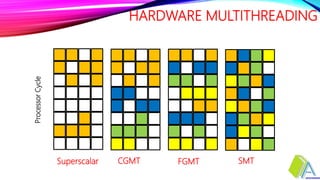
Hardware multithreading allows multiple threads to share the functional units of a single processor by switching between threads when one thread is stalled. There are three main types of hardware multithreading: coarse-grained multithreading switches threads on long latency events like L2 cache misses; fine-grained multithreading switches threads every clock cycle in a round-robin fashion for high throughput but poor single-thread performance; simultaneous multithreading combines fine-grained multithreading with superscalar processing to further improve throughput by hiding memory latency but increases conflicts for shared resources.