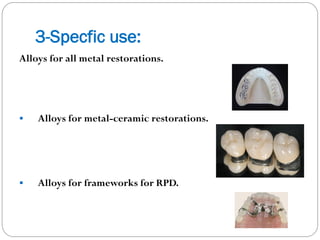
Dental casting alloys can be categorized as either noble metal alloys or base metal alloys. Noble metal alloys contain precious metals like gold, palladium, or silver and are commonly used to create indirect restorations through lost wax casting. Base metal alloys do not contain precious metals and provide a more economical option for removable partial denture frameworks and other restorations requiring high strength. Both alloy types aim to have suitable mechanical properties for their intended use as well as biocompatibility and corrosion resistance through alloying elements and microstructure design.


![Revision:
Metal:
It is an element which ionizes positively in solution.
Alloy:
It is the combination of 2 or more metals.
It allows combining of best properties of many metals for specific
purposes.
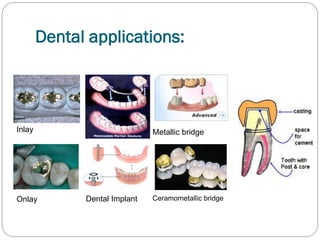
[Inlays, long span bridges, partial denture , etc.]
Shaping:
Metals & alloys are shaped by the dental casting technology.
It is the lost wax technique introduced by Taggart in 1907.
It is the process of turning wax pattern of restoration into metallic
one.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dentalcastingalloys-140212221658-phpapp01/85/Dental-casting-alloys-3-320.jpg)
![Revision:
Shaping:[Casting technology]
1. Create the wax pattern on the die.
2. Sprue the wax pattern.
3. Invest the wax pattern.
4. Burn out the invested pattern to create a mold.
5. Cast the molten metal.
6. De-investing.
7. Finishing & polishing.
8. Cementing.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dentalcastingalloys-140212221658-phpapp01/85/Dental-casting-alloys-4-320.jpg)
![Microstructure:[Cast structure]
This means grains [crystals regularity & repetition (crystalline)] &
grain boundaries[No regularity & no repetition(Amorphous)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dentalcastingalloys-140212221658-phpapp01/85/Dental-casting-alloys-5-320.jpg)

![Definition:
Solid solution alloy [S.S.] is a combination of 2 or more metals,
which are completely soluble in each other in both liquid & solid
states.
Properties:
It is stronger, harder but less ductile than the constituent
metals due to the difference in atomic size crystalline structure of
the alloy less than 15%. [solution hardening].
It is more ductile & resistant to tarnish & corrosion than
other types of alloys as S.S. is 1phase & homogenous.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dentalcastingalloys-140212221658-phpapp01/85/Dental-casting-alloys-7-320.jpg)

![1- Biological requirements:
not allergic.
cause no health hazards.
resistant to tarnish & corrosion.
This is achieved by :
-Use of solid solution alloy [1phase= homogenous]
-Use of noble alloy
-Use of base metal alloy with the passive layer.
It acts as corrosion barrier, because it is thin, non porous,
adherent & transparent surface oxide layer protecting the
underlying metal.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dentalcastingalloys-140212221658-phpapp01/85/Dental-casting-alloys-10-320.jpg)
![2- Functional requirements: :
a- all metallic restorations:
High yield strength:
to resist permanent deformation [Clinical ,Functional, failure]
High cantilever bending strength: to resist cantilever bending.
High transverse strength: to resist transverse bending.
High fatigue strength:
to resist cyclic loading.
High impact strength:
to absorb energy of fracture under sudden load.
High modulus of elasticity:to resist elastic deformation; for equal stress distribution
to preserve the supporting patient structures.
High ductility:
to facilitate burnishability
High resilience:
to absorb energy of elastic deformation so that not all the
stresses will be transmitted to the supporting patient structures
High toughness:
to absorb energy of fracture.
High hardness:
to preserve the finished & polished surface.
High sag resistance:
to resist plastic deformation during soldering [joining of
metallic parts by intermediate alloy]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dentalcastingalloys-140212221658-phpapp01/85/Dental-casting-alloys-12-320.jpg)
![2- Functional requirements:
b- ceramometallic restorations:
• The metal substructure [Coping] is first casted & then used to support the
brittle ceramic, which is built & fired on top.
• This restoration provides strength & aesthetics.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dentalcastingalloys-140212221658-phpapp01/85/Dental-casting-alloys-14-320.jpg)
![2- Functional requirements:
b- ceramometallic restorations:
Melting temperature of metal > Firing temperature of ceramic
to resist sag or melting of metal.
The coefficient of thermal expansion & contraction of metal slightly >α of porcelain
to bring the ceramic in state of compression which closes the cracks at the interface.
To strengthen ceramic. * To obtain compressive bonding between both of them.
Metal must form surface oxides layer
which react chemically with ceramic. [chemical bonding]
Metal must have surface roughness mechanical bonding with ceramic.
High modulus of elasticity
- No flexure Increase the fracture resistance of porcelain.
- Use in thin section Enough space for ceramics.
Metal must not discolor porcelain](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dentalcastingalloys-140212221658-phpapp01/85/Dental-casting-alloys-15-320.jpg)

