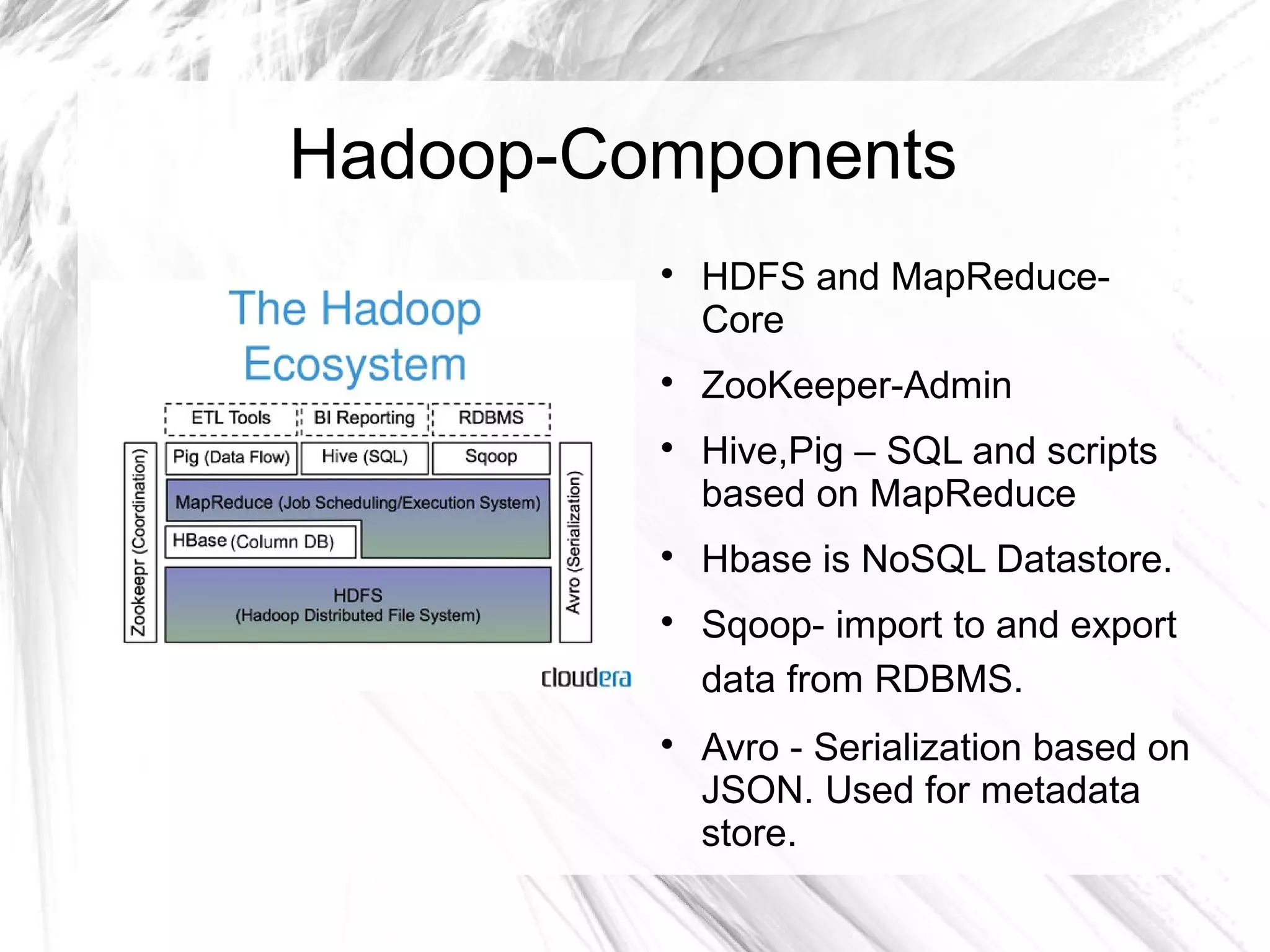
