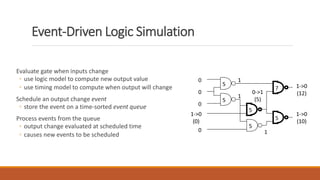
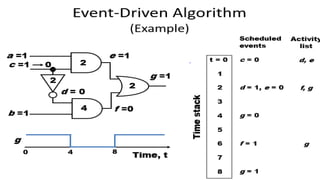
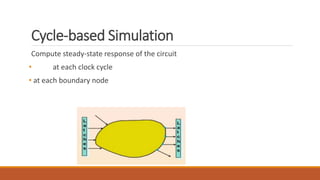
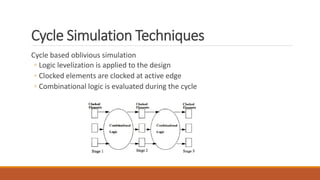
This document discusses HDL-based simulators. It defines simulation as modeling a design's function and performance. There are two main types of simulators: HDL-based and schematic-based. HDL-based simulators use an HDL language like VHDL to describe the design and testbench. These can be either event-driven or cycle-based. Event-driven simulators efficiently model all nodes and detect glitches. Cycle-based simulators compute the steady-state response at each clock cycle without detailed timing.