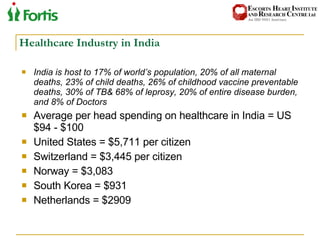
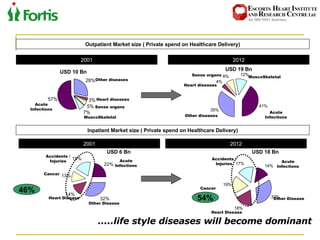
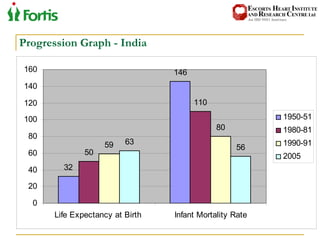
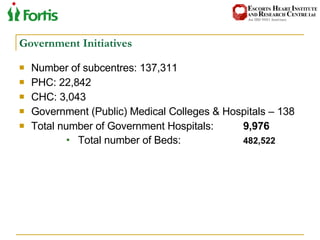
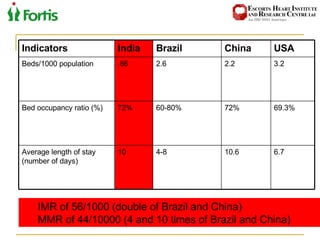
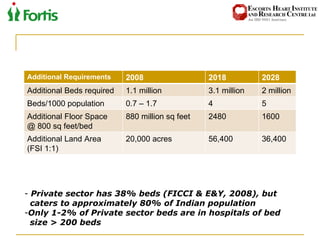
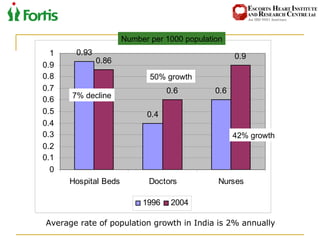
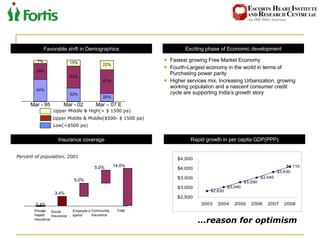
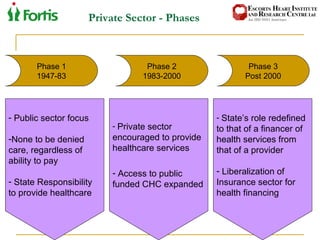
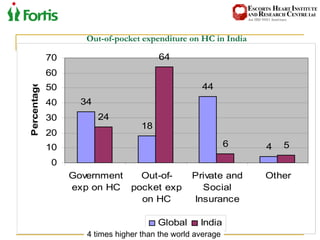
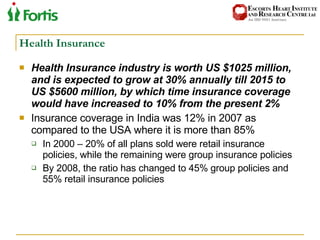
The document summarizes the Indian healthcare landscape. It notes that India has a large population but low spending on healthcare per capita compared to other countries. Healthcare is provided through both public and private sectors. The burden of disease is shifting from communicable to non-communicable diseases. Government initiatives aim to increase access through programs and infrastructure growth, but challenges remain around access, costs and quality across the public and private sectors. The healthcare industry is seen as a major growth opportunity in India.
![The Indian Healthcare Landscape Jim Dockins, FACHE Regional Director Fortis Healthcare Limited 731-256-0585 (US) [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fortis-090512110928-phpapp02/85/Fortis-1-320.jpg)