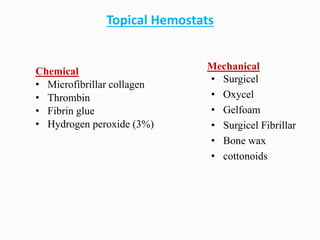
This document discusses hemostatic agents used in neurosurgery. It begins by explaining that control of bleeding without ligatures is important in neurosurgery. It then categorizes topical hemostats as chemical, mechanical, or thermal agents. Specific agents are discussed, including gelatin sponge, microfibrillar collagen, oxidized cellulose, thrombin, fibrin sealants, and hydrogen peroxide. Their mechanisms of action, appropriate usage, and potential complications are described. The document concludes by stating that all hemostatic agents are foreign bodies that can cause infection, and that proper surgical technique remains key, along with judicious use of hemostatic agents.



























![● Recent evidence suggest significant tissue damage in
surrounding functional brain.
● Intratumoral hydrogen peroxide injection during meningioma resection.
Roger Lichtenbaum,M.D. Neurosurgery 59[ONS Suppl 4.]:ONS-470–
ONS-473, 2006.
● Hydrogen peroxide–induced stroke: elucidation of the mechanism in vivo.
Melike Mut, M.D., Ph.D JNeurosurg 110:94–100,2009](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hemostatsinneurosurgerycopy-210621185724/85/Hemostats-in-neurosurgery-29-320.jpg)