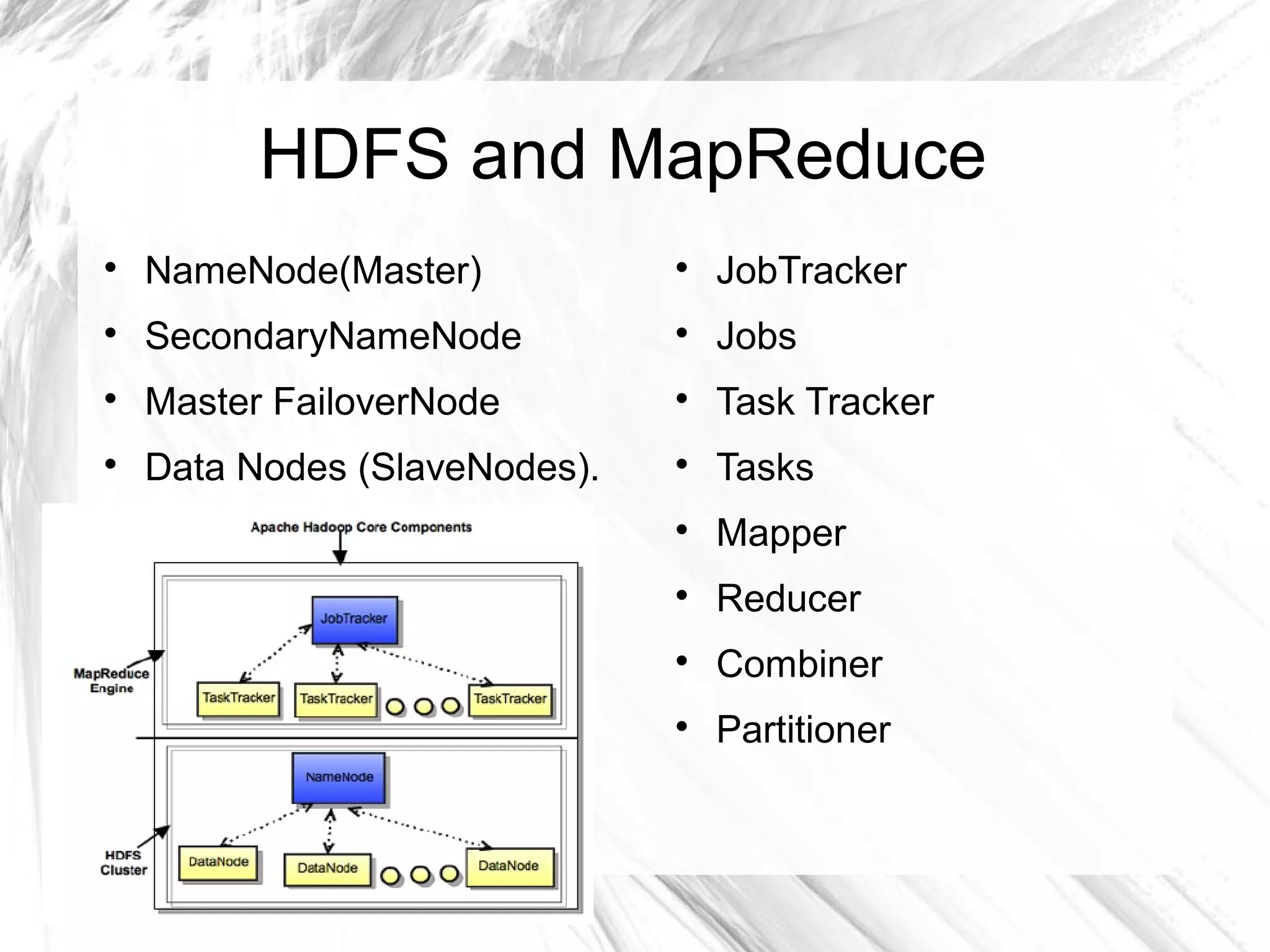
