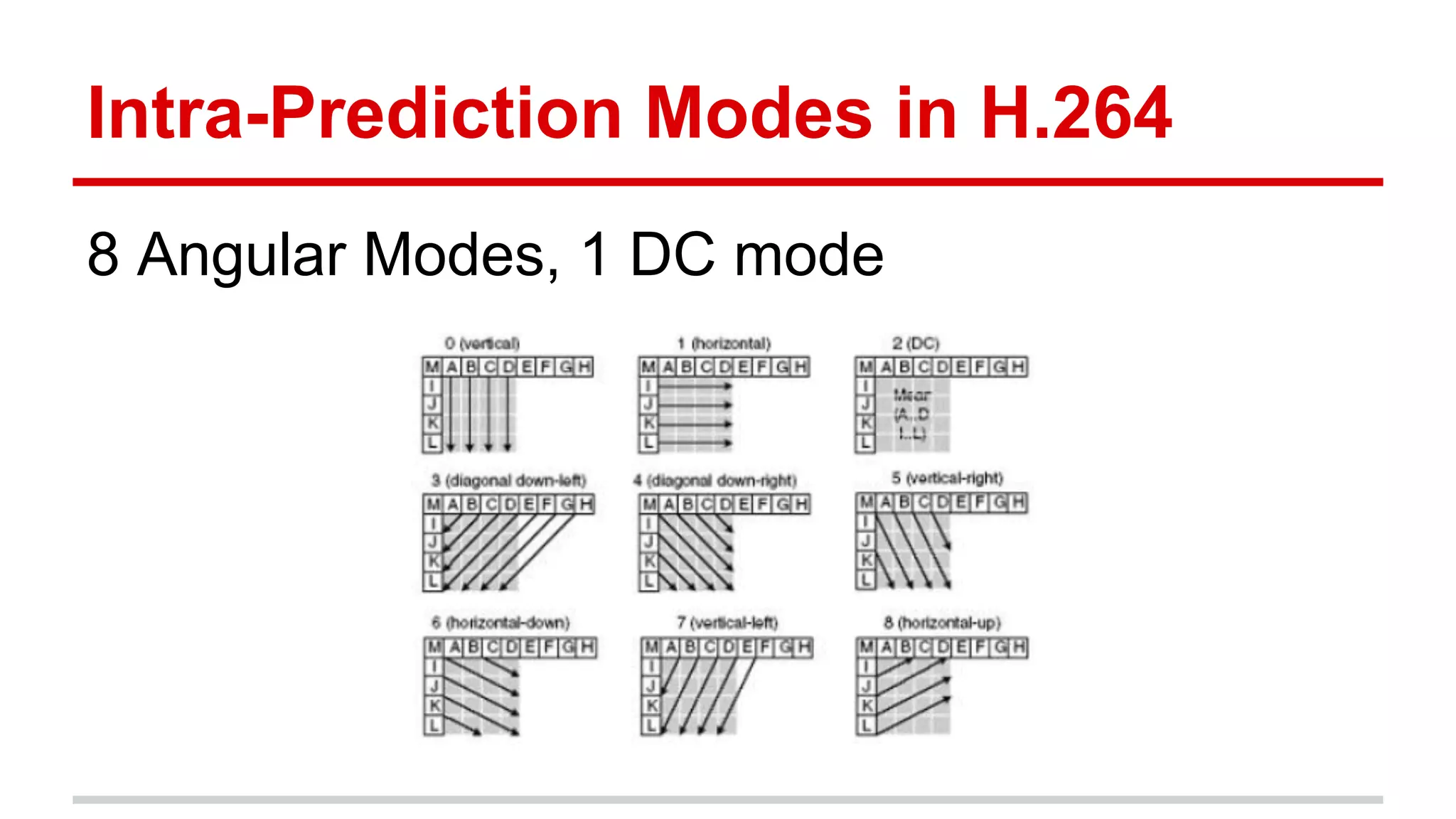
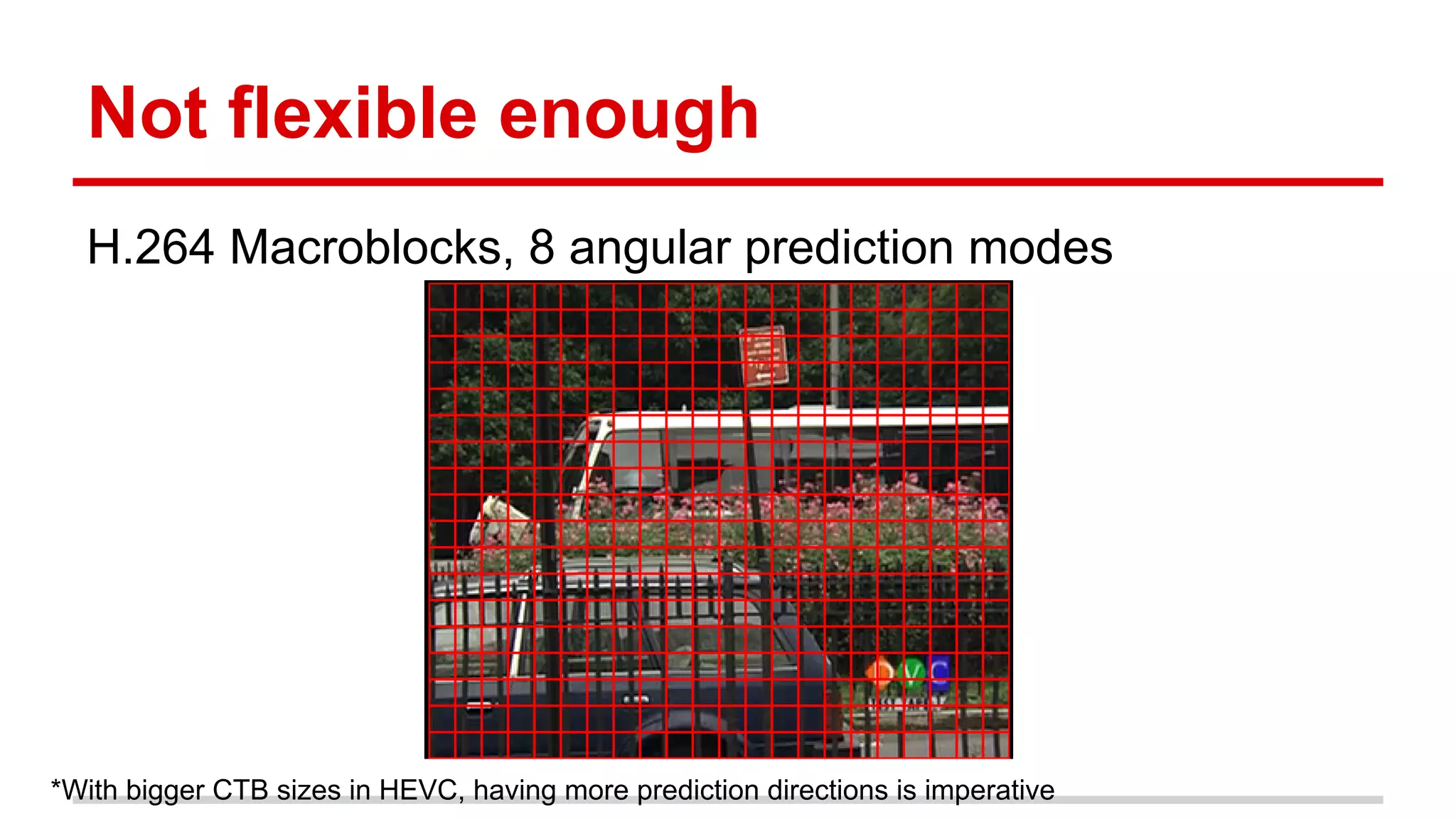
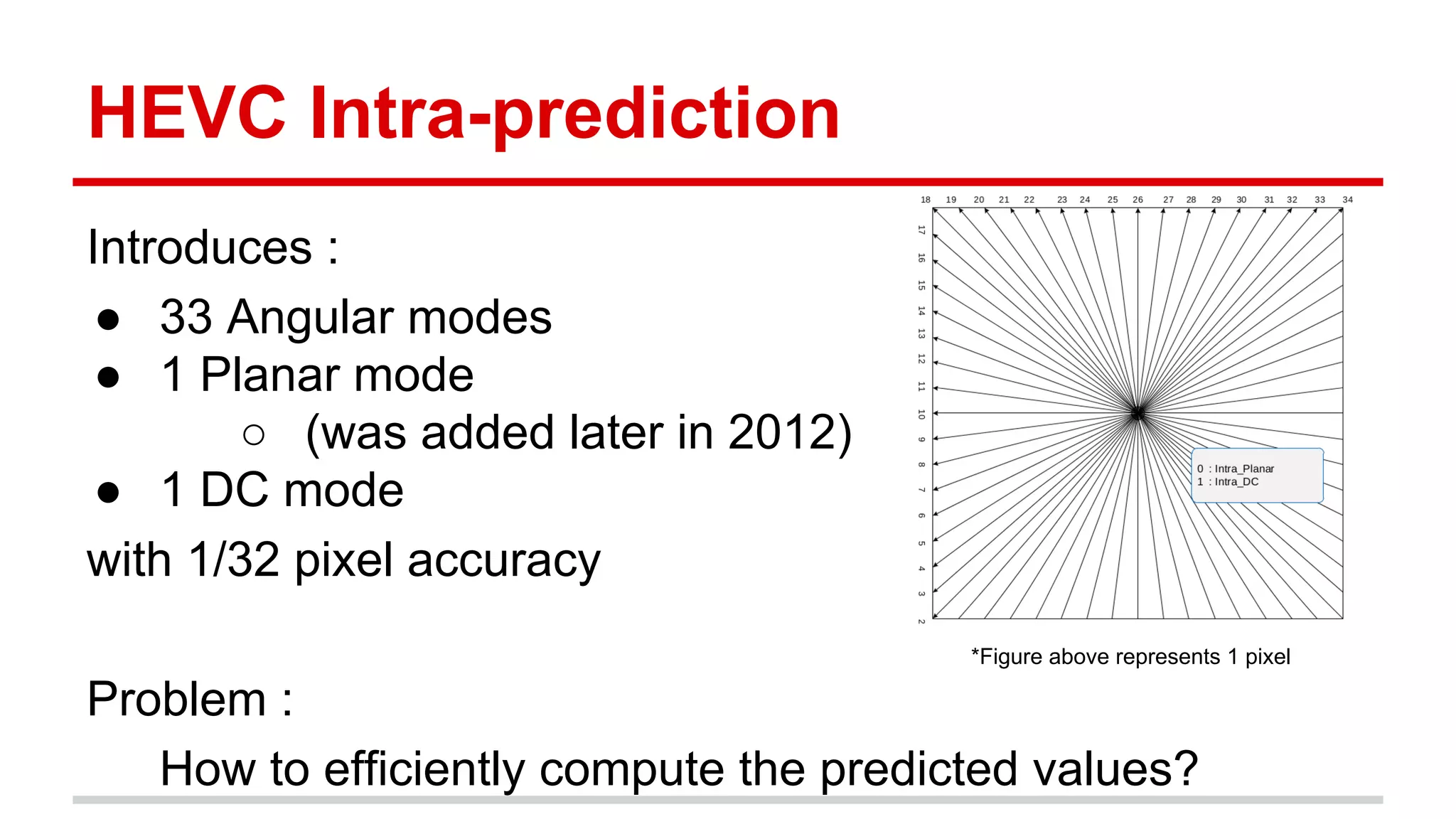
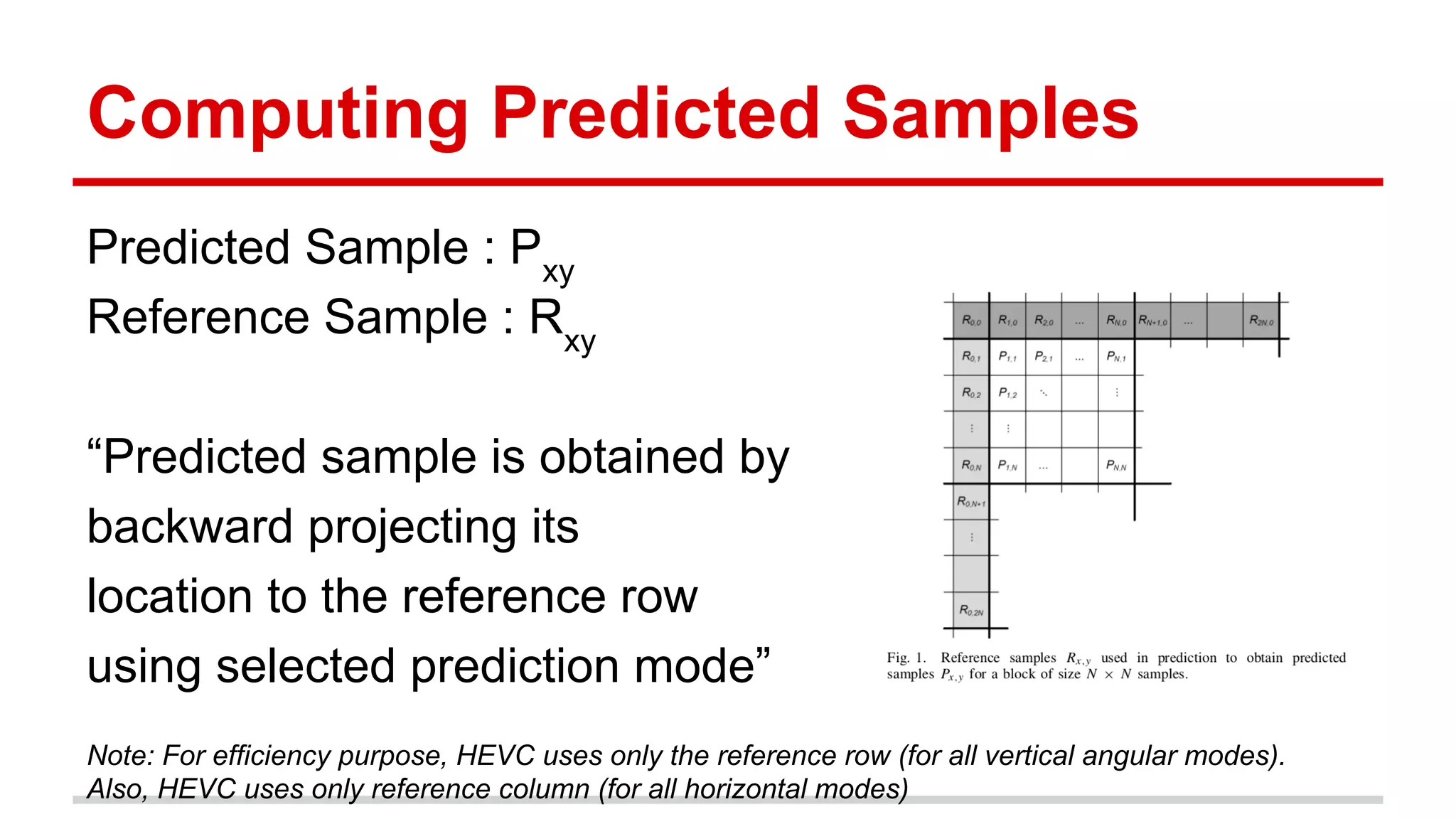
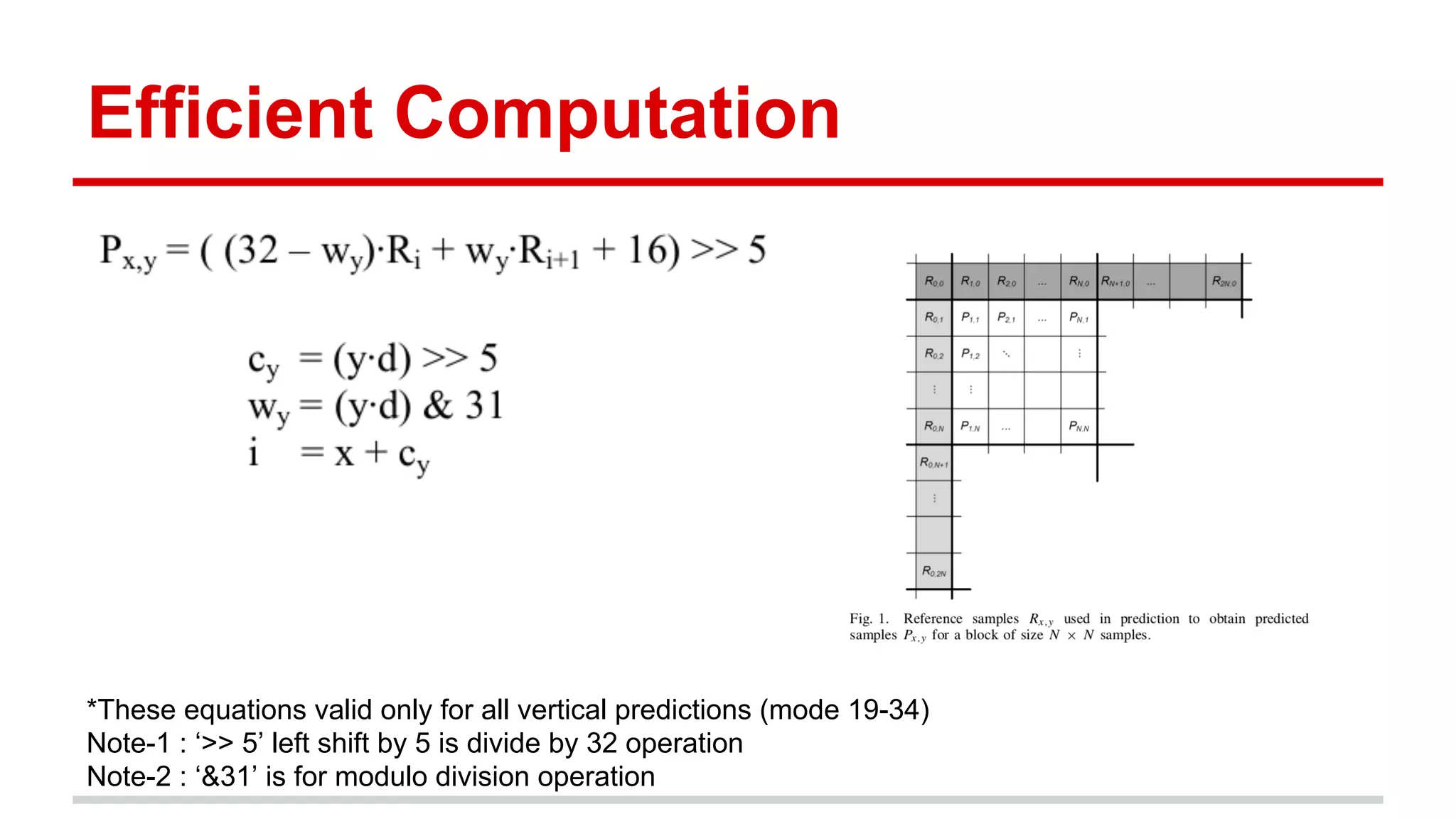
