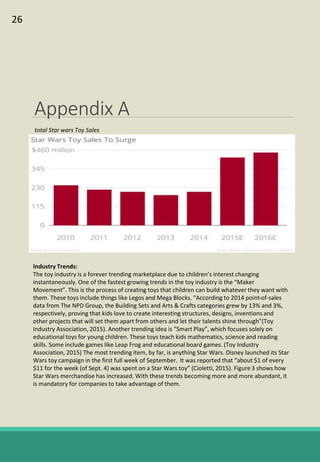
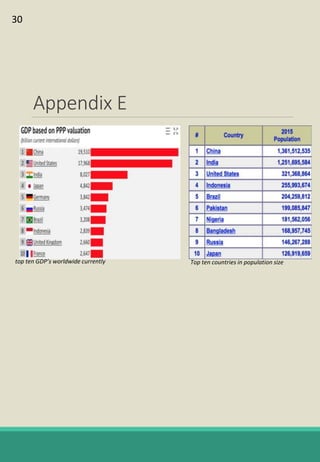
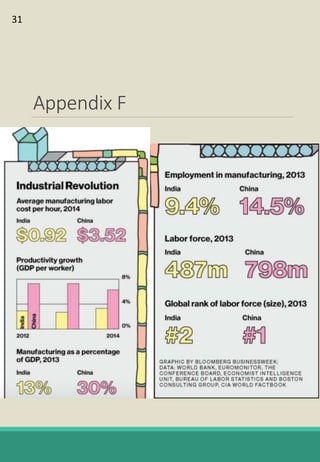
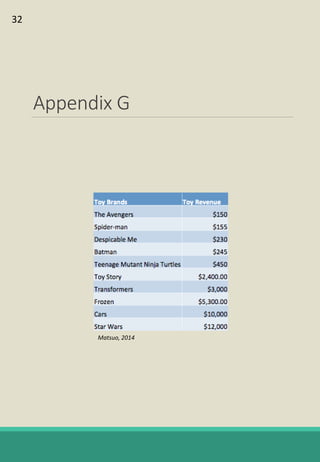
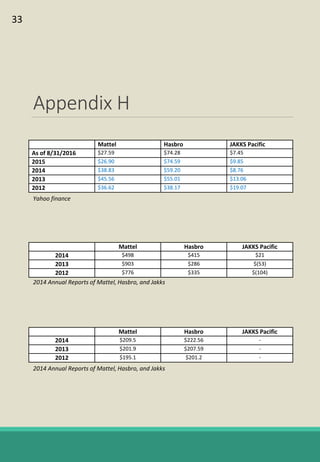
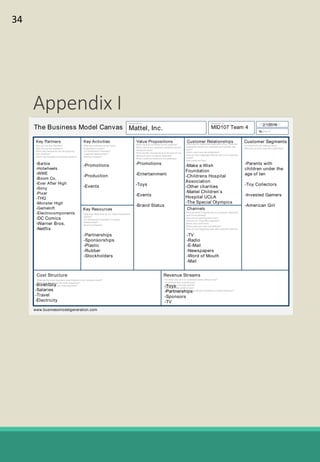
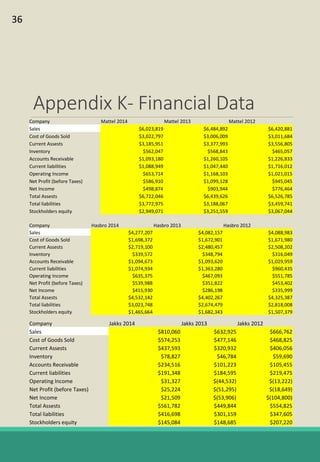
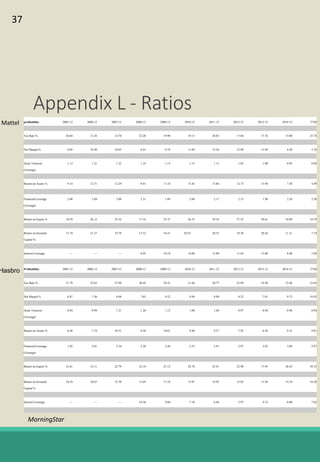
The document is a report analyzing the toy industry and Mattel Inc. specifically. It identifies three key success factors for companies in the toy industry: innovating products into digital entertainment, expanding into emerging markets, and advantageous licensing partnerships. The report ranks Mattel second compared to competitors Hasbro and JAKKS Pacific based on performance in these three areas. It provides recommendations to help Mattel improve, such as partnering with Electronic Arts to further establish a digital presence, gaining licensing rights to an upcoming movie to boost sales, and improving international reputation through retail partnerships in India and China.