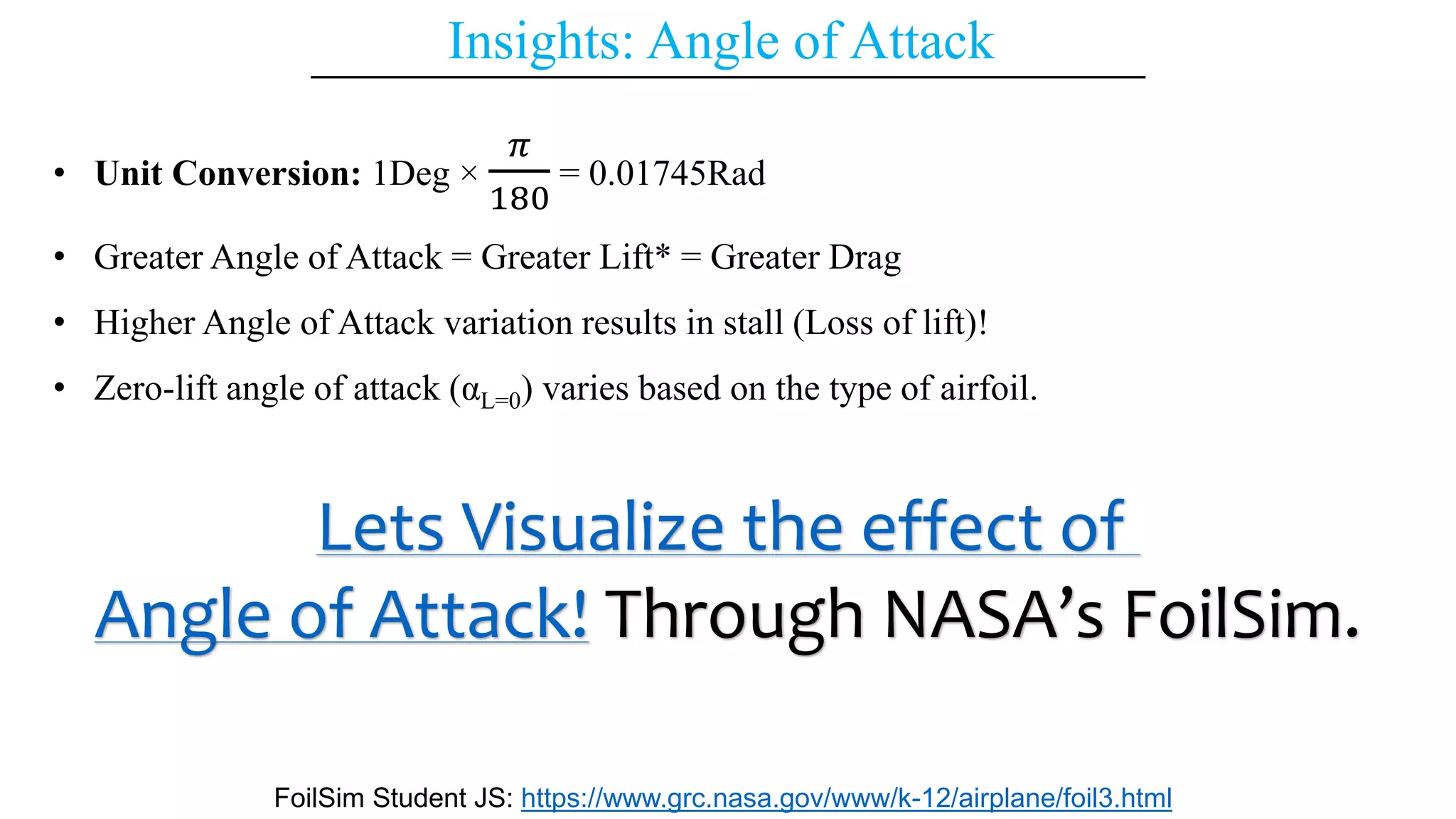
This document provides an overview of flight mechanics topics including angle of attack. It discusses the angle of attack (AOA) as the angle between the relative wind and chord line of an airfoil. Greater AOA results in greater lift but also greater drag. Higher AOA variation can cause stall from loss of lift. It recommends visualizing AOA effects using NASA's FoilSim tool. The document also outlines core topics like aircraft configurations, flight instruments, aerodynamic forces, airplane performance, stability, and dynamic stability to be covered.


![Angle of Attack (AOA)
Definition
The angle between the relative wind (V∞) and the chord line (the line
connecting Leading edge [LE] & Trailing edge [TE]) is the angle of attack a
of an airfoil.
JDougMcLeanatEnglishWikipedia/CCBY-SA
(https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)
• The Angle of Attack is abbreviated as (AOA).
• It is symbolized as “α”.
• In some literature, alternate reference line is considered instead of chord line.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/11fm-anglefoattack-200822030155/75/Angle-of-attack-Flight-Mechanics-GATE-Aerospace-4-2048.jpg)