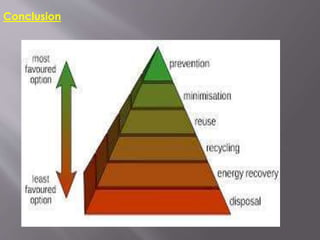
The document discusses hazardous waste management. It outlines five main types of hazardous waste: reactive, ignitable, medical, radioactive, and corrosive waste. It describes the characteristics of hazardous waste as ignitability, corrosivity, reactivity, and toxicity. The document then covers management strategies for different waste types, including segregating medical waste in color-coded bags, deep geological disposal of radioactive waste, and incineration of reactive, ignitable, and corrosive waste.

![1.Introduction
2.Types of hazardous waste
i]Reactive wastes
ii]Ignitable wastes
iii]Medical waste
iv]Radioactive waste
v]Corrosive waste
3.Characteristics of hazardous waste
i]Ignitability
ii]Corrosivity
iii]Reactivity
iv]Toxicity
4.Management of hazardous waste
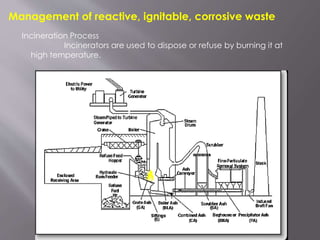
i]Management of reactive waste
ii]Management of ignitable waste
iii]Management of radioactive waste
iv]Management of corrosive waste
v]Management of medical waste
5.Conclusion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pavan-150906140617-lva1-app6892/85/Hazardous-waste-managment-2-320.jpg)

![Types of hazardous waste
i]Reactive wastes
ii]Ignitable wastes
iii]Medical waste
iv]Radioactive waste
v]Corrosive waste
1.Reactive wastes-
This wastes are unstable and tend to react vigorously
with air and water and other substances.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pavan-150906140617-lva1-app6892/85/Hazardous-waste-managment-4-320.jpg)


![Characteristics of hazardous waste-
i]Ignitability
ii]CorrosivitySSDSFDF
iii]Reactivity
iv]Toxicity
1.Ignitability-
This characteristic of hazardous waste is due to fires
under certain condition.
2.Corrosivity-
The characteristic of hazardous waste due to high
alkaline or acidic waste.
3.Reactivity-
This characteristic gives unstable property to
waste.
4.Toxicity-
It is the degree which substance can damage an](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pavan-150906140617-lva1-app6892/85/Hazardous-waste-managment-7-320.jpg)
![Management of Hazardous Waste
i]Management of reactive waste
ii]Management of ignitable waste
iii]Management of radioactive waste
v]Management of corrosive waste
v]Management of medical waste
Management of medical waste
1.Segretion of waste in color coded bags
2.Training to the staff of hospitals and medical research centers
3.Equipments](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pavan-150906140617-lva1-app6892/85/Hazardous-waste-managment-8-320.jpg)


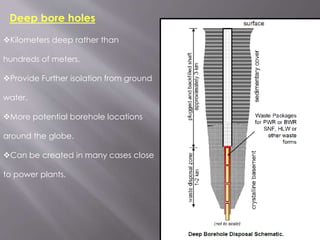
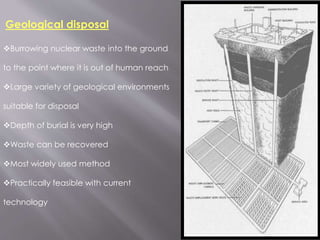
![Management of Radioactive Waste
i]Ocean dumping](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pavan-150906140617-lva1-app6892/85/Hazardous-waste-managment-11-320.jpg)