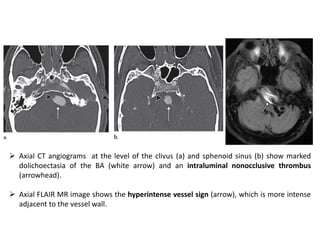
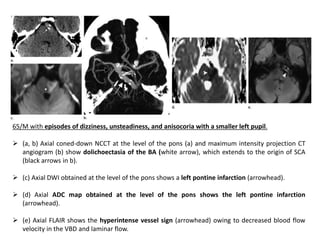
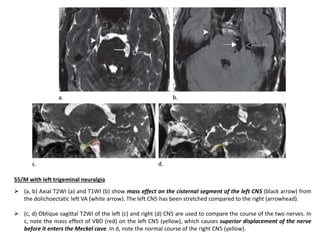
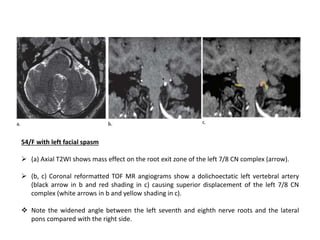
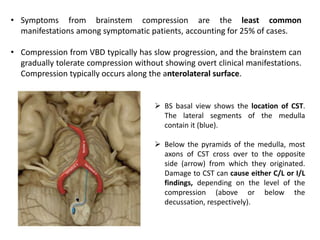
Vertebrobasilar dolichoectasia (VBD) is an abnormal elongation, dilation, and tortuosity of the vertebrobasilar arteries. It can cause both vascular events like strokes as well as compressive symptoms from pressure on surrounding structures. Common presentations include ischemic strokes, trigeminal neuralgia, and hemifacial spasm. Imaging plays a key role in the diagnosis of VBD using criteria like basilar artery diameter, laterality, and height of bifurcation on CT angiography and MRI. Both vascular complications and compression must be considered when evaluating patients.