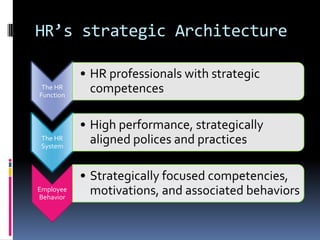
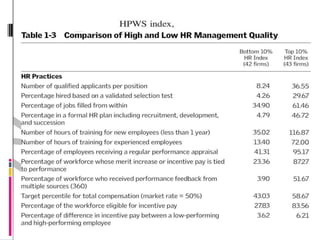
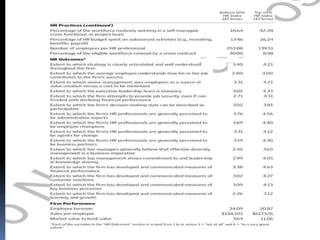
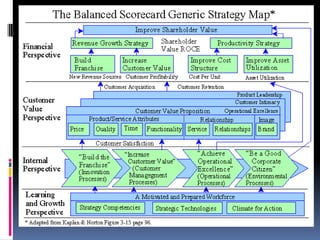
This case study discusses the challenge for HR to demonstrate its strategic value through effective measurement. It outlines an HR architecture with three components: the HR function with strategically competent professionals, an HR system of high-performance policies aligned with organizational strategy, and strategically-focused employee behaviors. Developing this architecture allows HR to create value by ensuring employee efforts support organizational vision and goals, while an HR measurement system can convincingly showcase its impact on business performance.