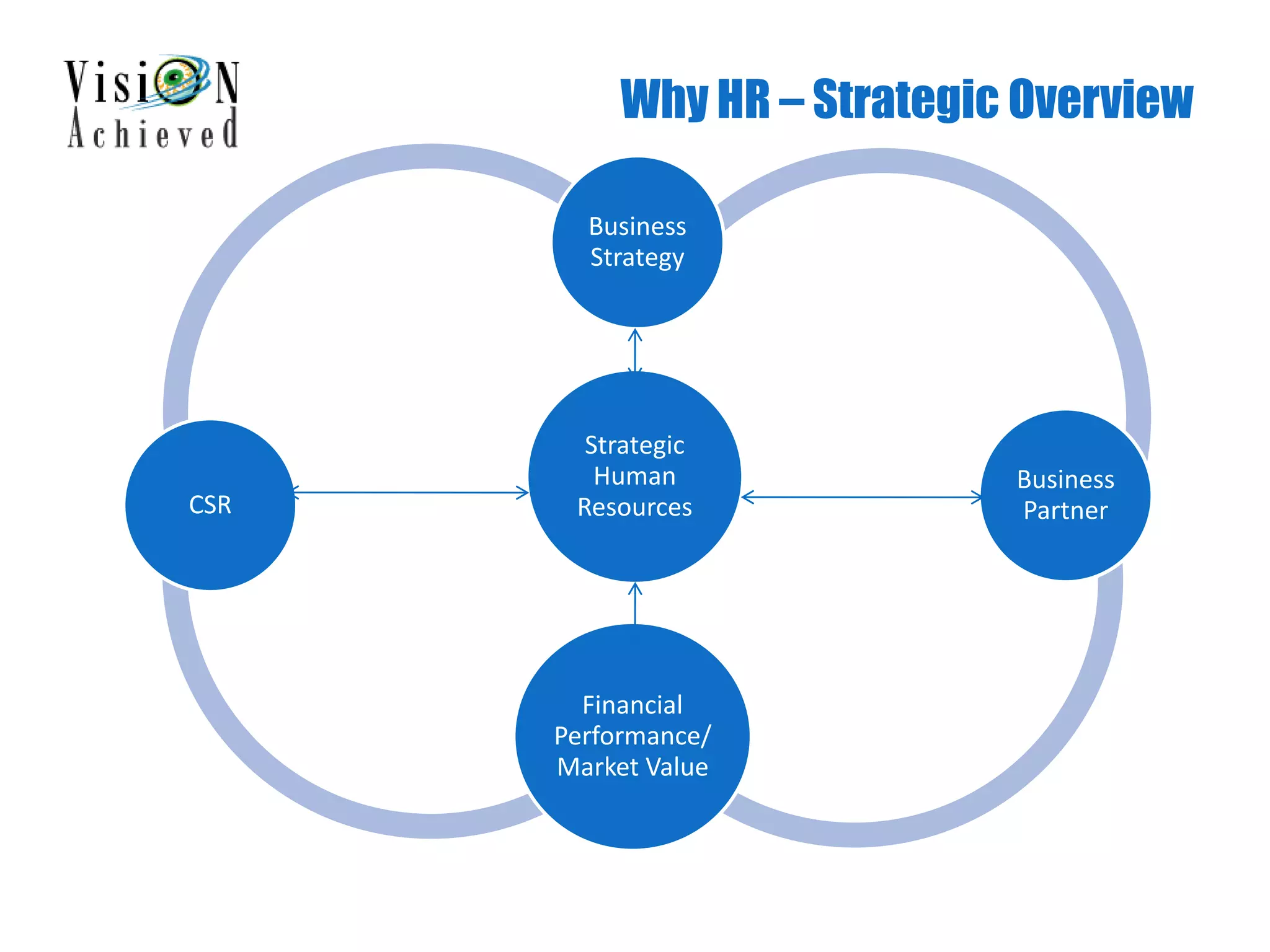
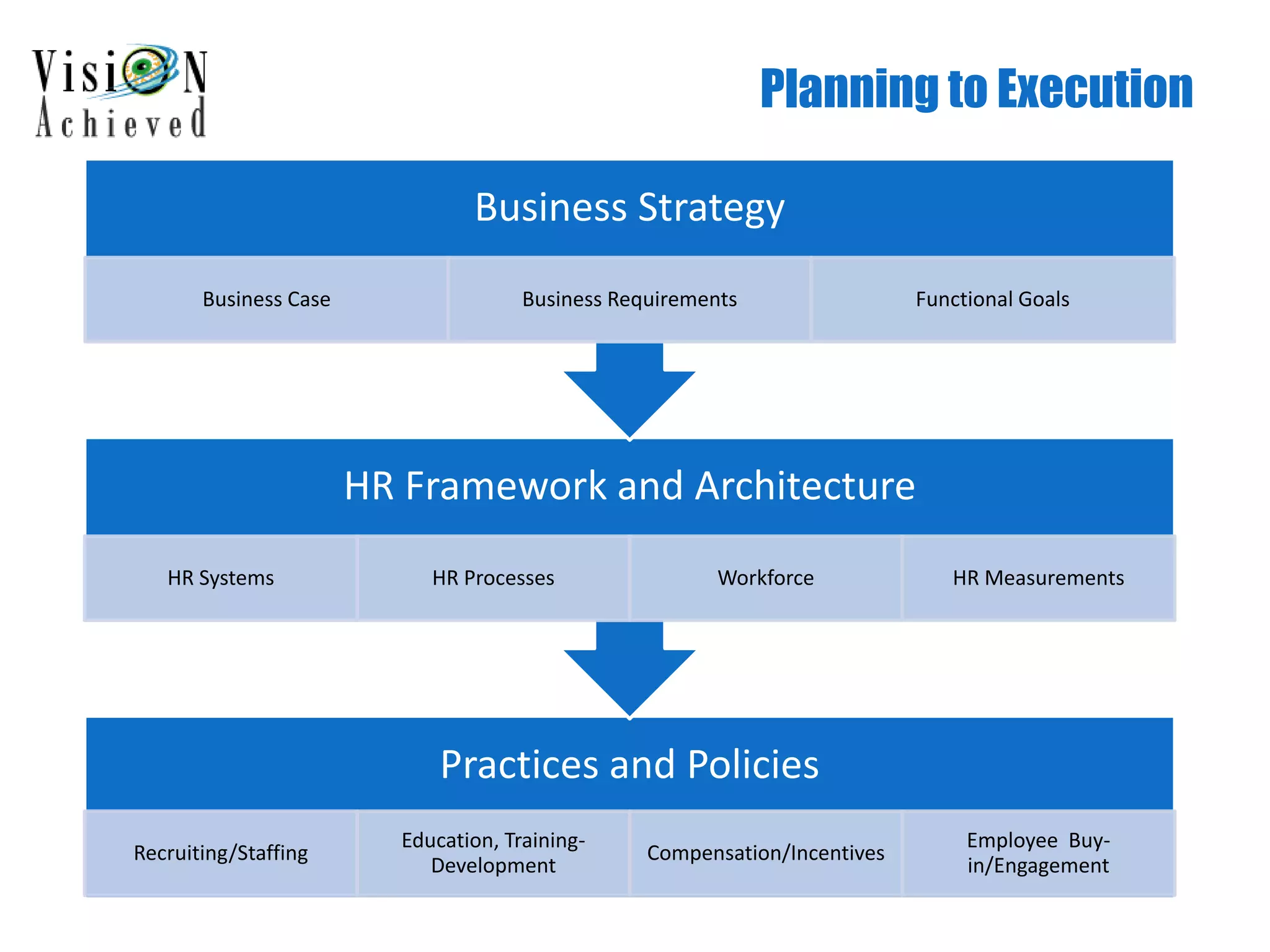
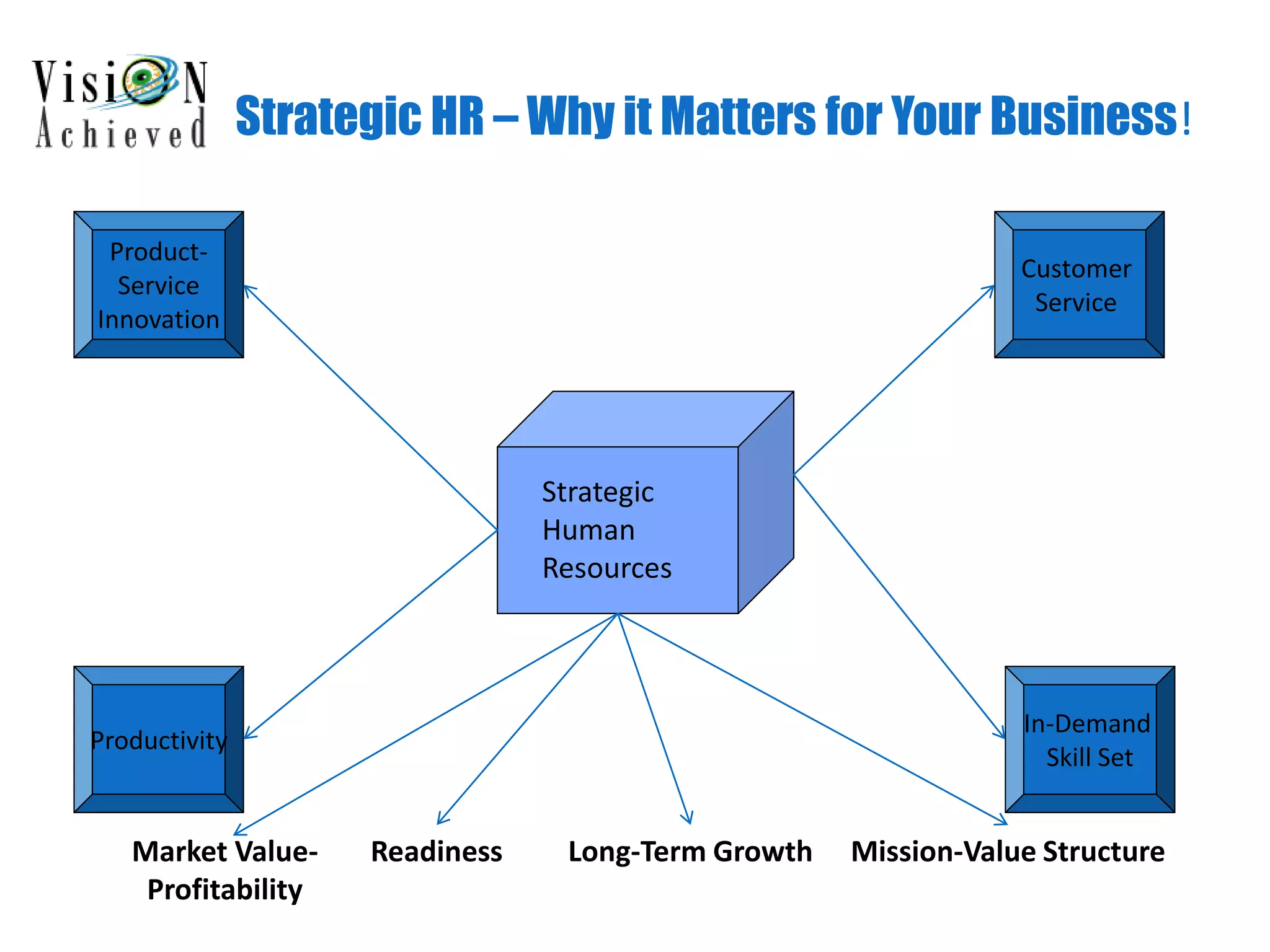
This document discusses the importance of strategic human resources (HR) for organizational success. It outlines how effective HR alignment with business goals can boost financial performance, innovation, and sustainability. The presentation covers steps to create an HR framework, including strategic planning, execution, and measurement. Case studies show how misaligned or reduced HR hurt companies, while strategic HR improved growth and market value. The key message is that a strategic HR architecture linking human capital objectives to business objectives is a competitive advantage and business differentiator.




![Why HR Matters
• The average financial analysts base 35% of his or her investment decision
on non-financial information – Harvard Business Review
• Companies with an effective and well executed strategic HR function have
half the turnover, four times the sales per employee, and a market to book
value of more than three times as large as those that do not – Academy of
Management Journal
• Companies that follow HR best [strategic] practices have more than 50%
higher market value than those who do not – Workforce Management
Strategic Human Resources is a Key Business Differentiator](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whyhrmattersworkingcopyrevised-140423105717-phpapp01/75/Why-HR-Matters-Working-Copy-Presented-in-2009-6-2048.jpg)