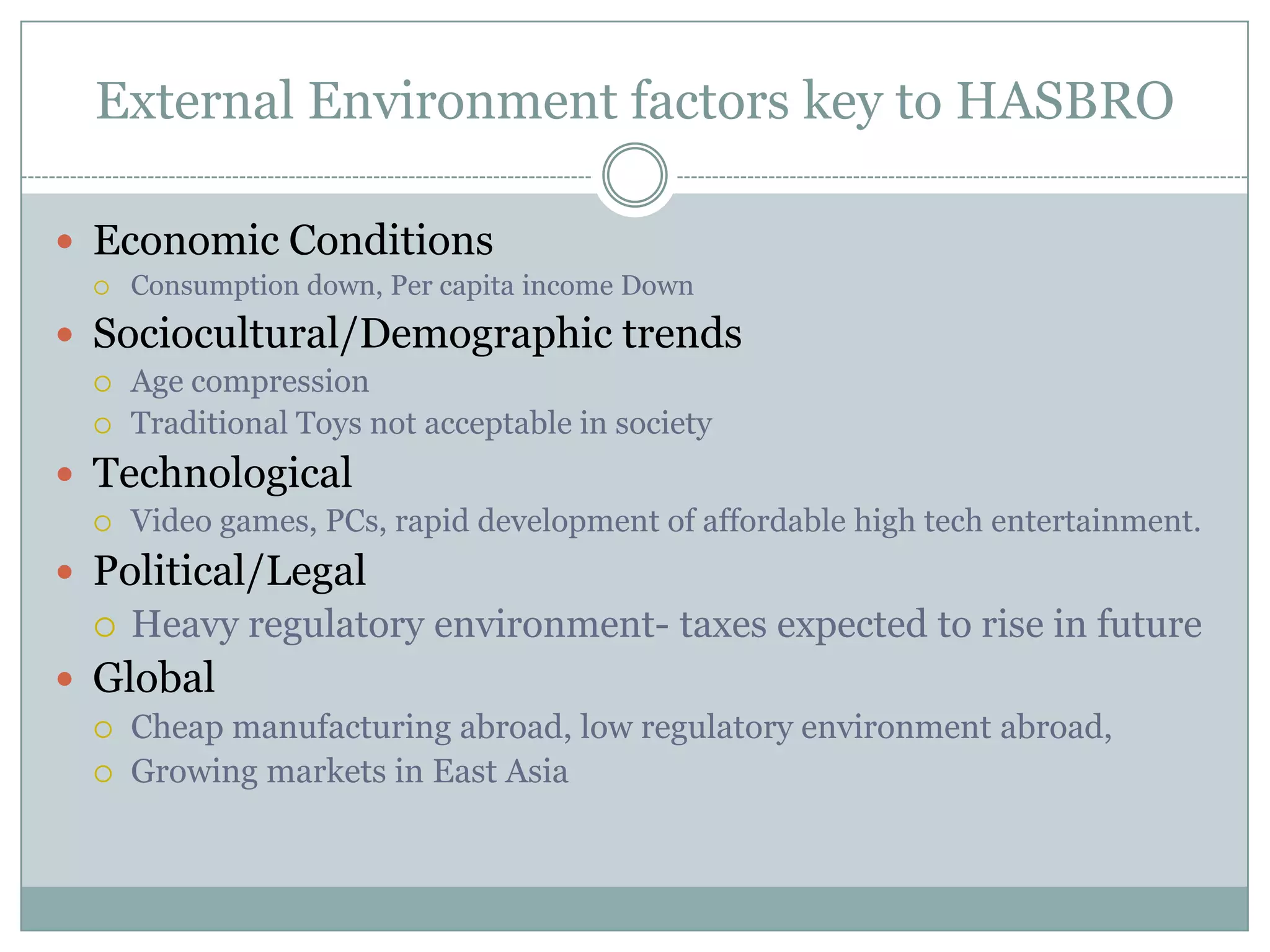
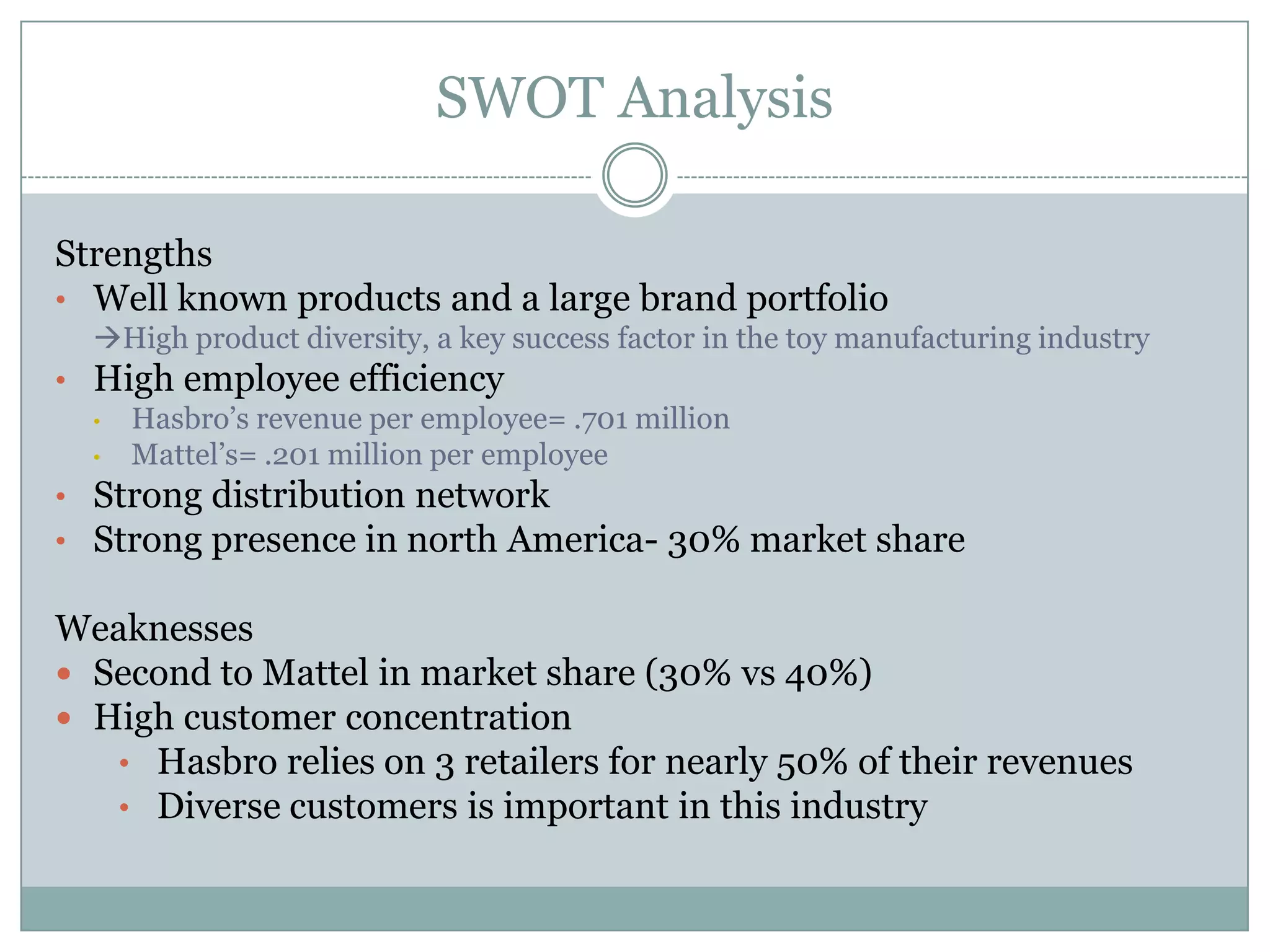
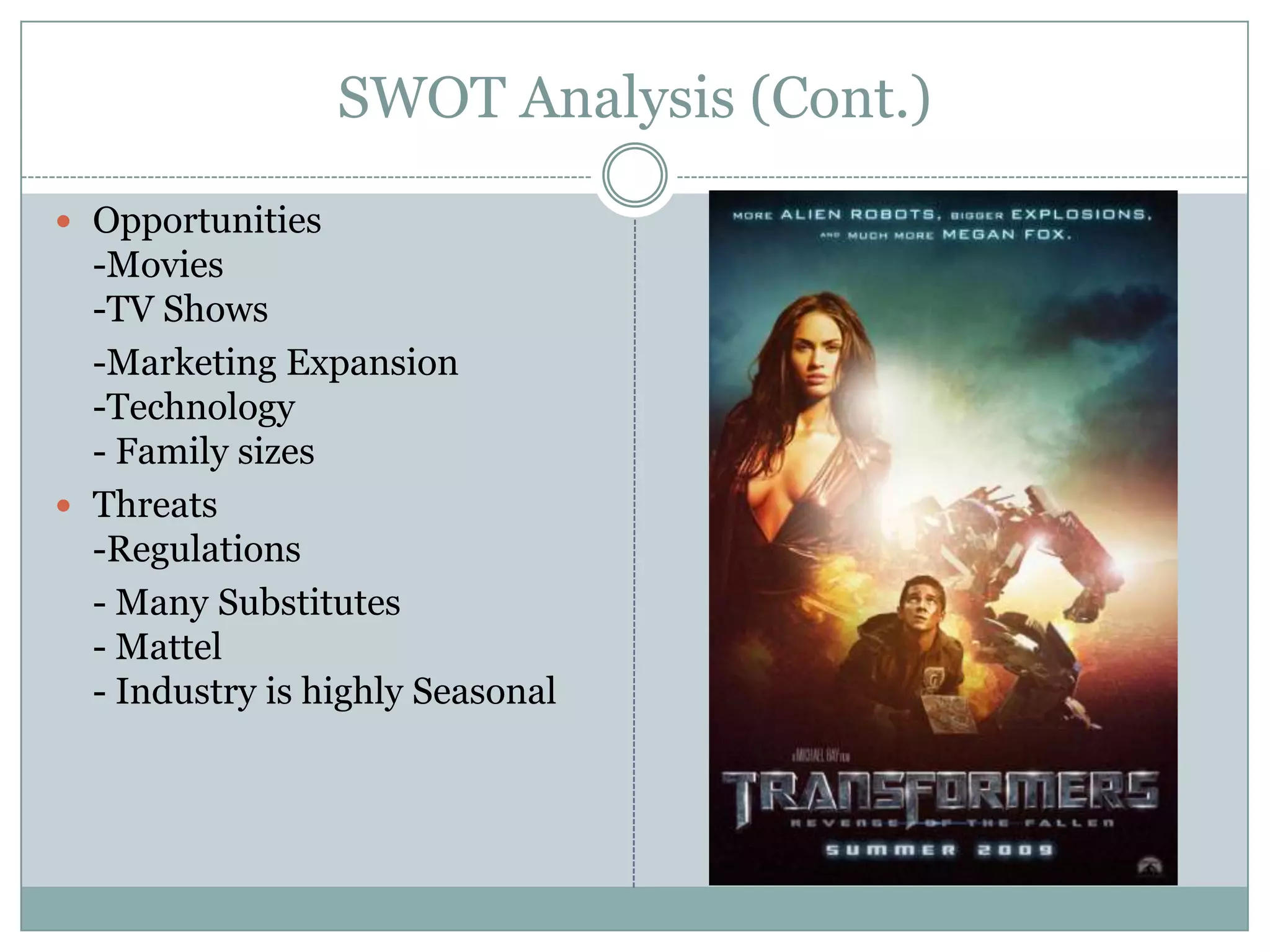
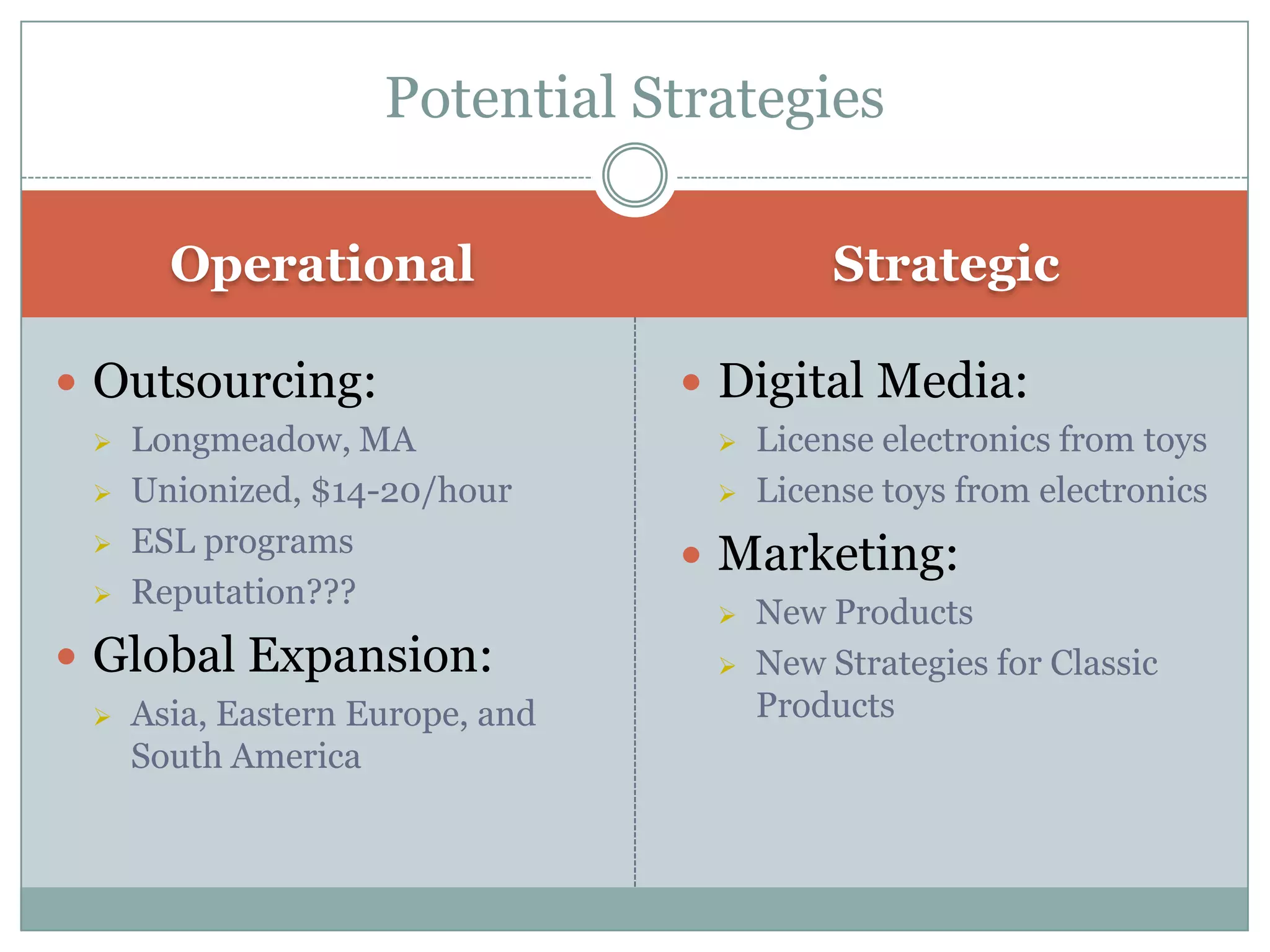
