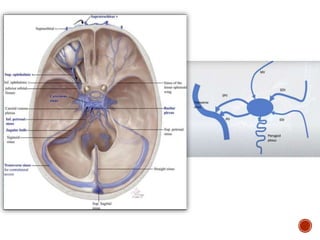
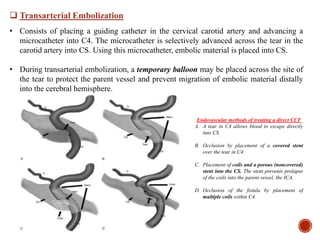
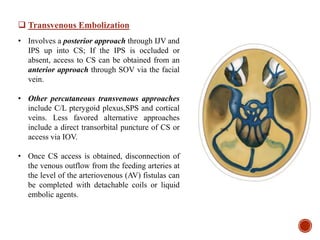
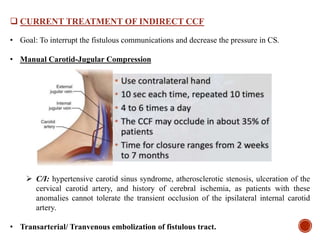
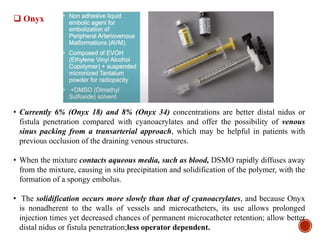
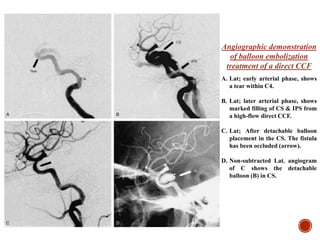
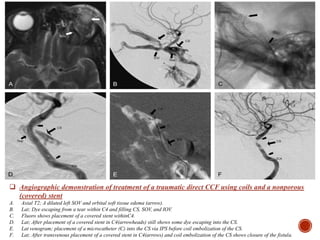
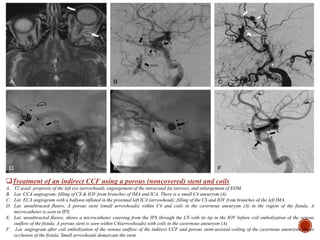
1. Carotid-cavernous fistulas (CCFs) refer to abnormal connections between the internal or external carotid arteries and the cavernous sinus, which can cause serious consequences if left untreated.
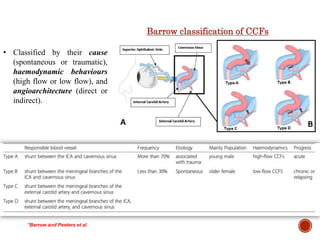
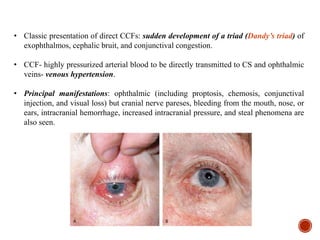
2. CCFs are typically classified as direct or indirect based on the arterial venous shunt. Direct CCFs present more severely with symptoms like exophthalmos, while indirect CCFs have a more gradual onset.
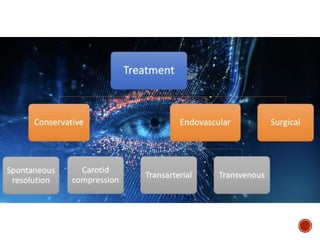
3. Current treatment options for direct CCFs include transarterial embolization using detachable balloons, coils, liquid embolic agents or covered stents to occlude the fistula while preserving artery patency. Indirect CCFs are often treated