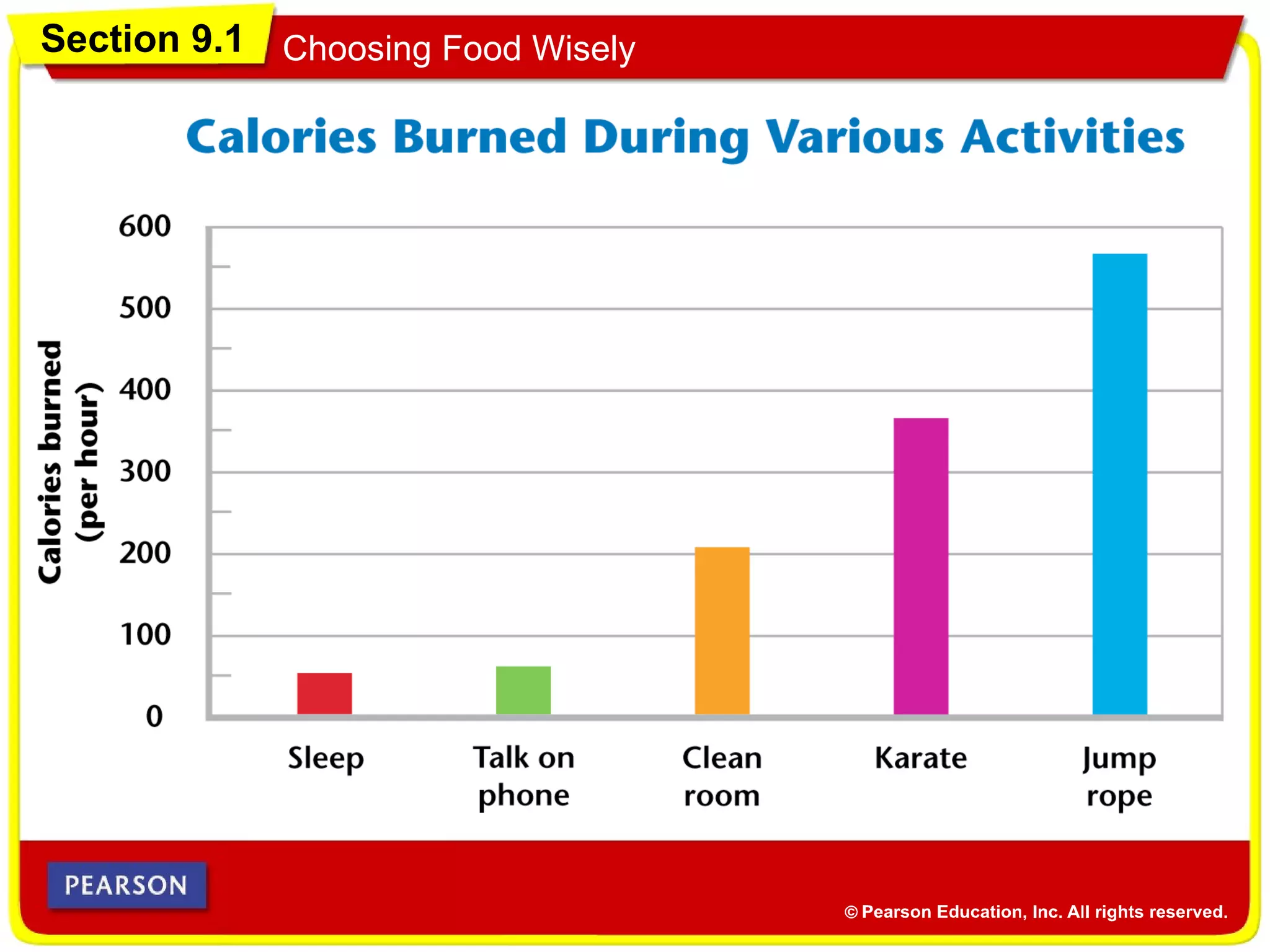
The document discusses guidelines for making healthy food choices and maintaining a healthy weight. It covers factors that influence food choices like hunger, appetite, nutrition needs, and cultural background. It also discusses evaluating food labels, calculating a healthy weight range using BMI, risks of being underweight or overweight, and dietary guidelines for conditions like diabetes or vegetarianism. The key is choosing a balanced, nutritious diet and maintaining a active lifestyle.













