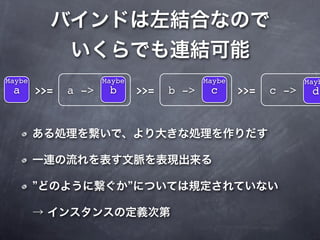
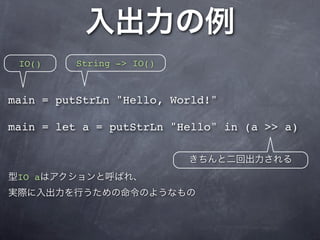
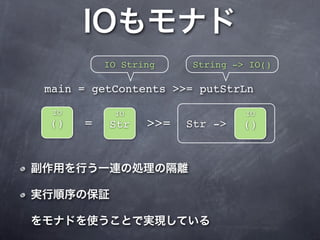
The document describes a Haskell program that translates characters in one string to characters in another string. It defines a translate function that maps characters from the first string (set1) to the corresponding characters in the second string (set2). A translateString function applies the translate function to a given string, and the main function gets the set1 and set2 strings from arguments, reads stdin, applies translateString, and writes the result to stdout, catching any errors.













![1 import java.util.Scanner;
2
3 public class IOSample {
4
5 public static void main(String[] args) {
6
7 Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
8
9 System.out.println(" ");
10 String str = scan.next(); //
11 System.out.println(" "+ str);
12 }
13 }
( )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/haskell-110915084708-phpapp01/85/Haskell-14-320.jpg)
![1 import java.util.Scanner;
2
3 public class IOSample {
4
5 public static void main(String[] args) {
6
7 Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
8
9 System.out.println(" ");
10 String str = scan.next(); //
11 System.out.println(" "+ str);
12 }
13 }
( )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/haskell-110915084708-phpapp01/85/Haskell-15-320.jpg)





![‘A’ ‘B’ ‘C’ ‘D’
1 bools = [True, False, True] :: [Bool]
2
3 -- "ABCD"
4 letters = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'] :: [Char]
5
6 --
7 empty = [] :: [Int]
8
9 -- 1
10 notEmpty = [[]] :: [[Float]]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/haskell-110915084708-phpapp01/85/Haskell-22-320.jpg)
![1 --
2 (False, 'A') :: (Bool, Char)
3
4 -- ( )
5 ("Name", True, 123) :: (String, Bool, Int)
6
7 --
8 ('a', (False, 'b')) :: (Char, (Bool, Char))
9
10 --
11 (['a', 'b', ‘c’], [False, True]) :: ([Char], [Bool])
12
13 --
14 [('a', False), ('b', True)] :: [(Char, Bool)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/haskell-110915084708-phpapp01/85/Haskell-23-320.jpg)


![1 twice :: (Int -> Int) -> Int -> Int
2 twice f x = f (f x)
3 Int
4 isDigit :: Char -> Bool
Int
5 isDigit c = c >= '0' && c <= '9'
6
7 -- map :: (a -> b) -> [a] -> [b]
> twice (*2) 3
12
> map (+1) [1, 2, 3, 4]
[2, 3, 4, 5]
> map isDigit ['a', '0', 'b', '9']
[False, True, False, True]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/haskell-110915084708-phpapp01/85/Haskell-26-320.jpg)
![> length [1, 3, 5, 7]
4
> length [True, False]
2
> length [length, length, length]
3
length :: [a] -> Int
map :: (a -> b) -> [a] -> [b]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/haskell-110915084708-phpapp01/85/Haskell-27-320.jpg)


![1 -- [λxy. x+y]
2 add x y = x + y
3 add' = x -> (y -> x + y)
4 add'' = x y -> x + y
5
6 --
7 -- const x y = x
8 const :: a -> (b -> a)
9 const x = _ -> x
10
11 --
> map (x -> x * 2 + 1) [1, 3, 5, 7]
[3, 7, 11, 15]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/haskell-110915084708-phpapp01/85/Haskell-30-320.jpg)
![> [x^2 | x <- [1..5]]
[1,4,9,16,25]
> [(x, y) | x <- [1,2,3], y <- [4,5]]
[(1,4),(1,5),(2,4),(2,5),(3,4),(3,5)]
1 --
2 factors :: Int -> [Int]
3 factors n = [x | x <- [1..n], n `mod` x == 0]
4 --
5 primes :: Int -> [Int]
6 primes n = [x | x <- [2..n], factors x == [1, x]]
> factors 100
[1,2,4,5,10,20,25,50,100]
> primes 50
[2,3,5,7,11,13,17,19,23,29,31,37,41,43,47]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/haskell-110915084708-phpapp01/85/Haskell-31-320.jpg)
![1 --
2 factorial :: Int -> Int
3 factorial 0 = 1
4 factorial n = n * factorial (n - 1)
5
6 --
7 product :: Num a => [a] -> a
8 product [] = 1
9 product (n:ns) = n * product ns
1 2 3 4
1:[2,3,4] 4:[]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/haskell-110915084708-phpapp01/85/Haskell-32-320.jpg)
![1 qsort :: Ord a => [a] -> [a]
2 qsort [] = []
3 qsort (x:xs) = qsort smaller ++ [x] ++ qsort larger
4 where
5 smaller = [a|a <- xs, a <= x]
6 larger = [a|a <- xs, a > x]
> qsort [100, 23, 37, 3, 55, 68, 49]
[3,23,37,49,55,68,100]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/haskell-110915084708-phpapp01/85/Haskell-33-320.jpg)


