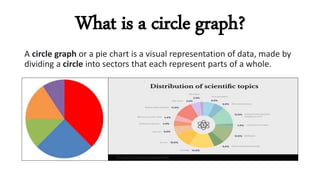
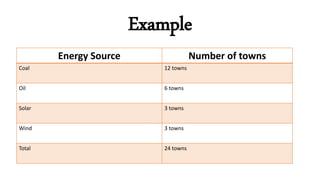
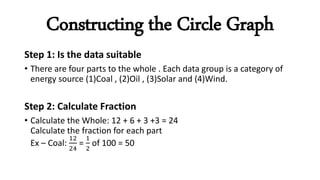
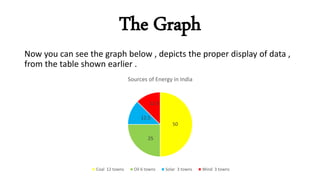
The document explains the concept and construction of circle graphs, also known as pie charts, which visually represent data by dividing a circle into sectors. It outlines the properties of circle graphs and provides step-by-step instructions for plotting them, including determining suitability, calculating percentages, drawing the graph, and labeling it. An example using energy sources in towns illustrates the application of these concepts.