![Section 9.2 Safely Managing Your Weight
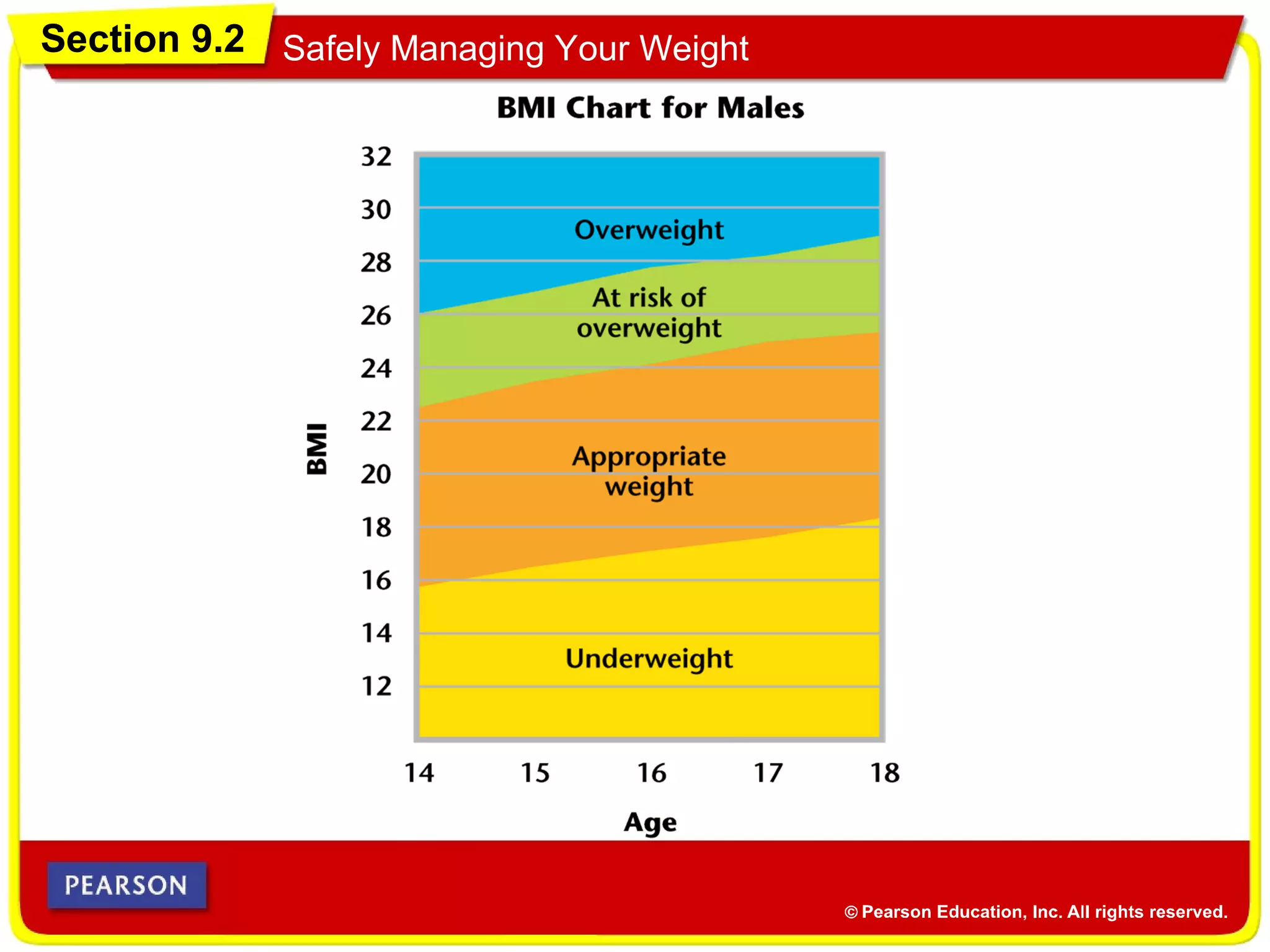
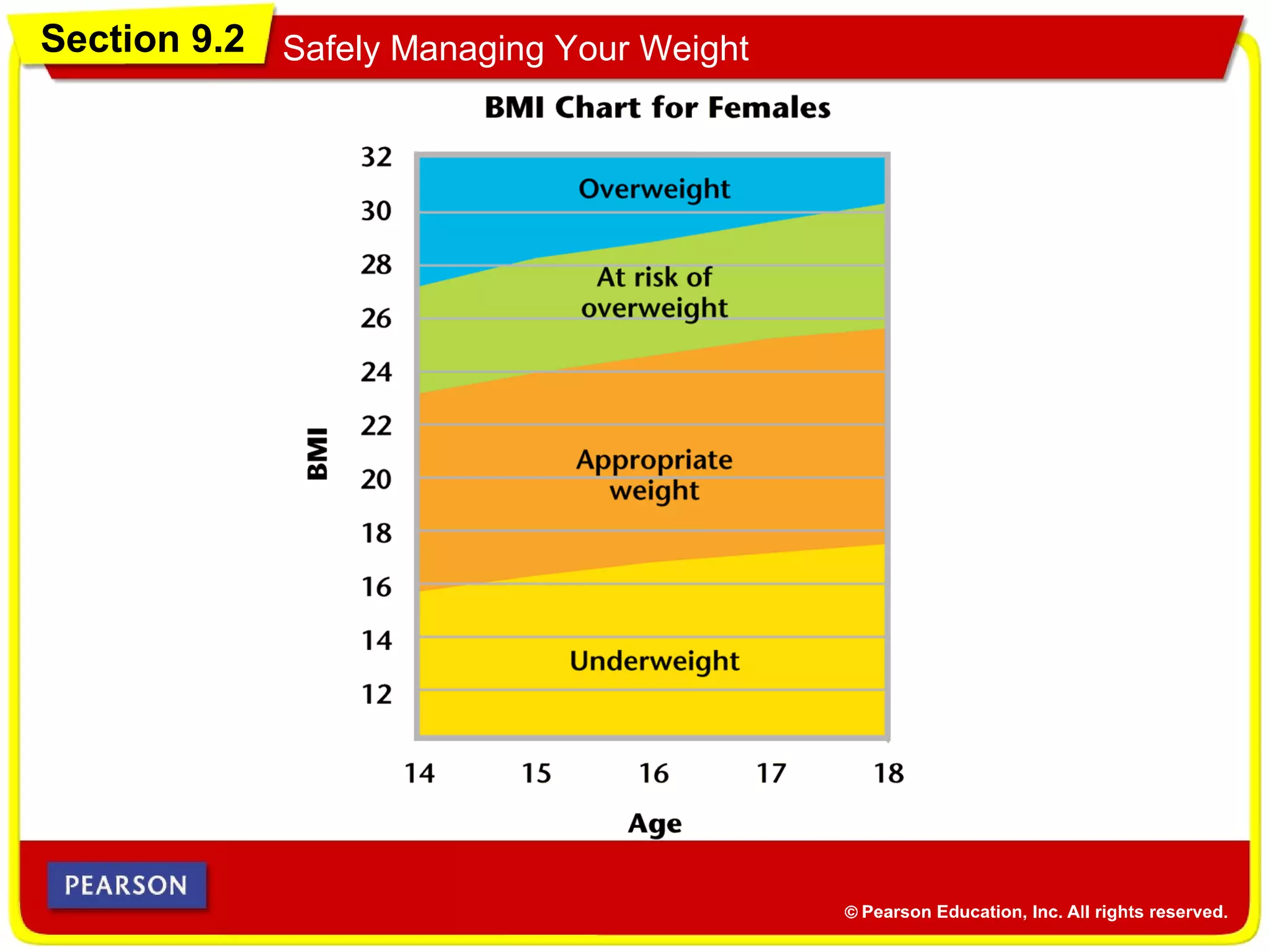
• Body mass index (BMI) is a ratio of your weight to
your height.
Body Mass Index
• Follow these steps to calculate your BMI.
BMI =
Weight (in pounds)
[Height (in inches)]2( ) x 703
1. Multiply your height (in inches) by your height (in
inches).
2. Divide your weight (in pounds) by the number
from Step 1.
3. Multiply the number from Step 2 by 703.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter9combinedppt-140517113724-phpapp02/75/Health-Course-Chapter-9-15-2048.jpg)