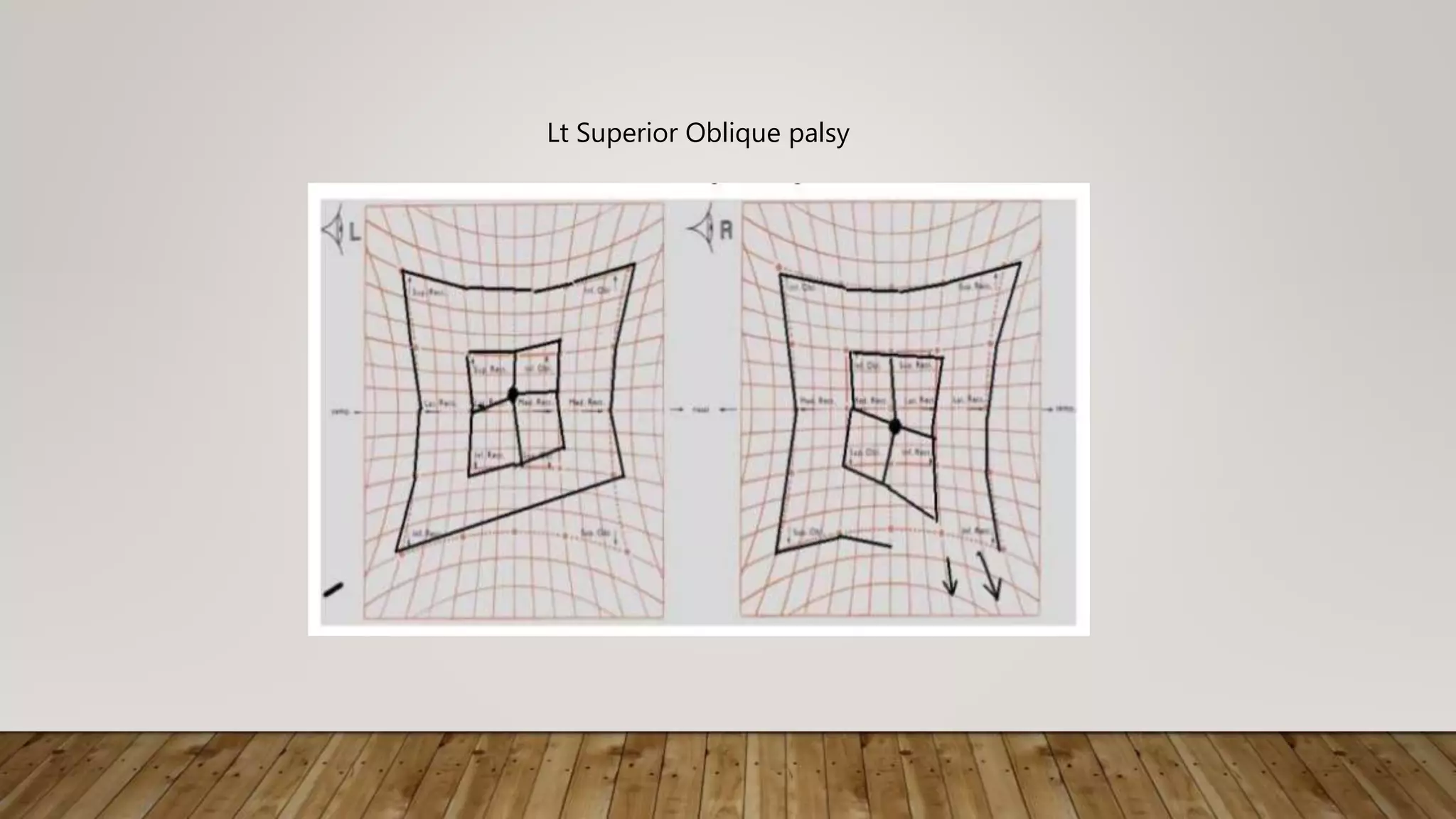
The Hess screen test involves presenting lights in different positions of gaze on a screen and having the patient superimpose lights while viewing through colored lenses to dissociate the eyes. This allows evaluation of eye muscle function and detection of underaction or overaction. Key details include:
- The Hess screen contains lights indicating positions of gaze and is viewed through red-green lenses to dissociate the eyes.
- The procedure involves illuminating lights and having the patient superimpose them while viewing through the lenses.
- Interpretation of the plotted results can detect muscle underaction or overaction, indicating conditions such as nerve palsies or restrictions in eye movement.