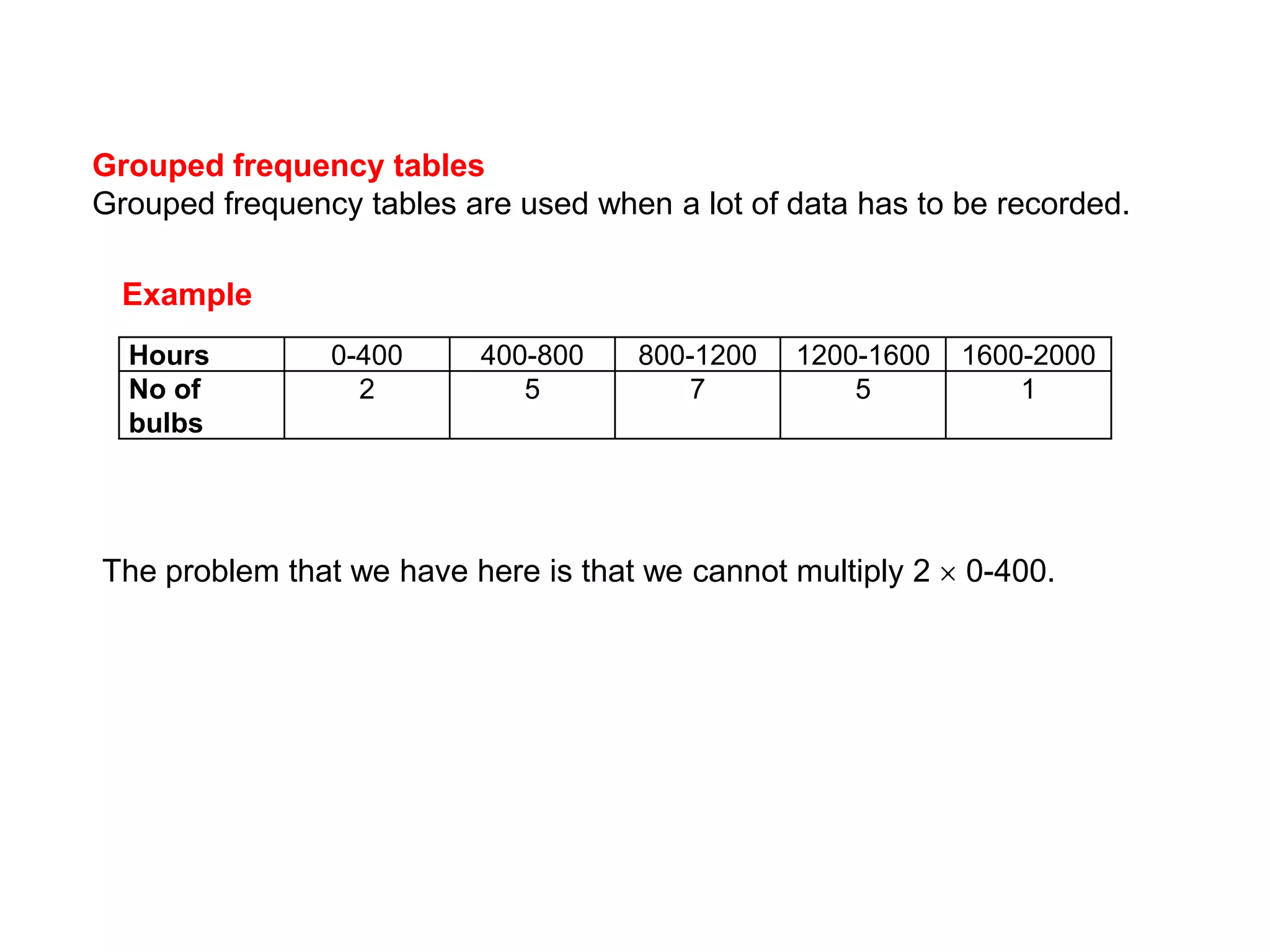
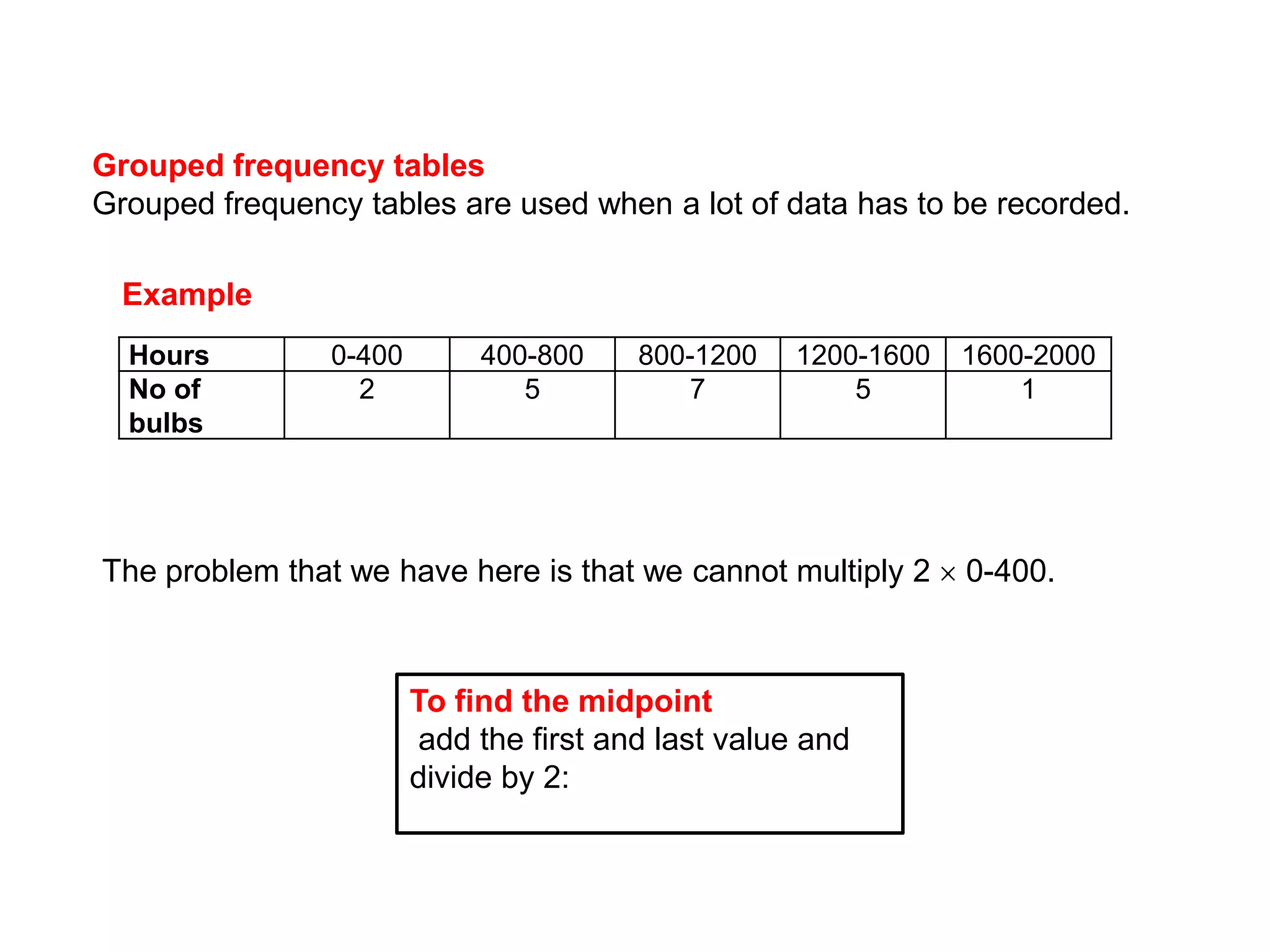
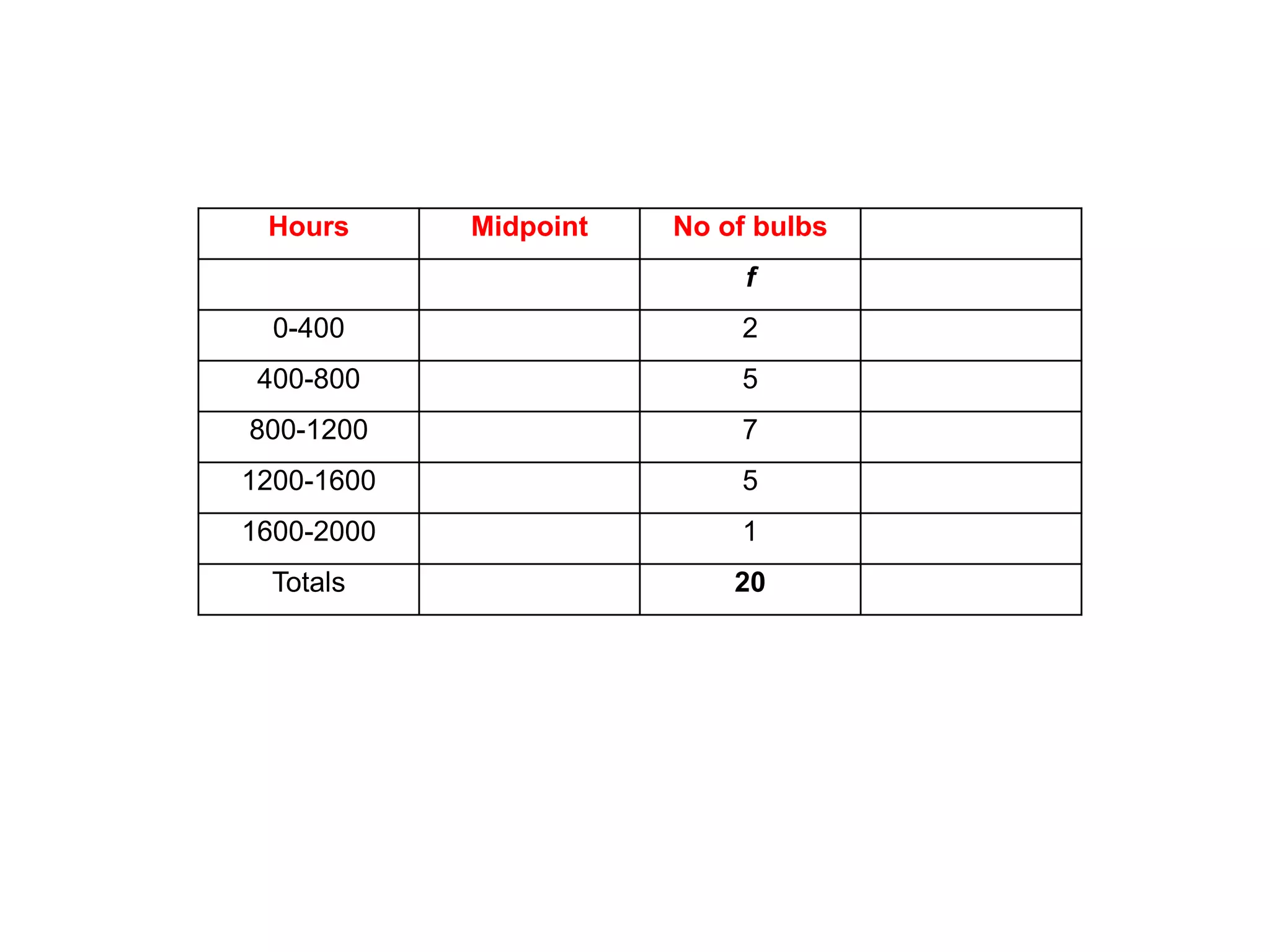
