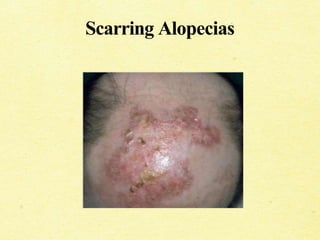
Alopecia is defined as hair loss from areas where hair normally grows. There are several types of alopecia including alopecia areata (patchy hair loss), alopecia totalis (total hair loss of the scalp), alopecia universalis (total hair loss of the entire body), and androgenetic alopecia (male or female pattern baldness). Causes can include autoimmune conditions, certain medications, medical conditions, radiation/chemotherapy, and genetics. Diagnosis involves history, physical exam, and sometimes blood tests. Treatment options include minoxidil, finasteride, corticosteroid injections, wigs, hair transplants, massage, and UV light therapy.