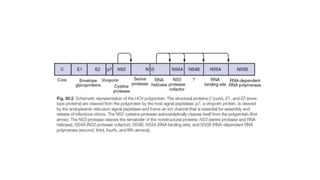
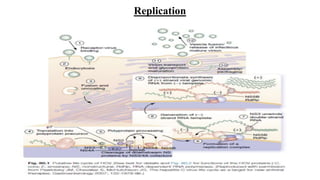
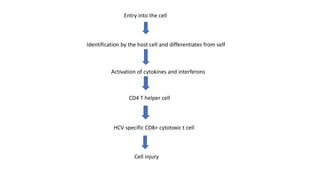
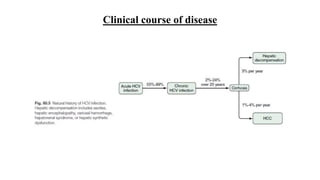
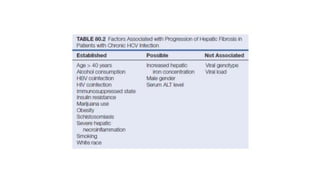
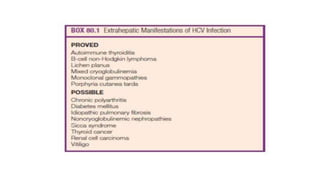
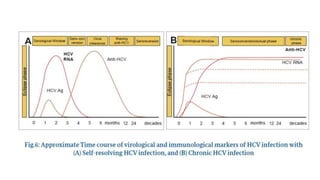
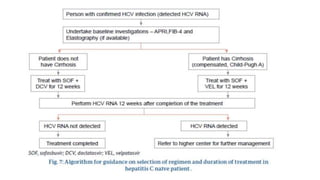
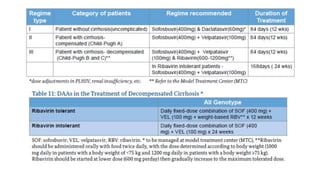
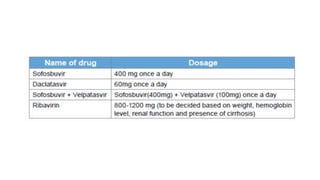
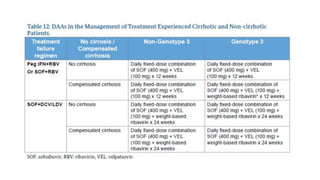
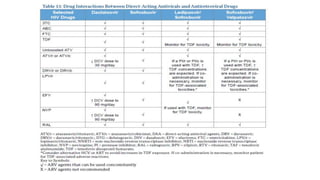
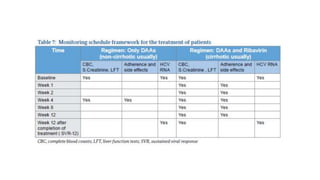
Hepatitis C is caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV), which is a single-stranded RNA virus from the Flaviviridae family. It is transmitted through blood and bodily fluids. HCV replicates within liver cells and evades the immune system, leading to persistent infection in some cases. Symptoms are often mild or absent. Diagnosis involves testing for HCV antibodies or RNA. Treatment involves direct-acting antiviral drugs, which have high cure rates. Special populations like those with HIV/HCV coinfection, kidney disease, or other liver diseases may require modified treatment approaches.