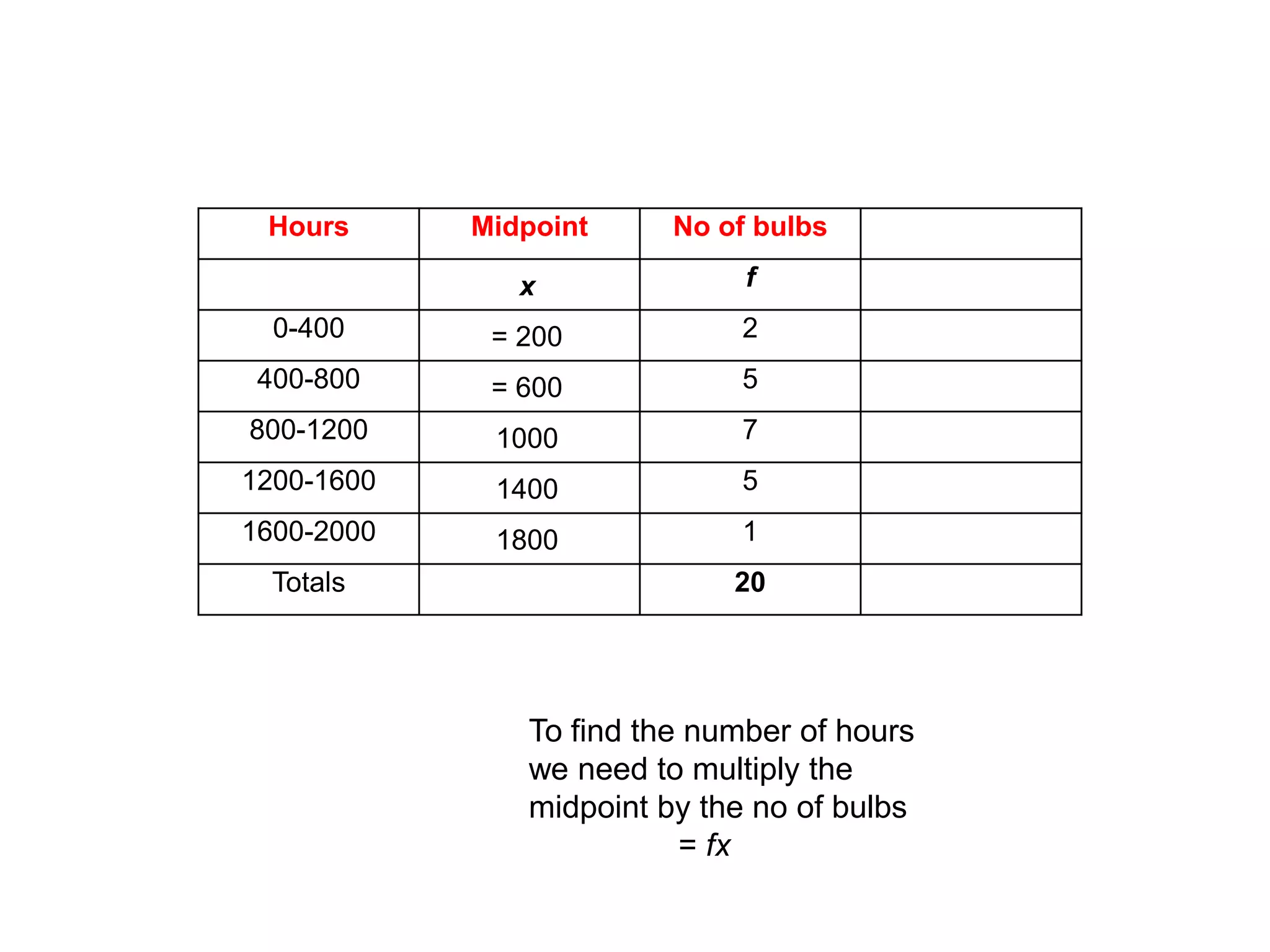
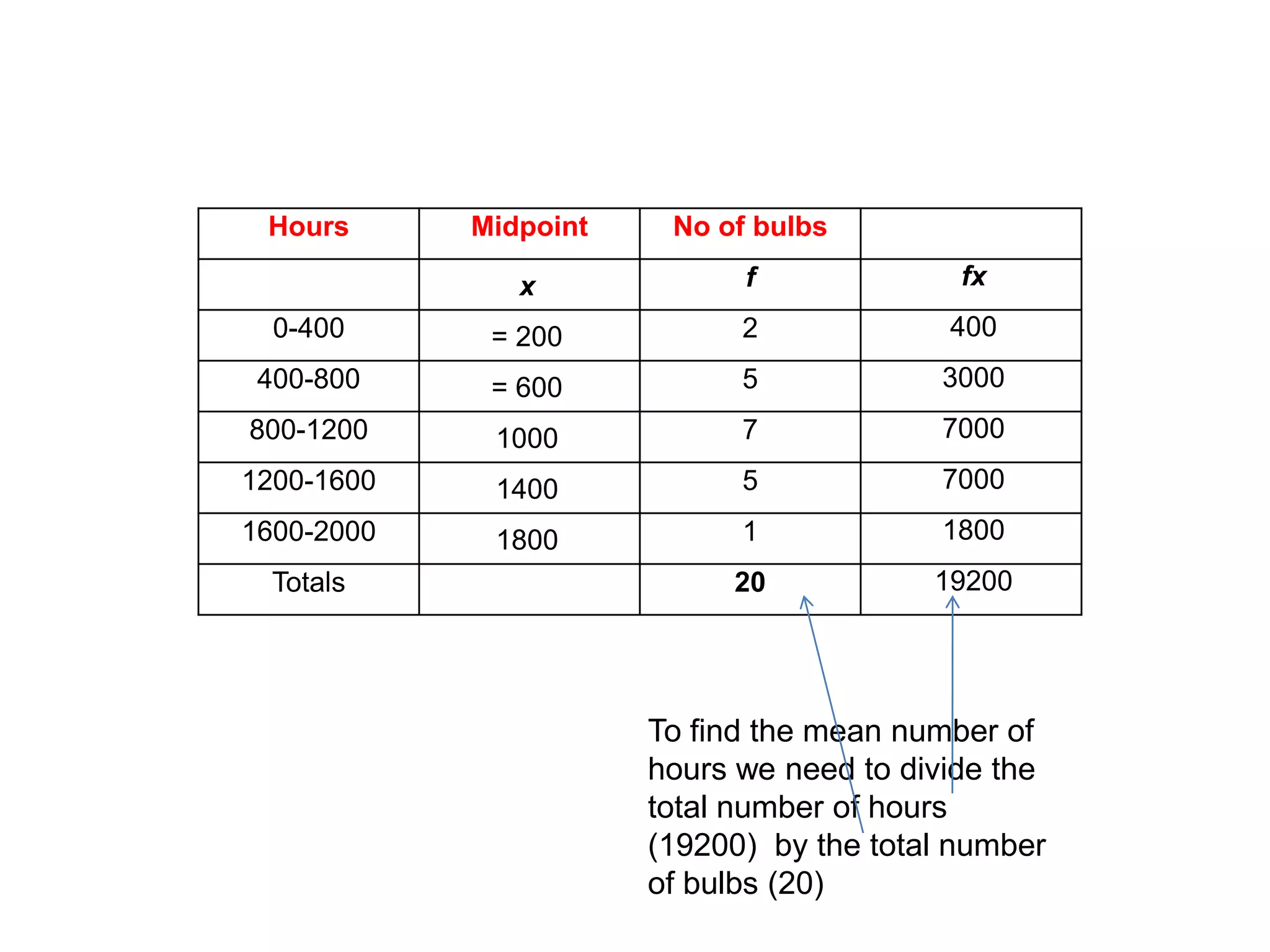