![1- General classification:
Definitions
Noble metal is the one which retains a lustrous metallic surface
resisting tarnish & corrosion during casting, soldering & service.
i.e. It is stable in its elemental form.
Its nobility indicates the inertness of the element in relation to the
standard EMF series.
Noble metals: gold [Au] + platinum group.
The Platinum group:
-light group: -Ruthenium [Ru], rhodium [Rh], palladium [Pd].
-heavy group: -Osmium [Os], iridium [Ir], platinum [Pt].
Precious metals: noble metals + silver [Ag].
The base metal: the one which is reactive to atmosphere.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dentalcastingalloys-140212221658-phpapp01/85/Dental-casting-alloys-18-320.jpg)

![2-Mechanical properties:
Classification:
Type
% Elongation
[Ductility]
Type I [Soft]
140 MPa
Low hardness.
18% minimum. Inlay
Type II
[Medium]
140-200 MPa
Medium
hardness.
18%minimum.
Onlay
Type III [Hard]
Strength &
hardness
from type
I-IV
Yield stress
Hardness
Restoration
200-340 MPa
High hardness.
12%minimum.
Crown
Short bridge.
Type IV [Extra
hard]
340- 500 MPa
Extra high
hardness.
1o%minimum.
Crown
Long bridge
Post & Core
Partial denture
Ductility %
Elongation
from type I-IV](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dentalcastingalloys-140212221658-phpapp01/85/Dental-casting-alloys-20-320.jpg)
![2-Mechanical properties:
This classification is more clinically relevant, because:
The yield stress indicates
-Clinical [functional] failure of the restoration.
The hardness indicates
-The ease of finishing & polishing.
-The ability to retain the finished & polished surface.
The % elongation [Ductility] indicates
-The ability of the restoration for adjustment & burnishing.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dentalcastingalloys-140212221658-phpapp01/85/Dental-casting-alloys-21-320.jpg)

![Gold Restorations
Types:
1. Direct gold restorations.[Pure gold]
2. Indirect gold restorations.[Gold alloy Dental cast noble alloy]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dentalcastingalloys-140212221658-phpapp01/85/Dental-casting-alloys-24-320.jpg)

