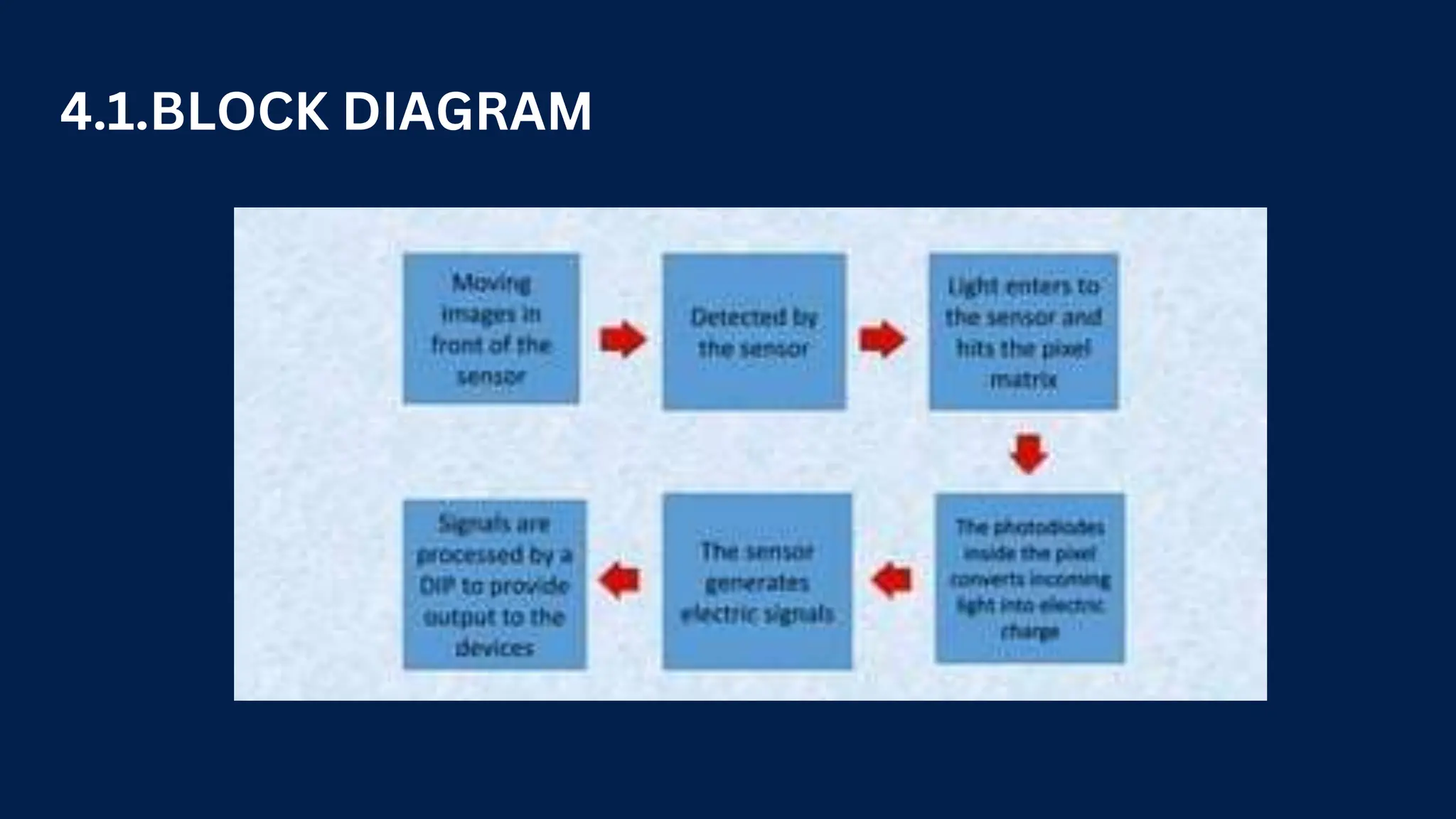
Touchless touch screens allow interaction without direct physical contact by using infrared sensors or gesture recognition. They started being experimented with in the 1980s and gained popularity with Microsoft Kinect in 2010. Touchless screens can now be found in applications like public information kiosks, medical equipment, gaming consoles, and smart homes. Researchers continue improving the technology to make touchless screens more accurate, affordable, accessible, and environmentally friendly.