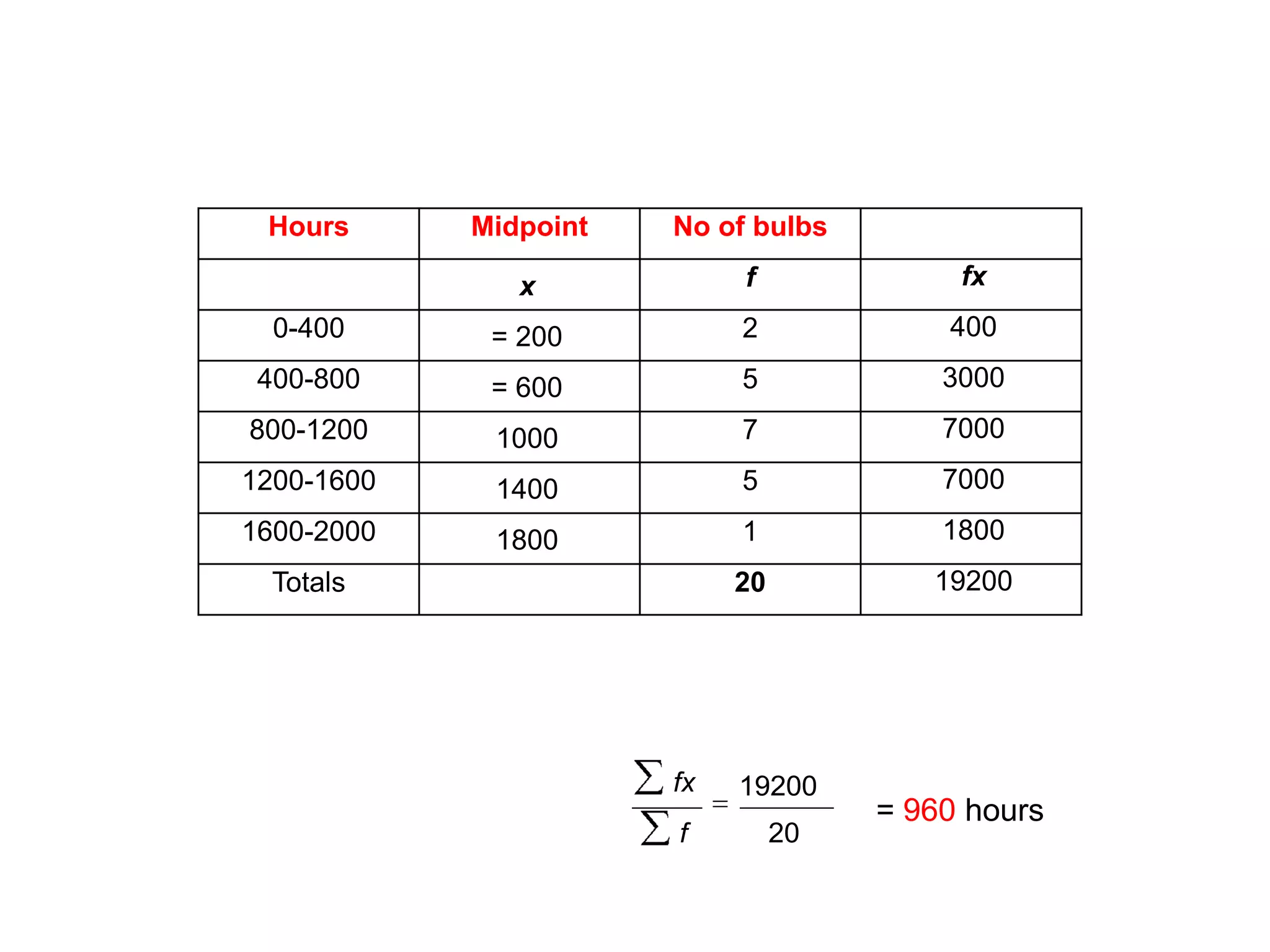
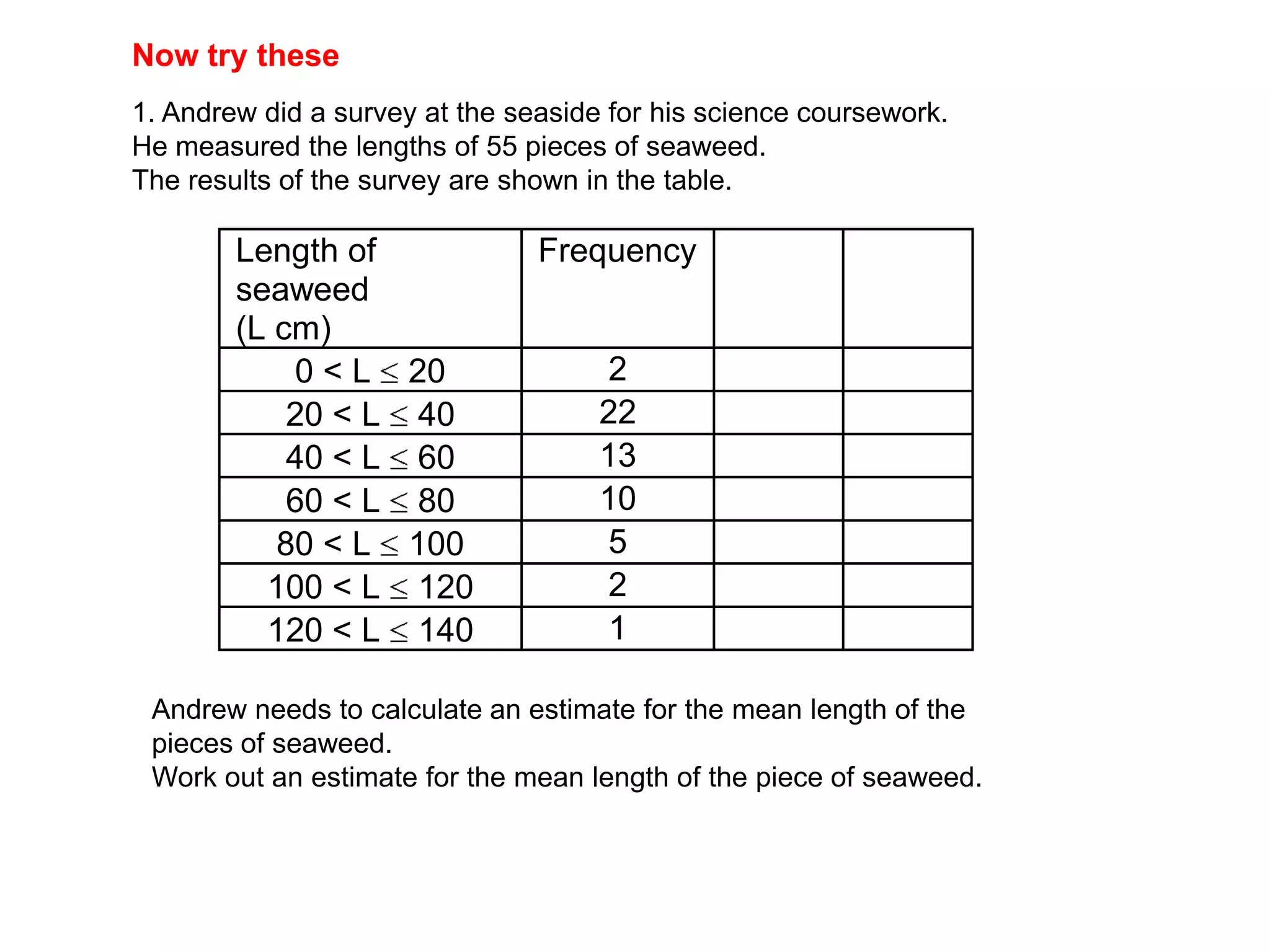
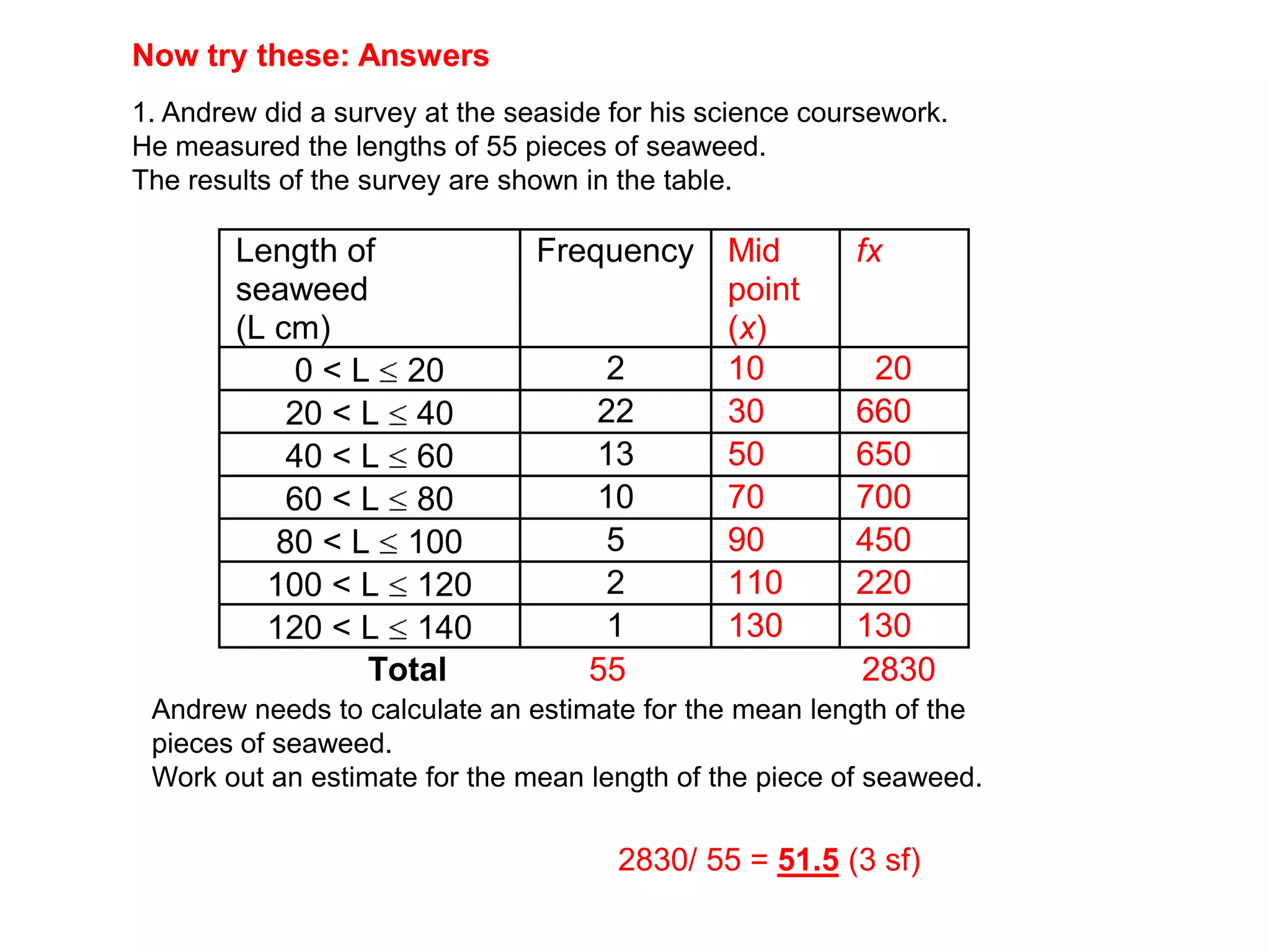
