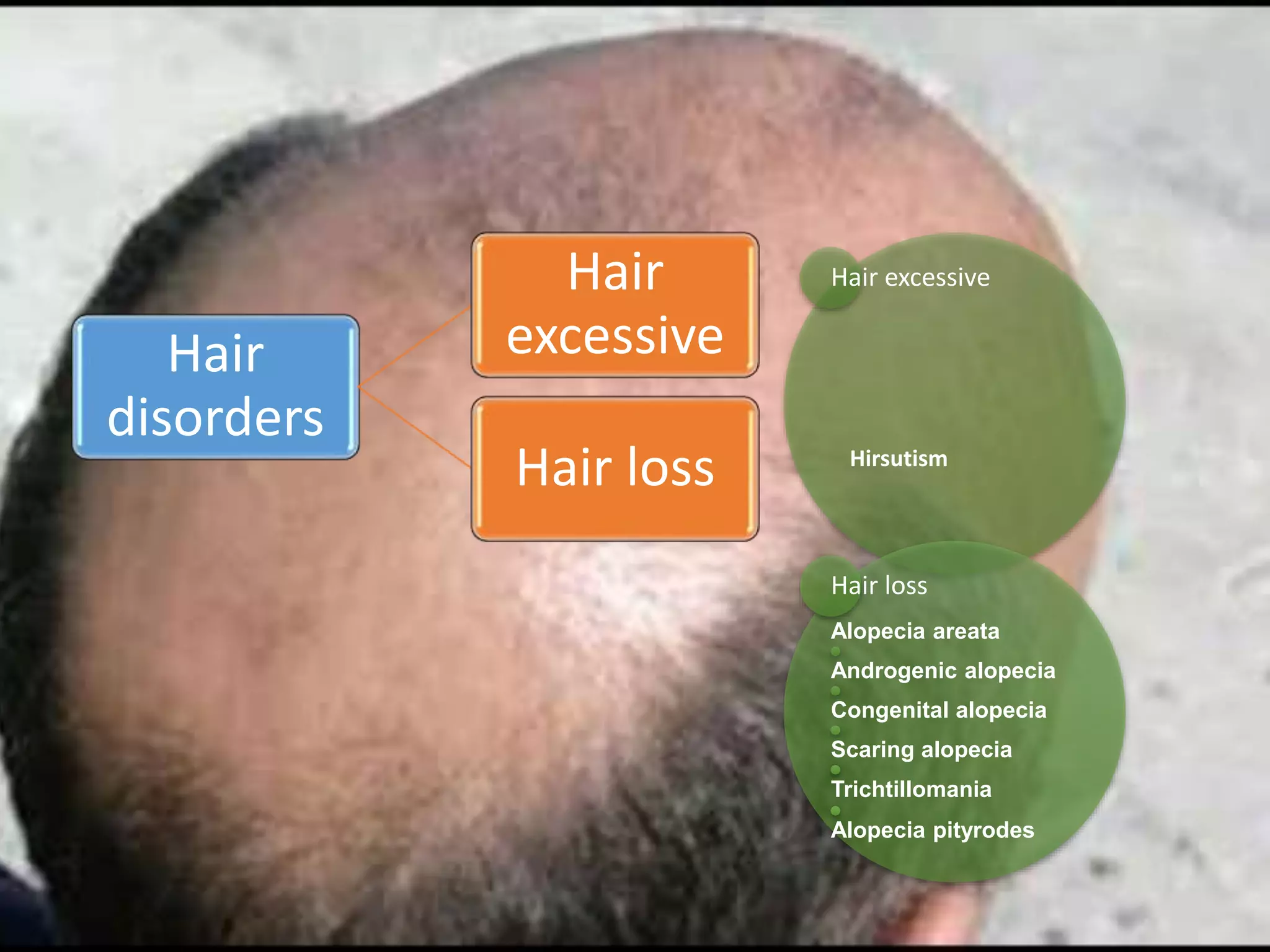
1) Hirsutism is defined as excessive terminal hair growth in androgen-dependent areas of the body in women, which grows in a typical male distribution pattern. It is often caused by androgen overproduction or increased sensitivity to androgens. Diagnosis is usually clinical and confirmed with laboratory testing. Treatment options include oral contraceptives, spironolactone, and anti-androgens.
