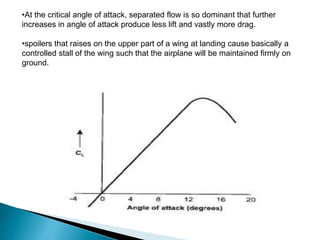
The document defines aircraft stall and describes the different regions of airflow over wings. It explains that a stall occurs when the angle of attack increases beyond a critical point, reducing lift. Stall protection systems calculate two maximum angles of attack to limit the actual angle and prevent stalling. In contrast, stall warning systems only provide indications to pilots of approaching stall without limiting control. The stall protection system and method aims to allow maximum performance while preventing prolonged stalling.