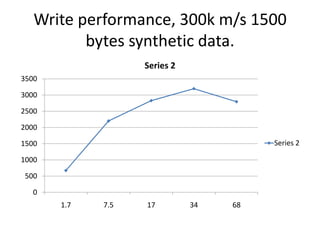
This document summarizes the key points from a review of a Hadoop/HBase proof of concept (POC). It includes performance tests of HBase write performance on Amazon AWS and Dell hardware. The AWS instances achieved 3,500-4,000 packets per second while the Dell hardware was slower at around 3,500 packets per second. Tuning the Dell hardware configuration and optimizing HBase regions and compactions could potentially improve write performance. The document also covers read performance tests and filtering techniques to improve query performance on large datasets.