![1 -- !
2 summary :: [Integer] -> Integer
3 summary [] = 0
4 summary (n:ns) = n + summary ns
5
6 -- ( )
7 summary' :: [Integer] -> Integer
8 summary' xs = f xs 0
9 where
10 f [] sum = sum
11 f (y:ys) sum = f ys (y + sum)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/haskell-110915084708-phpapp01/85/Haskell-36-320.jpg)


![1 ones :: [Int]
2 ones = 1 : ones
3
4 -- ( )
5 sieve :: [Int] -> [Int]
6 sieve (p:xs) = p : sieve [x|x <- xs, x `mod` p /= 0]
7
8 primes :: [Int]
9 primes = sieve [2..] head ones
= {head ones }
> head ones head (1:ones)
1 = {head }
> take 10 primes 1
[2,3,5,7,11,13,17,19,23,29]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/haskell-110915084708-phpapp01/85/Haskell-39-320.jpg)




![6 -- set1 set2
7 translate :: String -> String -> Char -> Char
8 translate [] _ c = c
9 translate (x:xs) [] c = if x == c then ' ' else translate xs [] c
10 translate (x:xs) [y] c = if x == c then y else translate xs [y] c
11 translate (x:xs) (y:ys) c = if x == c then y else translate xs ys c
12
13 --
14 translateString :: String -> String -> String -> String
15 translateString set1 set2 str = map (translate set1 set2) str
16
17 usage :: IOError -> IO ()
18 usage e = do putStrLn "Usage: ex14 set1 set2"
19 putStrLn "Translates characters in set1 on stdin to the corresponding"
20 putStrLn "characters from set2 and writes the translation to stdout."
21
22 --
23 main :: IO ()
24 main = (do [set1,set2] <- getArgs
25 contents <- hGetContents stdin
26 putStr $ translateString set1 set2 contents) `catchError` usage](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/haskell-110915084708-phpapp01/85/Haskell-47-320.jpg)
![6 -- set1 set2
7 translate :: String -> String -> Char -> Char
8 translate [] _ c = c
9 translate (x:xs) [] c = if x == c then ' ' else translate xs [] c
10 translate (x:xs) [y] c = if x == c then y else translate xs [y] c
11 translate (x:xs) (y:ys) c = if x == c then y else translate xs ys c
12
13 --
14 translateString :: String -> String -> String -> String
15 translateString set1 set2 str = map (translate set1 set2) str
16
17 usage :: IOError -> IO ()
18 usage e = do putStrLn "Usage: ex14 set1 set2"
19 putStrLn "Translates characters in set1 on stdin to the corresponding"
20 putStrLn "characters from set2 and writes the translation to stdout."
21
22 --
23 main :: IO ()
24 main = (do [set1,set2] <- getArgs
25 contents <- hGetContents stdin
26 putStr $ translateString set1 set2 contents) `catchError` usage](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/haskell-110915084708-phpapp01/85/Haskell-48-320.jpg)


![lookup :: Eq a => a -> [(a, b)] -> Maybe b
players = [(6, "Nakata"), (11, "Darvish"), (41, "Inaba")]
> lookup 11 players
Just "Darvish"
> lookup 212 players
Nothing](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/haskell-110915084708-phpapp01/85/Haskell-51-320.jpg)
![1 pacific = [("Fs", [(6, "Nakata"), (11, "Darvish"), (41, "Inaba")]),
2 ("SH", [(3, "Matsunaka"), (21, "Wada"), (47, "Sugiuchi")]),
3 ("Es", [(18, "Tanaka"), (21, "Iwakuma"), (32, "Matsui")])]
4
5 lookupName :: String -> Int -> Maybe String
6 lookupName t n = case (lookup t pacific) of
7 Just players -> lookup n players
8 Nothing -> Nothing
> lookupName "Fs" 41
Just "Inaba"
…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/haskell-110915084708-phpapp01/85/Haskell-52-320.jpg)
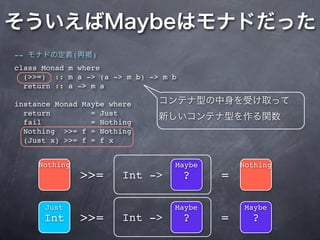
![1 pacific = [("Fs", [(6, "Nakata"), (11, "Darvish"), (41, "Inaba")]),
2 ("SH", [(3, "Matsunaka"), (21, "Wada"), (47, "Sugiuchi")]),
3 ("Es", [(18, "Tanaka"), (21, "Iwakuma"), (32, "Matsui")])]
4
5 lookupName :: String -> Int -> Maybe String
6 lookupName t n = case (lookup t pacific) of
7 Just players -> lookup n players
8 Nothing -> Nothing
9
10 lookupName' t n = lookup t pacific >>= lookup n
> lookupName' "Es" 18
Just "Tanaka" [(Int, b)] -> Maybe b
> lookupName' "Fs" 18
Nothing Maybe [(Int, String)]
> lookupName' "DH" 21
Nothing
--
(>>=) :: m a -> (a -> m b) -> m b
lookup :: Eq a => a -> [(a, b)] -> Maybe b](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/haskell-110915084708-phpapp01/85/Haskell-54-320.jpg)