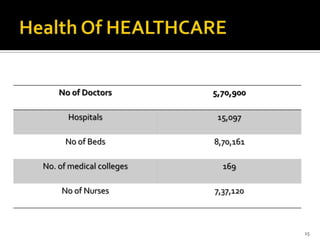
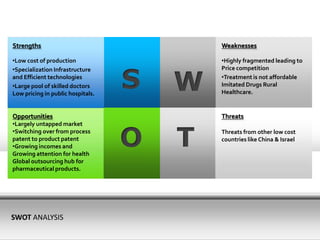
The healthcare sector in India is large and growing, valued at over $34 billion in recent years. Key segments driving growth include hospital services, medical tourism, and medical devices. Historically, healthcare in India was based on traditional Ayurvedic methods and voluntary work, but the government now emphasizes primary care and the private sector has grown to meet demand. Factors fueling healthcare growth include India's expanding population and economy, the rise of chronic and infectious diseases, and growth in the pharmaceutical industry. The government is taking initiatives to invest in healthcare and regulate the sector.