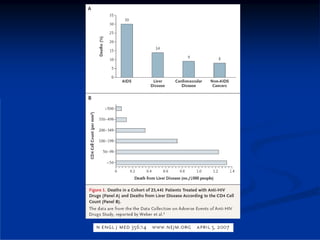
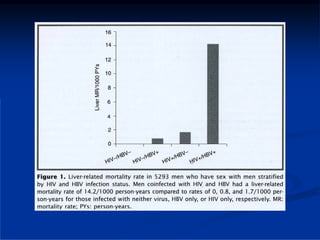
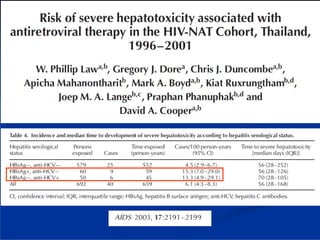
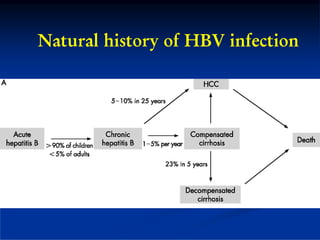
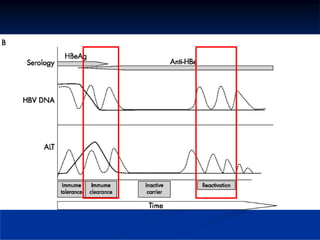
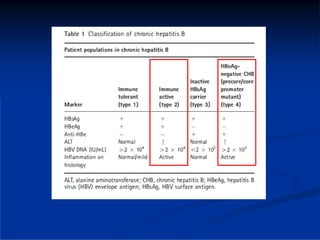
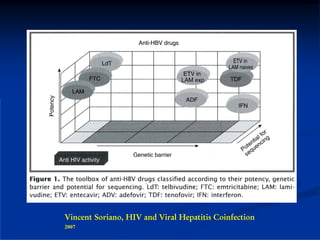
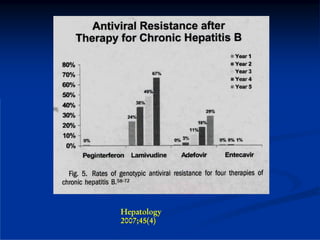
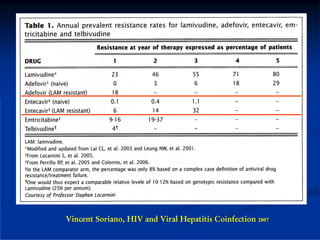
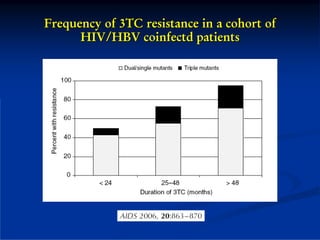
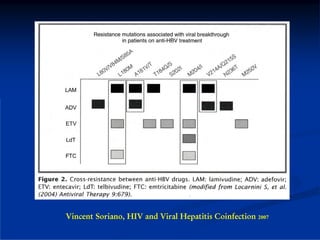
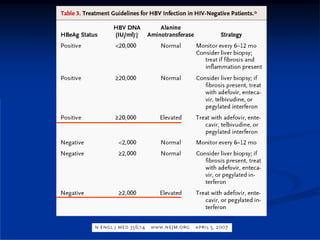
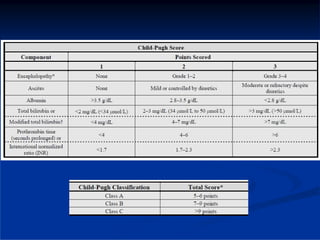
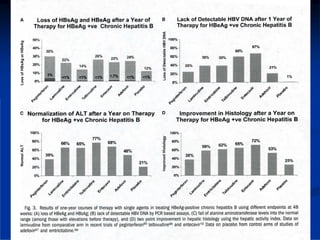
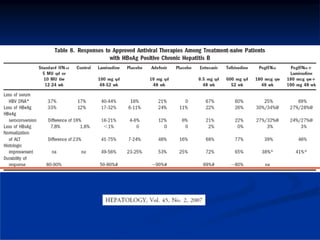
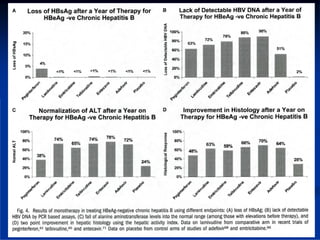
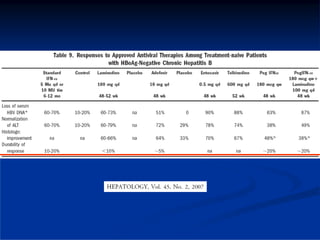
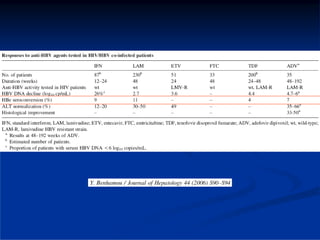
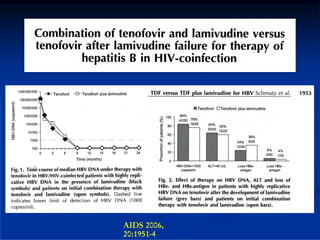
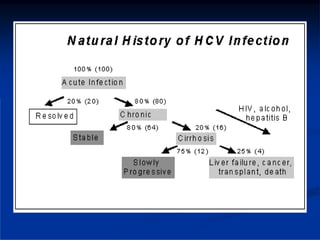
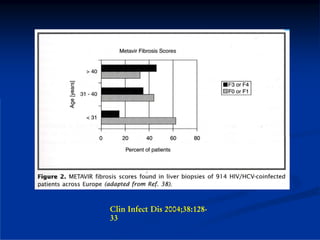
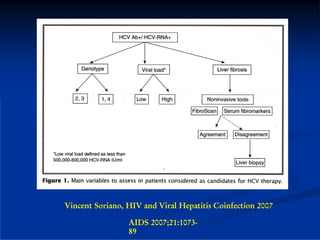
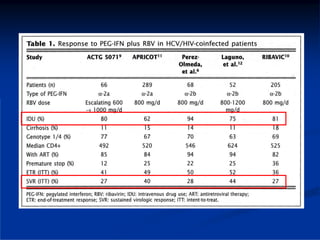
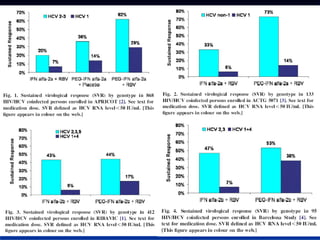