![Indirect gold restorations
General characteristics of gold[Au]:
Weak, soft, flexible, ductile & malleable.
Resist tarnish & corrosion.
Yellow color.
Melting temperature:1083ºC.[Relatively low]
Density:19g/cm3.
Coefficient of thermal expansion:14 Χ 10-6 /ºC.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dentalcastingalloys-140212221658-phpapp01/85/Dental-casting-alloys-27-320.jpg)
![Alloying elements in gold alloys for
all metallic restorations:
strength , hardness & stiffness; ductility
.·. Add to gold:
Platinum, Palladium, Silver & Copper
Solution Hardening due to difference in atomic size [less than15%]
Copper [Cu]
Hardening Heat Treatment
Iridium ,Ruthenium ,Rhodium
Grain Refiner
Coarse grains
Less grains
Less grain boundaries
Fine grains
More grains
More grain boundaries](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dentalcastingalloys-140212221658-phpapp01/85/Dental-casting-alloys-28-320.jpg)
![ Color:
.·. Add to gold
Platinum Palladium & Silver
Copper
To produce white color.
To enrich yellow color.
Cast-ability:
Silver
Ag in the molten state occludes gases porous casting.
Cu in the gold alloy will prevent this gas occlusion.
Ag reacts with sulfur tarnish layer on gold alloy.
Pd in the gold alloy prevent this reaction. [3:1]
Palladium
Pd in the molten state absorbs hydrogen porouscasting.
Zinc [Zn]
It acts as scavenger for oxides during manufacturing.
It increases fluidity of molten alloy by decreasing its surface
tension improving cast-ability.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dentalcastingalloys-140212221658-phpapp01/85/Dental-casting-alloys-29-320.jpg)
![Alloying elements in gold alloys for
ceramometallic restorations:
Melting temperature. Coefficient of thermal expansion &
contraction.
Platinum , Palladium [of high melting temperatures]
To obtain surface oxides.
Iron, Tin, Indium
Strength, hardness & stiffness.
Platinum , Palladium
Solution hardening due to difference in atomic size less than15%.
Iron
Reacts with platinum forming intermetallic compound, which precipitates
within the solid solution.[Precipitation hardening]
Neither Silver or especially Copper is added, because they
produce greenish discoloration to the ceramic.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dentalcastingalloys-140212221658-phpapp01/85/Dental-casting-alloys-30-320.jpg)



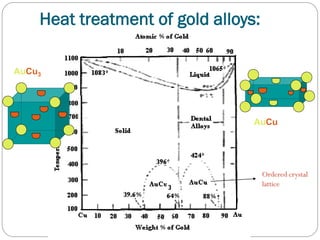
![• Heat Treatment of Gold Alloys: Au:Cu ≥88:12 [Types III & IV]
Disorder –Order Transformation
Softening heat treatment
REVERSIBLE
Procedures: Heat the alloy to 700ºC for
10 minutes then quench.
Effect:
Proportional limit, tensile strength &
hardness.
Hardening heat treatment[Age hardening]
Procedures: Heat the alloy to 424ºC
for 2minutes then cool to 250ºC over 30
minutes, then quench.
Effect:
Proportional limit, tensile strength &
hardness.
Ductility.
Modulus of elasticity is not affected.
Ductility.
Modulus of elasticity is not affected.
• Indicated for adjusting, burnishing &
• Indicated for service as oral restoration
polishing.
• Microstructure:
Disordered face centered cubic substitutional
solid solution.
delivered to the patient.
• Microstucture:
Precipitation of ordered face centered tetragonal
superlattice in disordered face centered
cubic substitutional solid solution.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dentalcastingalloys-140212221658-phpapp01/85/Dental-casting-alloys-36-320.jpg)
![• Heat Treatment of Gold Alloys: Au:Cu ≥88:12[Types III & IV]
Disorder- Order Transformation:
Explanation:
The thermal treatment provide the atoms with sufficient energy for
atomic diffusion.
This permits for regional ordering & precipitation of these superlattice in
the alloy structure Structural discontinuities Strengthening.
Factors affecting the amount of transformation:
The process depends on :
1. Composition of the alloy.
2. Temperature.
3. Time.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dentalcastingalloys-140212221658-phpapp01/85/Dental-casting-alloys-37-320.jpg)



