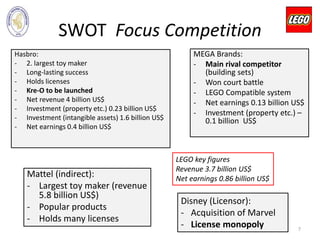
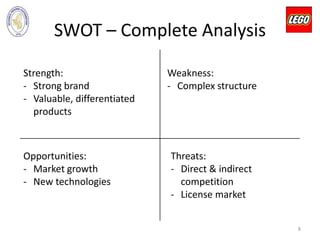
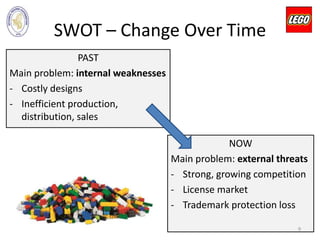
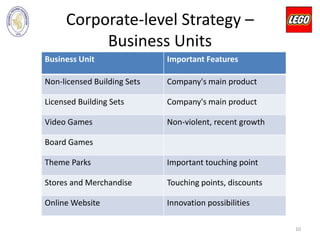
The document outlines LEGO Group's business strategies, including a detailed SWOT analysis highlighting strengths like a strong brand and product quality, weaknesses such as a complex structure, and external threats from competition. It analyzes the company's historical growth, key figures, and corporate-level strategies for market positioning and target segmentation. Recommendations for improvement include developing proprietary stories, enhancing community engagement, and maintaining market dominance in the toy industry.