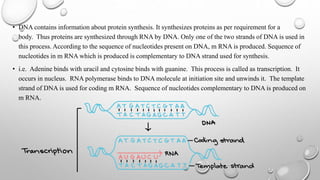
1. Genes are pieces of DNA that contain instructions for traits and are made up of different arrangements of bases including adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine.
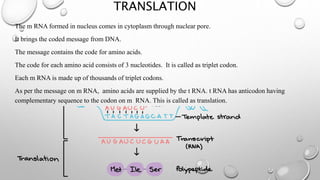
2. DNA carries hereditary information in the form of genes on structures called chromosomes in cell nuclei. It directs the synthesis of proteins through a process involving transcription of DNA into mRNA and translation of mRNA into proteins.
3. Mutations, or changes in genes, over time due to errors in DNA replication or exposure to mutagens can lead to evolution as mutations result in hereditary changes and variations between organisms that natural selection can act upon.