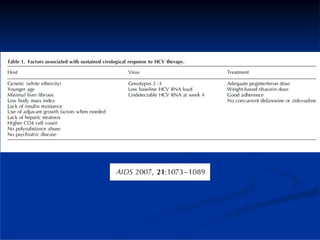
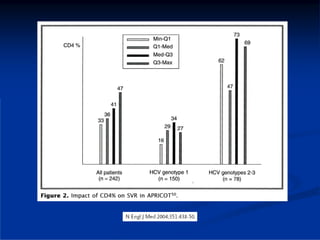
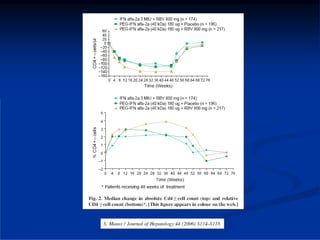
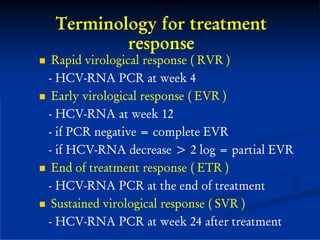
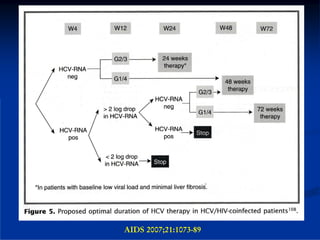
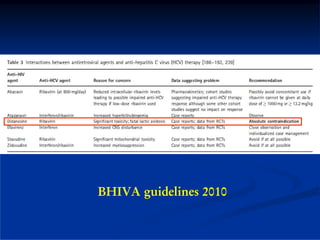
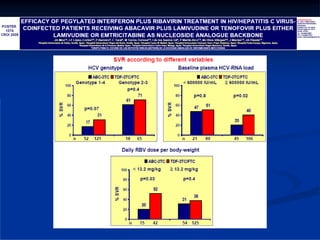
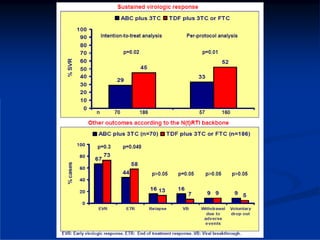
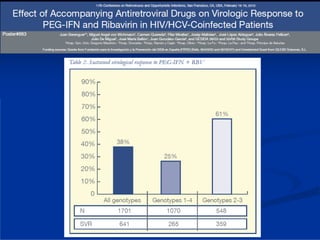
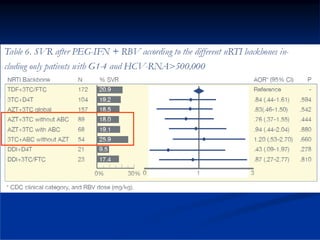
This document discusses HIV/HBV and HIV/HCV co-infections, providing perspectives from Thailand on optimal management. It outlines the natural history of HBV infection and conflicting results on whether telbivudine has activity against HIV. Guidelines are presented on determining active liver disease, treating HBV infection based on ART status, causes of transaminitis in coinfected patients, treating HCV infection, and contraindications for interferon and ribavirin use. Terminology for treatment response such as rapid virological response and sustained virological response is also defined.