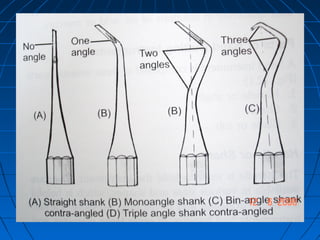
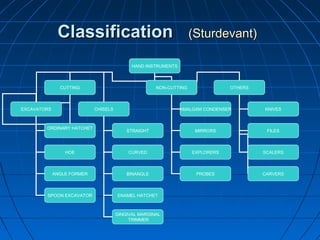
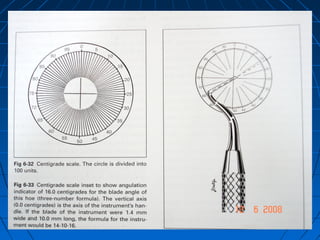
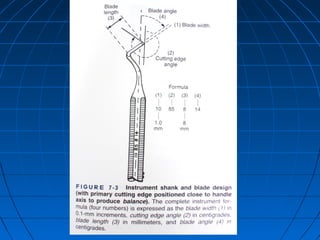
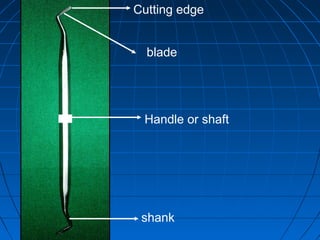
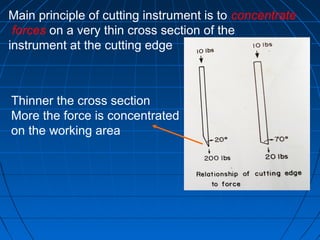
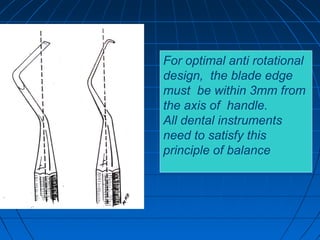
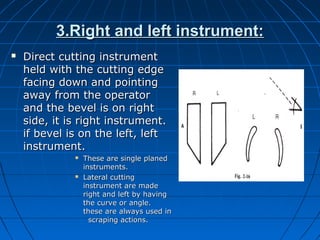
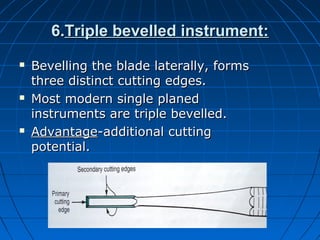
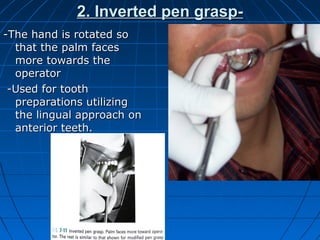
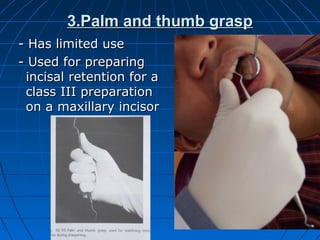
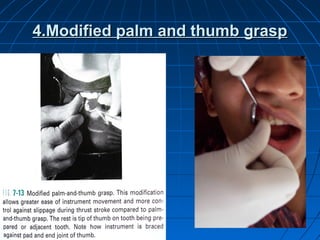
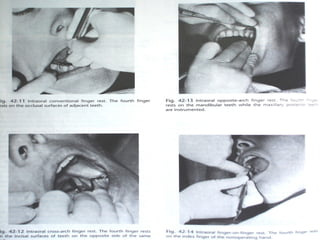
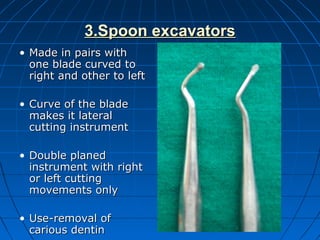
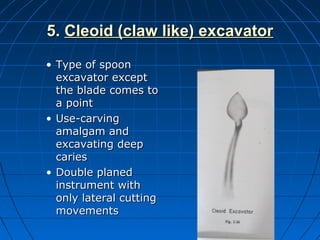
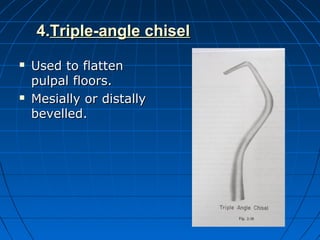
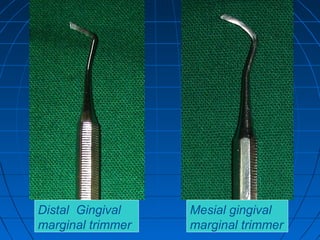
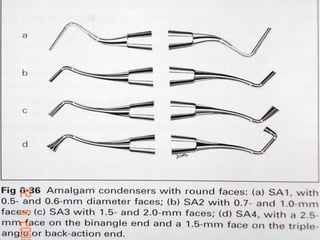
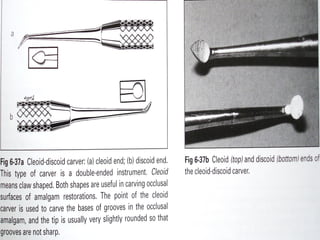
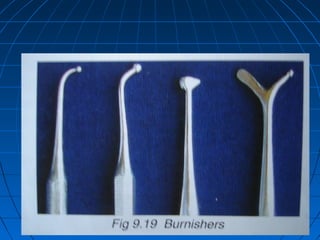
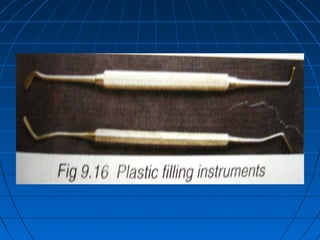
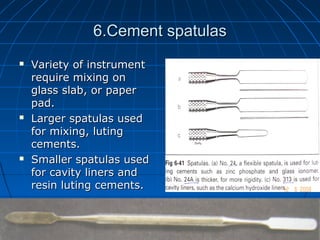
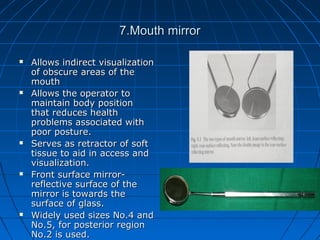
Hand instruments are essential tools for restorative dentistry. They are made from materials like stainless steel, carbon steel, and carbide to provide durability and sharp cutting edges. Instruments are classified based on their purpose, such as cutting or condensing, and their design features such as blade width, length, and angles. Proper instrument design concentrates force on the thin cutting edge. Instruments are also designed to balance within 3mm of the handle for control during use. Right and left versions are produced based on blade bevel orientation or curve. Hand instruments require maintenance like sharpening and sterilization to function effectively.