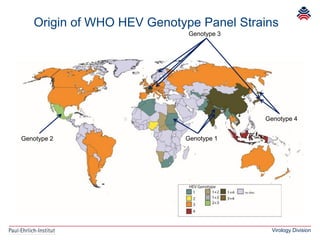
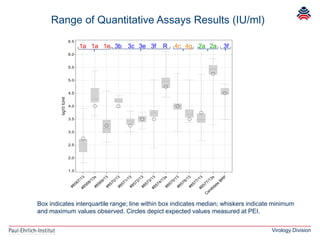
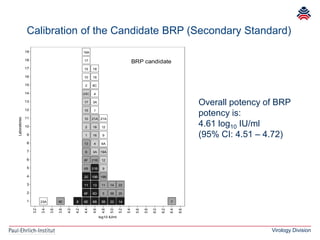
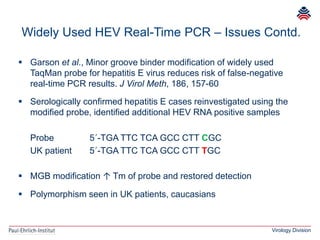
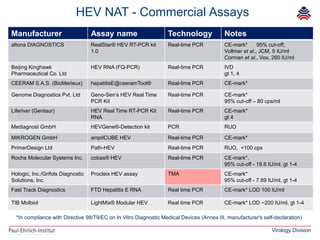
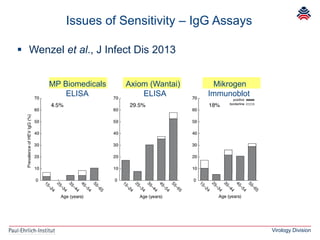
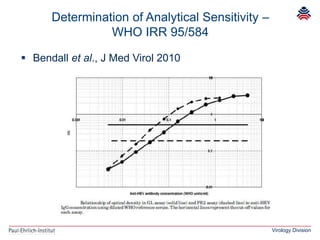
The document summarizes a meeting presentation about hepatitis E virus (HEV) diagnostics and standardization. It discusses the need for accurate HEV diagnosis, issues with current assays, and efforts to develop international standards for HEV RNA testing led by the Paul-Ehrlich-Institut. This included two collaborative studies establishing the first WHO International Standard for HEV RNA and developing a reference panel representing all HEV genotypes to improve assay performance evaluation.