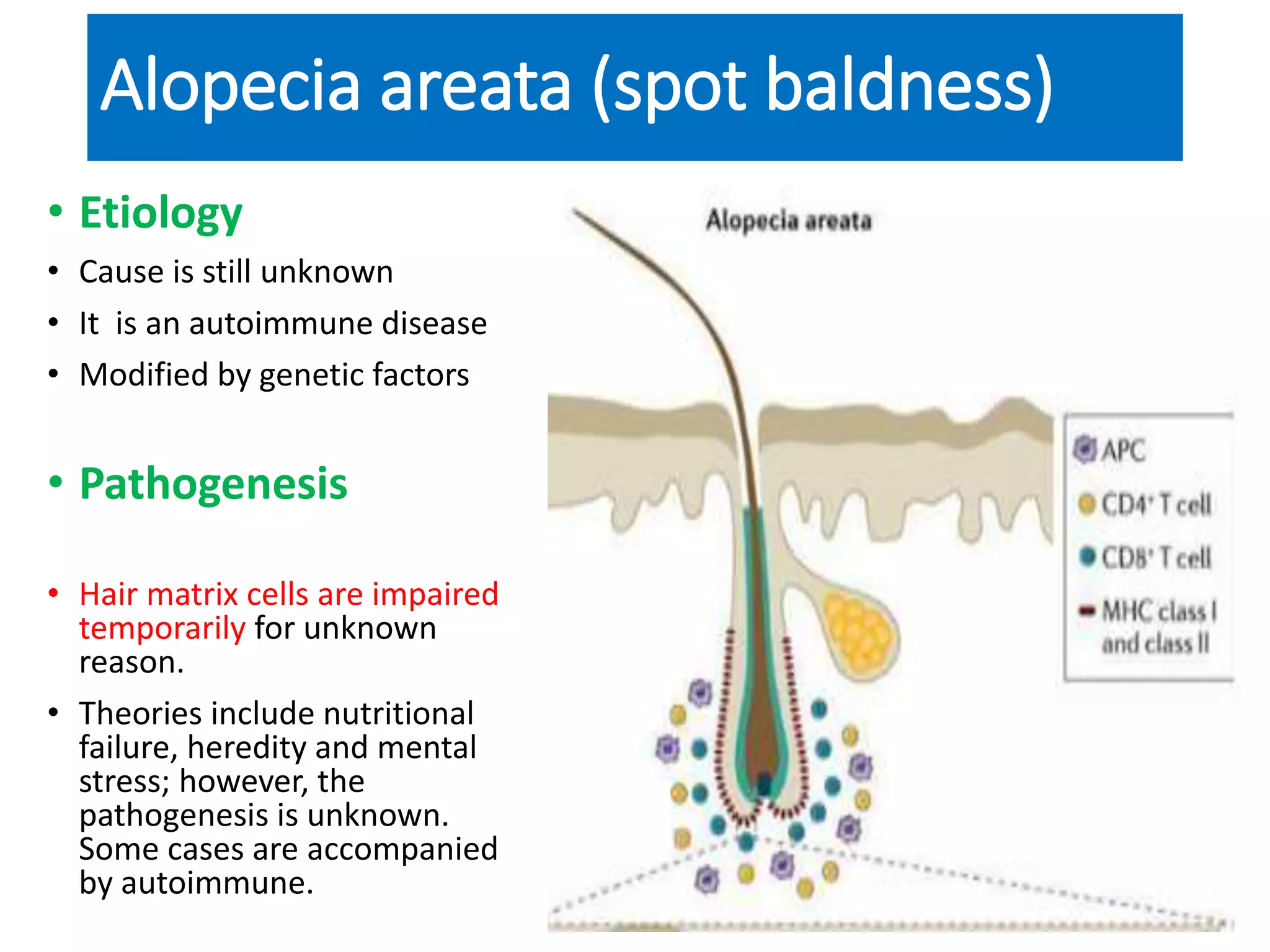
2) Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease causing patchy, non-scarring hair loss. It affects the scalp and sometimes other hair-bearing areas. Treatment focuses on reducing inflammation and regrowth of hair. Options include topical corticosteroids, immunotherapy, and supportive