![Mechanical properties:
Strength & hardness increase from Type I t o Type IV gold alloys.
Ductility [%elongation] decreases from Type I to Type IV gold
alloys.
2.
When compared to base metal alloys, gold alloys are:
Slightly weaker [Lower yield &ultimate strength]
Less stiff [Flexible, Lower modulus of elasticity] Used in thick
section to flex with the same degree as base metal alloys.
More ductile [Higher% elongation] More burnishable
Accurate fit restoration.
Less hard Easier to be finished & polished.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dentalcastingalloys-140212221658-phpapp01/85/Dental-casting-alloys-41-320.jpg)
![Physical properties & casting :
Color:
Gold alloys are either yellow or silvery white according to the alloying elements.
Melting temperature: 870˚C – 1050˚C.
Gold alloys can be easily melted by the reducing zone of gas air torch in carbon
crucible.
Casting shrinkage : 1.6%.
Use -Gypsum bonded investment.
-Phosphate bonded investment mixed with H2o.
Density: 15.2 – 16.8gm/cm3.[high density]
Use air pressure or centrifugal casting machine.
Better cast-ability, when compared to base metal alloys.
Cooling:
It is performed according to the type of the alloy.
-Slow or rapid cooling for Types I & II gold alloys.
-For Types III & IV cooling is done regarding to soft or hard condition.
3.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dentalcastingalloys-140212221658-phpapp01/85/Dental-casting-alloys-42-320.jpg)
![ Finishing & Polishing :
Acid pickling [immersion in warm hydrochloric acid solution] to remove
surface oxides.
Finishing & polishing are done by regular methods.
Recast:
Gold alloys can be recast.
Microstructure:
Small equi-axed grains.
Joining of metals
By soldering, using - Hard high fusing solder [gold solder]
- Boric acid flux
-Anti-flux
N.B.: Gold alloys cannot be spot welded ,as they are
characterized by high electrical conductivity No localized
heating for the area to be joined](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dentalcastingalloys-140212221658-phpapp01/85/Dental-casting-alloys-43-320.jpg)
![
1.
2.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Other Noble Alloys
Types:
Depending on the relative content of silver & palladium, there are:
Palladium silver. [60% - 30%]
Silver palladium.[70% - 25%]
Properties:
The recommended ratio [3 : 1] between silver & palladium is followed to
avoid silver sulfide formation.
Palladium is essential for high sag resistance & lowering α.
Silver is used to balance the low α to be slightly higher than that of ceramic
in ceramometallic restoration.
Presence tin & gallium is essential to provide surface oxides.
Their tendency to gas absorption during melting produces porous casting.
Their lower density requires greater centrifugal force for casting.
Their lower ductility results in lower burnishability.
They are substitutes for gold alloys Types III& IV.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dentalcastingalloys-140212221658-phpapp01/85/Dental-casting-alloys-44-320.jpg)

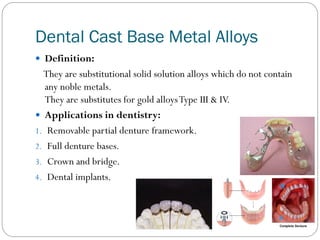
![Dental Cast Base Metal Alloys
Alternatives to gold alloys:
Due to continuous increased price of gold, alternative dental
casting alloys has been introduced for Types III & IV gold
alloys such as:
Economy gold alloys.
Silver palladium alloys.
Palladium silver alloys.
Base metal alloys. [Further cost reduction]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dentalcastingalloys-140212221658-phpapp01/85/Dental-casting-alloys-46-320.jpg)

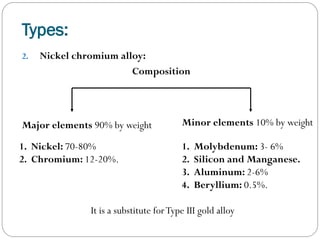
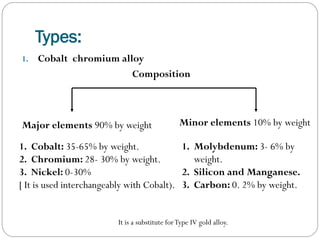
![ Role of each element in cobalt chromium & nickel chromium alloys:
Major elements:
1- Cobalt
2- Nickel
Strength.
Hardness.
Modulus of elasticity.
Strength.
Hardness.
Modulus of elasticity.
Ductility.
Nickel is allergic .[female>male] gingival discoloration, swelling or
redness
.˙. Nickel free base metal alloys has been introduced.
3- Chromium
Tarnish &corrosion resistance by passive layer.
Passive layer is an oxide layer , which is thin,
uniform, nonporous, adherend & transparent.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dentalcastingalloys-140212221658-phpapp01/85/Dental-casting-alloys-51-320.jpg)