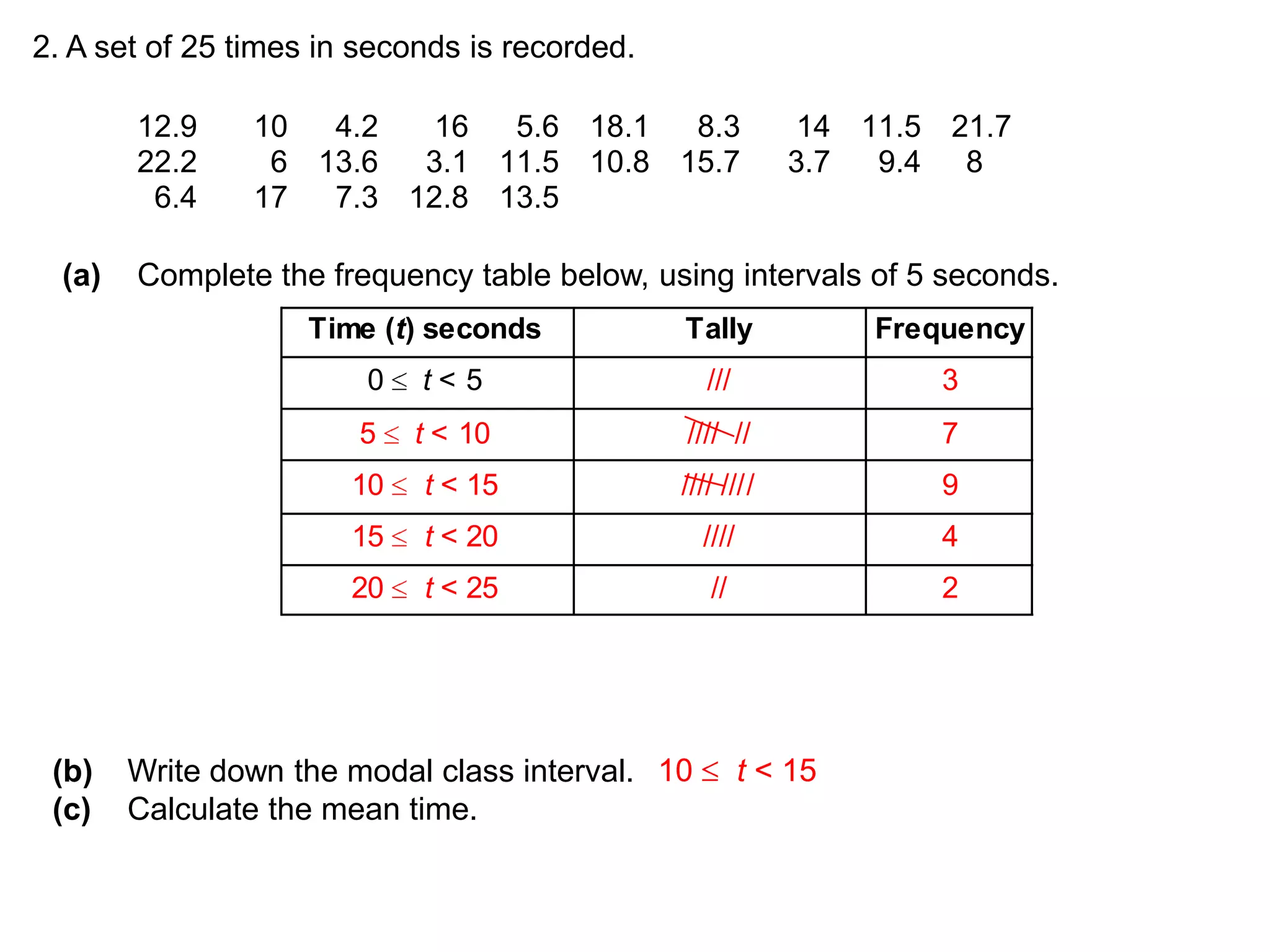
This document discusses how to find the mean from grouped data using grouped frequency tables. Grouped frequency tables are used to record large data sets. To find the mean, you first calculate the midpoint of each group by adding the upper and lower bounds and dividing by 2. You then multiply each midpoint by its frequency and sum these values. Finally, you divide the total sum by the total number of data points to obtain the mean. Examples are provided to demonstrate calculating means from grouped frequency tables.