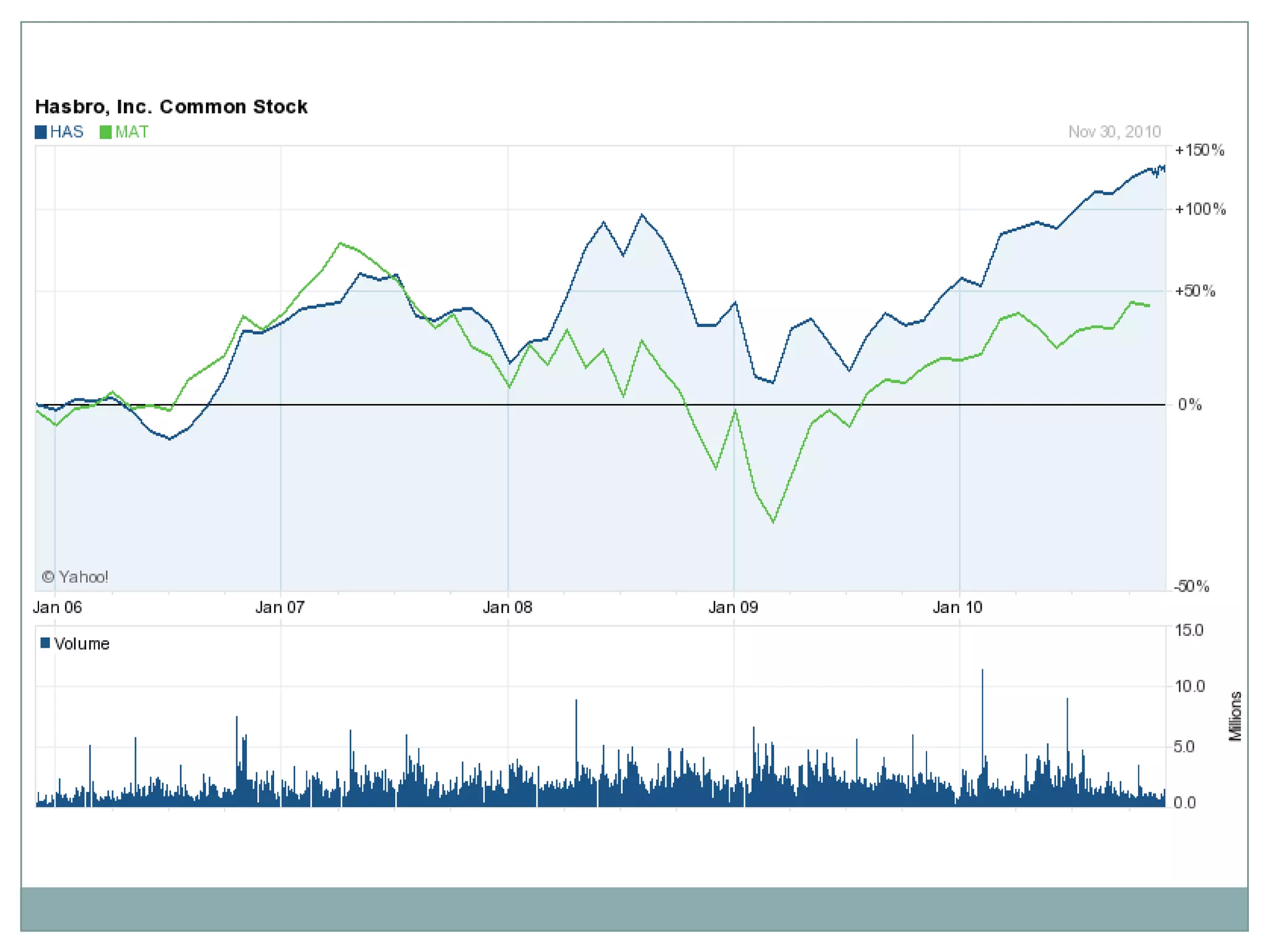
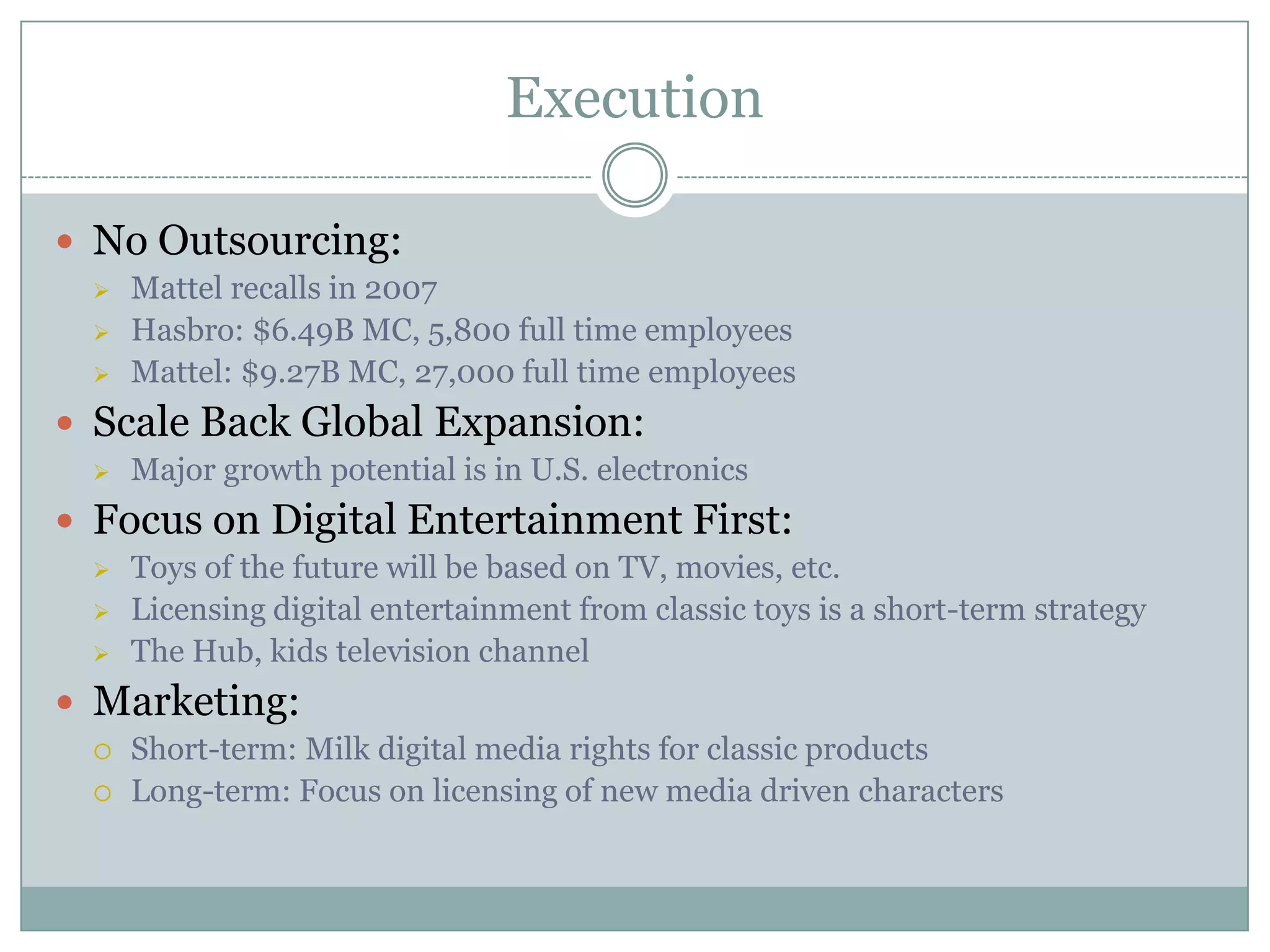
Hasbro is one of the largest toy companies in the world founded in 1923. It has a large portfolio of well-known toy brands such as Transformers, My Little Pony, and Monopoly. While Hasbro has a strong brand portfolio and distribution network, it faces threats from increasing regulations and many substitute products. Potential strategies for Hasbro include outsourcing manufacturing, expanding globally, developing digital media like video games based on its brands, and marketing strategies to leverage its classic toy brands in new digital entertainment. However, focusing first on creating new digitally-driven characters and entertainment may be a better long-term strategy than short-term exploitation of existing toy brands.