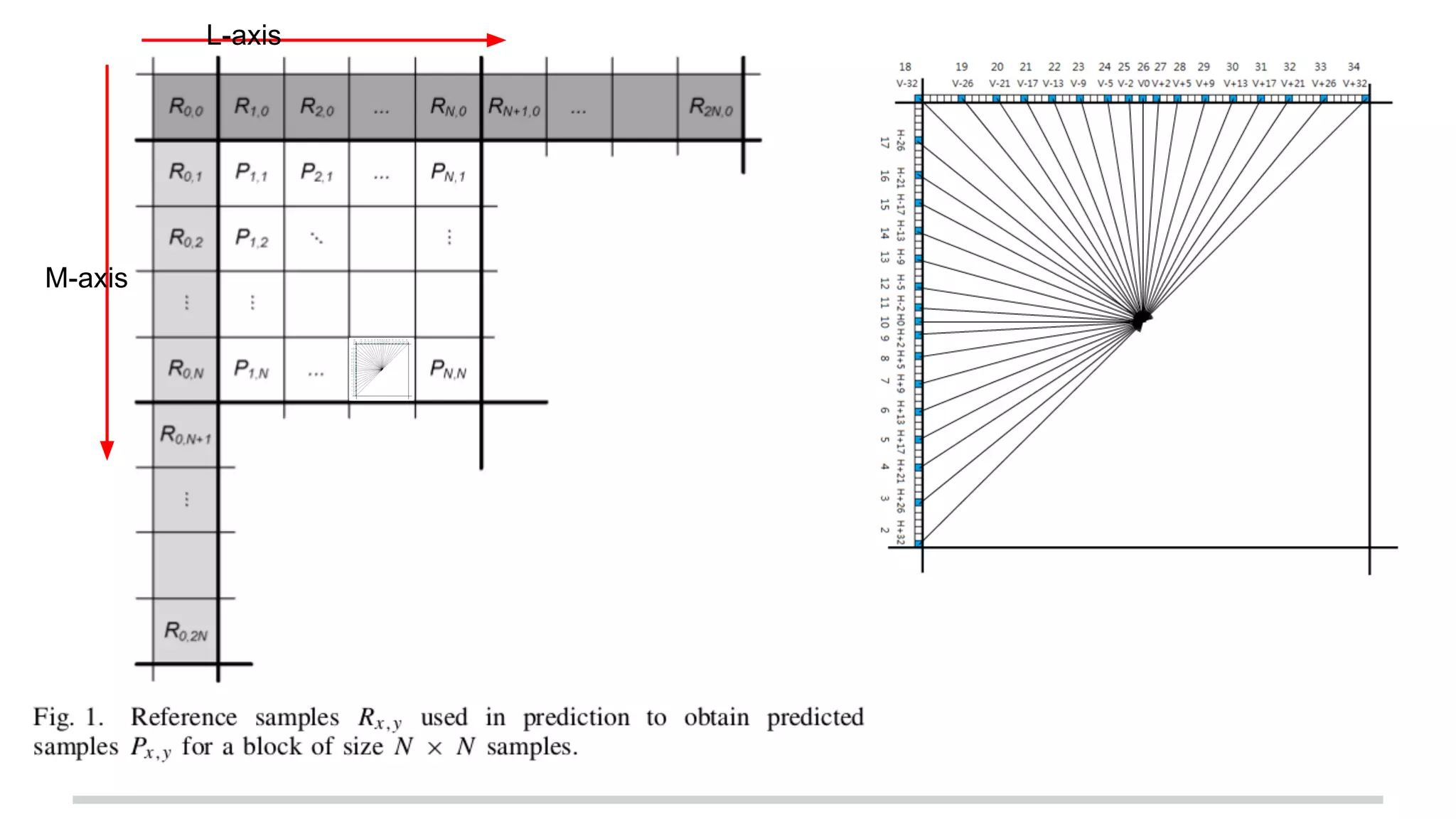
The document discusses the High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC) standard, its features, and its advancements over the previous H.264/AVC standard, including support for higher resolutions and improved compression rates. HEVC introduces a variety of coding units and prediction modes for efficient video compression, stressing the importance of intra prediction which utilizes neighboring pixel correlations. Experimental results demonstrate that HEVC achieves superior coding efficiency compared to H.264, highlighting its performance capabilities in terms of distortion and bit rate.








![Dealing with values outside reference rows
In this case, row is extended by projecting left reference
column.
For performance reasons
copying rightmost value*
*Negligible effect for compression performance JCTVC-C046. [12]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hevcintra-codingmtrecgroupmeeting-140827012627-phpapp02/75/HEVC-intra-coding-30-2048.jpg)