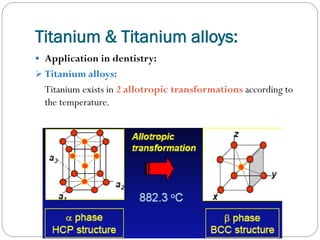
![Types:
3.
Titanium & Titanium alloys:
Introduction:
Titanium is named after the Titans, the powerful sons of the
earth in Greek mythology.
Application in dentistry:
Commercially pure titanium. [CpTi]
There are 4 grades of CpTi according to oxygen [0.18- 0.4%]
& iron [0.2- 0.5%] with different properties & applications.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dentalcastingalloys-140212221658-phpapp01/85/Dental-casting-alloys-54-320.jpg)



![Properties:
Mechanical properties:
N.B.:
Mechanical properties of CpTi are similar to gold alloy Types III & IV.
While those of titanium alloys are similar to cobalt chromium and nickel
chromium alloys.
When compared to gold alloys, the base metals are:
Slightly stronger [Higher yield & ultimate strength]
Double stiffer [Double modulus of elasticity] Used in thin section & still
retain their rigidity.
Less ductile [Lower % elongation] Less burnishable.
Harder [1/3] Difficult to be finished & polished but retain their surface
for longer time.
2.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dentalcastingalloys-140212221658-phpapp01/85/Dental-casting-alloys-59-320.jpg)
![3.
Physical properties & casting:
Color:
Silvery white.
Melting range: ~1400ºC.
They need complicated & expensive technique for melting e.g. Melting in
ceramic crucible by oxygen acetylene flame or electric induction.
They are very reactive to the atmosphere. .·. Vacuum casting is required.
They are of high sag resistance, an advantage for soldering &
ceramometallic restoration.
Casting shrinkage:~2.3%[High casting shrinkage]
Use dental carbon free investment with stable oxides.
Phosphate bonded investment mixed with special liquid.
Silicate bonded investment with vents.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dentalcastingalloys-140212221658-phpapp01/85/Dental-casting-alloys-60-320.jpg)
![Physical properties & casting:
Density: 4-8gm/cm3 [Low density]
They need high casting force to obtain complete casting.
They should be cast using special designed casting machines to produce
high casting force.
However, they are useful in construction of bulky restorations [e.g. upper
denture] due to the light weight, which aids in retention of the appliance &
comfortable feeling for the patient.
Cooling:
Bench cooling.
Finishing & polishing:
Acid pickling should be avoided, as it attacks the passive layer.
They are difficult to be finished & polished due to their high hardness.
Sandblasting & electrolytic etching are essential.
3.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dentalcastingalloys-140212221658-phpapp01/85/Dental-casting-alloys-61-320.jpg)
![Properties:
3.
Physical properties & casting:
Recast:
They can not be recast due to their high technique sensitivity,
which can affect both their microstructure & properties.
Microstructure:
Coarse grains.
Heat treatment:
The mechanical properties of cobalt chromium alloys are not
improved by heat treatment.
The ductility of nickel chromium alloys can be improved by
dissolution of carbides at the grain boundaries.
Heat treatment of titanium alloys is complicated.[Out of scope]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dentalcastingalloys-140212221658-phpapp01/85/Dental-casting-alloys-62-320.jpg)
![Physical properties & casting:
Joining of metals:
By soldering using: -Hard low fusing solder
-Fluoride containing flux [capable of removing
the passive layer at the site of soldering]
-Anti-flux
N.B.:
The lab work of dental base metal alloys is very difficult due to:
- High melting point.
- High reactivity to atmosphere.
- Low density.
- Difficult in finishing & polishing.
- Inability to recast.
- Poor burnishability.
- High casting shrinkage.
3.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dentalcastingalloys-140212221658-phpapp01/85/Dental-casting-alloys-63-320.jpg)