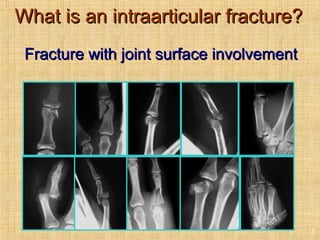
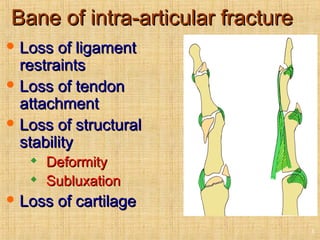
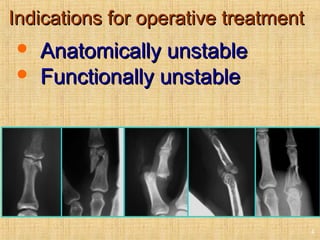
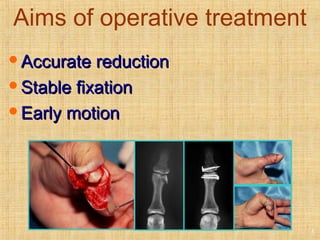
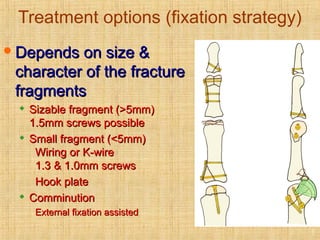
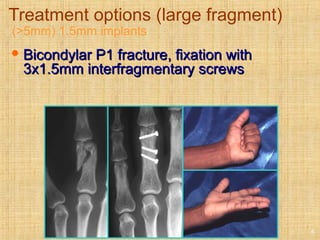
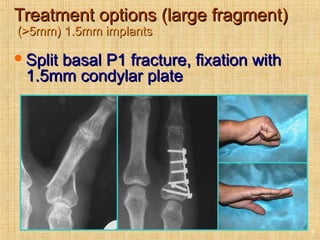
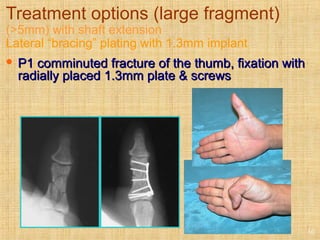
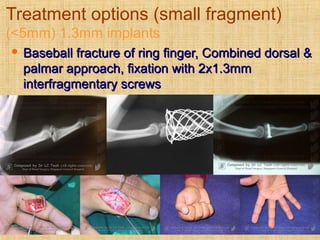
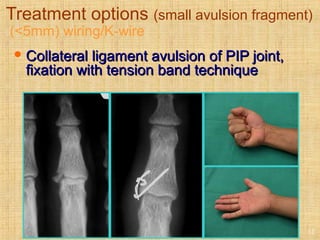
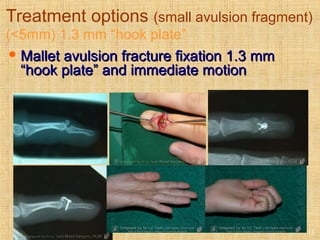
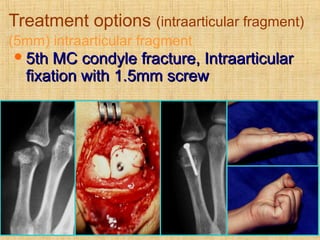
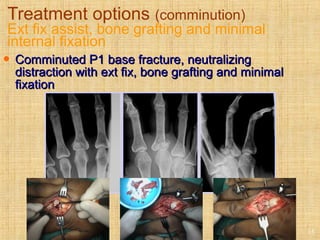
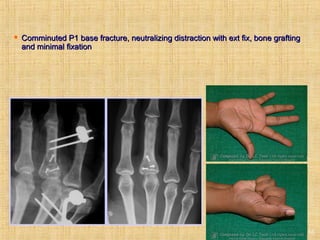
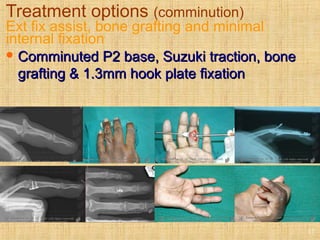
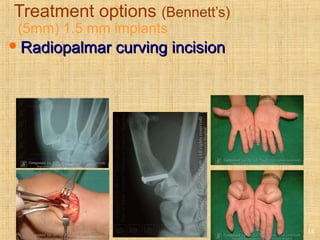
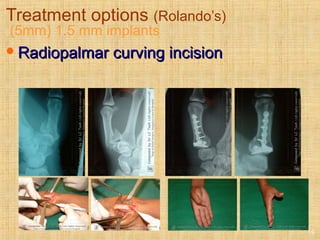
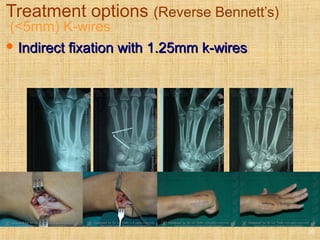
This document discusses intra-articular fractures of the hand and treatment options. Intra-articular fractures involve joint surfaces and can lead to deformity, subluxation, and loss of stability if not treated properly. Operative treatment is indicated for anatomically or functionally unstable fractures and aims for accurate reduction, stable fixation and early motion. The fixation strategy depends on the size and characteristics of the fracture fragments, ranging from screws and plates for large fragments to wiring, K-wires or hook plates for small fragments. Comminuted fractures can be treated with external fixation, bone grafting and minimal internal fixation. Various surgical approaches are used depending on the specific fracture.