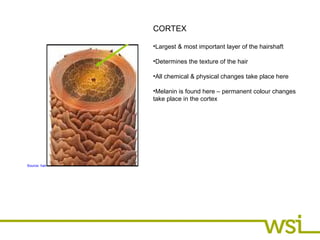
The hair consists of three layers - the medulla, cortex, and cuticle. The medulla is the inner core and may contain melanin. The cortex is the largest layer and determines hair texture and holds melanin. The cuticle is the outer protective layer.
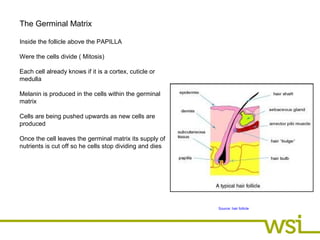
The hair follicle contains the papilla, germinal matrix, and hair bulb. The papilla supplies nutrients to the germinal matrix where new hair cells are produced. These cells are pushed up through the hair bulb where they harden into the hair shaft before exiting the skin surface.