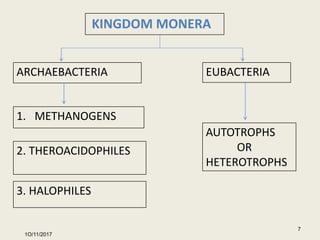
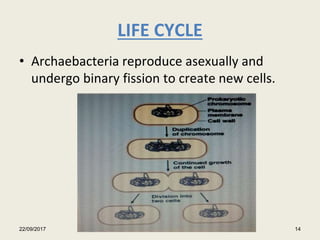
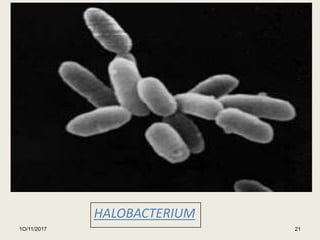
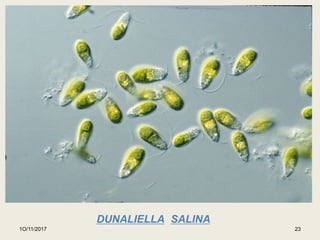
The document summarizes information presented in a seminar on halophiles. It defines halophiles as organisms that can live in high salt concentrations. It discusses where halophiles are found, how they are classified, and examples like archaea, Halobacterium, and Dunaliella salina. It explains the mechanisms halophiles use to survive in high salt, including osmoregulation, accumulating compatible solutes, and taking in salt. It also outlines their applications in industries like cosmetics, food coloring, and wastewater treatment.