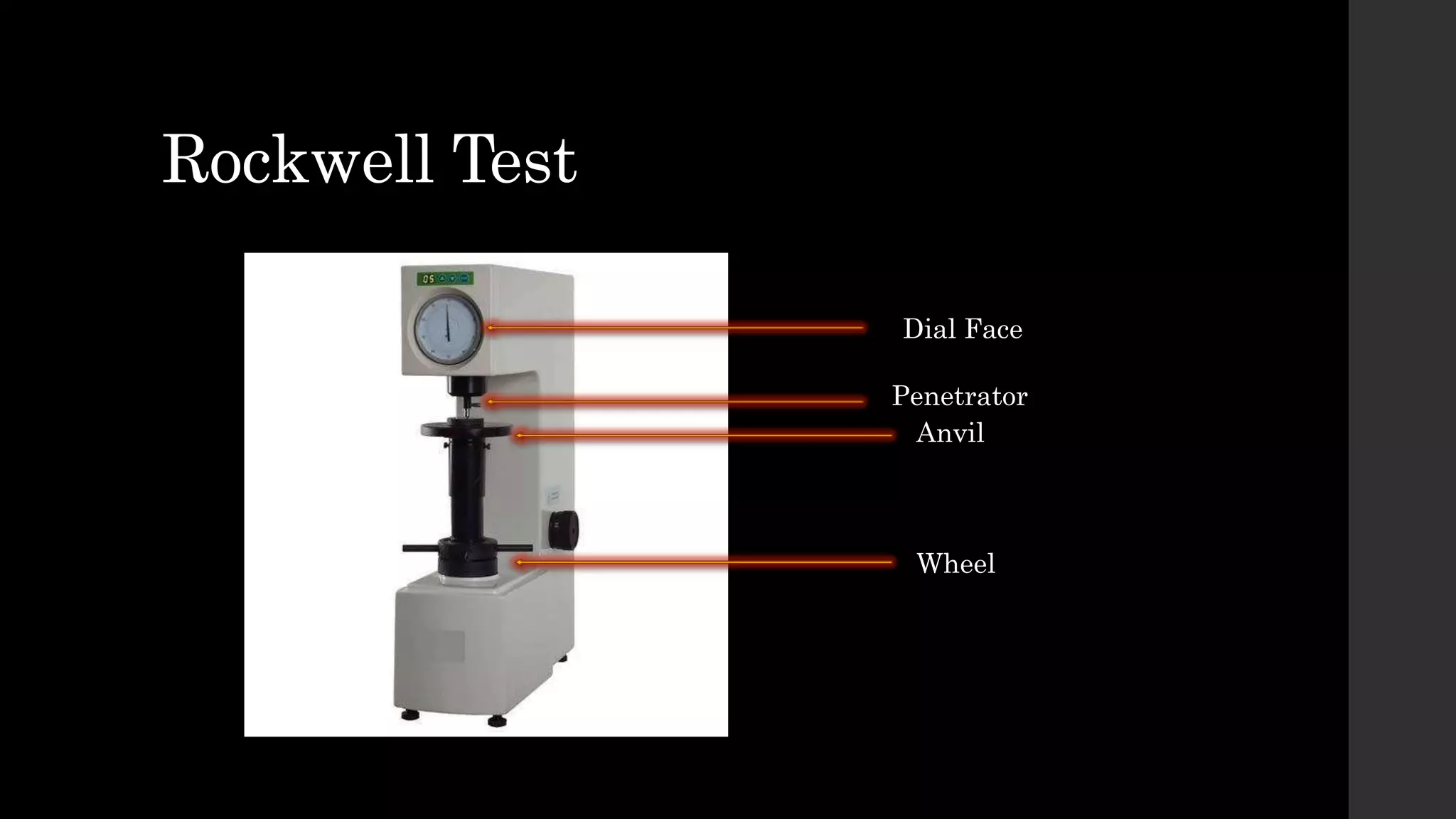
The document discusses the hardness of materials, defining it as the resistance to scratching, abrasion, or plastic deformation. It outlines three principal testing methods: scratch testing, rebound hardness, and indentation testing, along with several hardness measurement units and specific tests such as Brinell, Rockwell, Vickers, Mohs, and Scleroscope tests. Each test method has its procedures and suits different material types, providing various scales of hardness measurement.