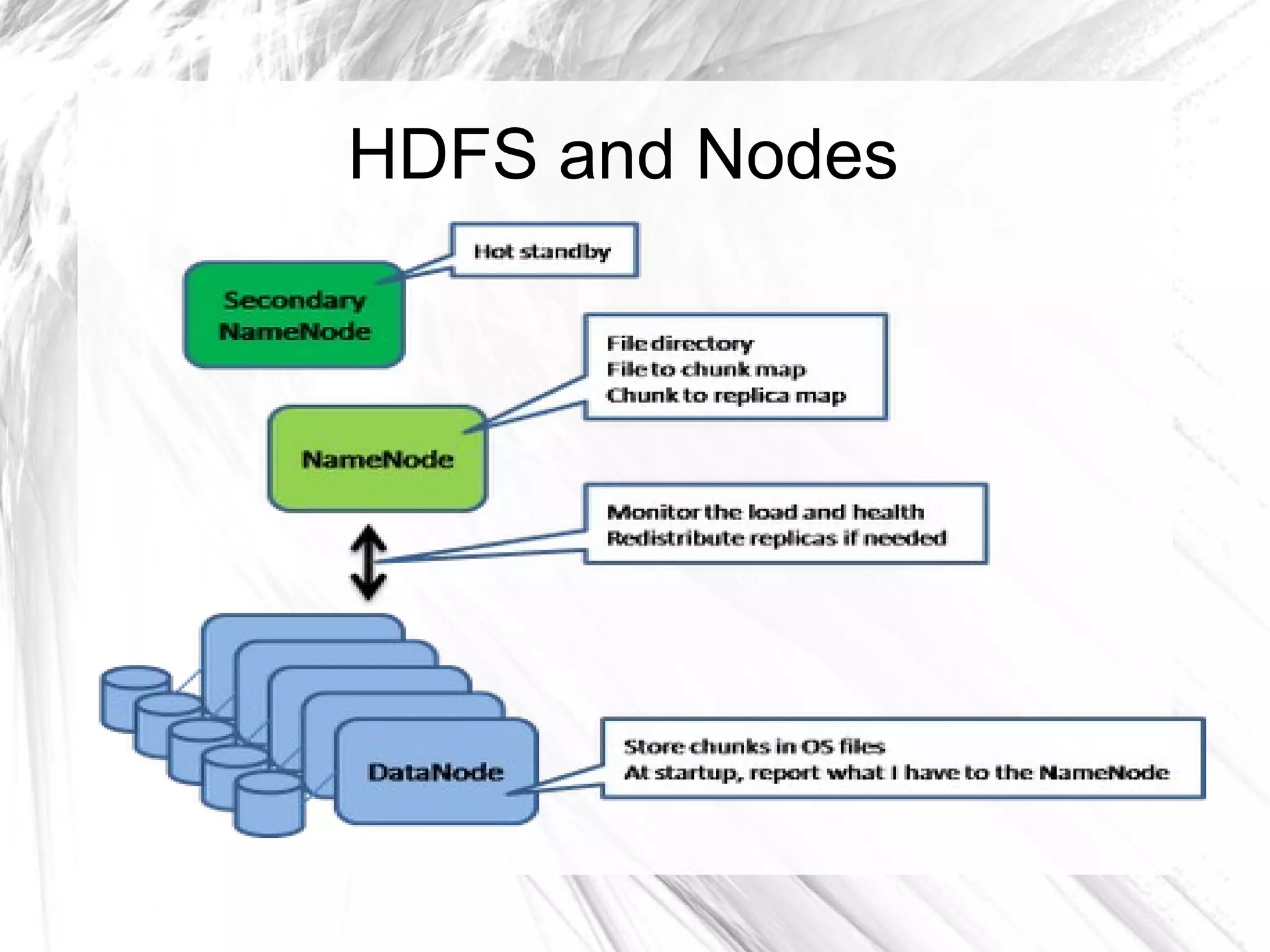
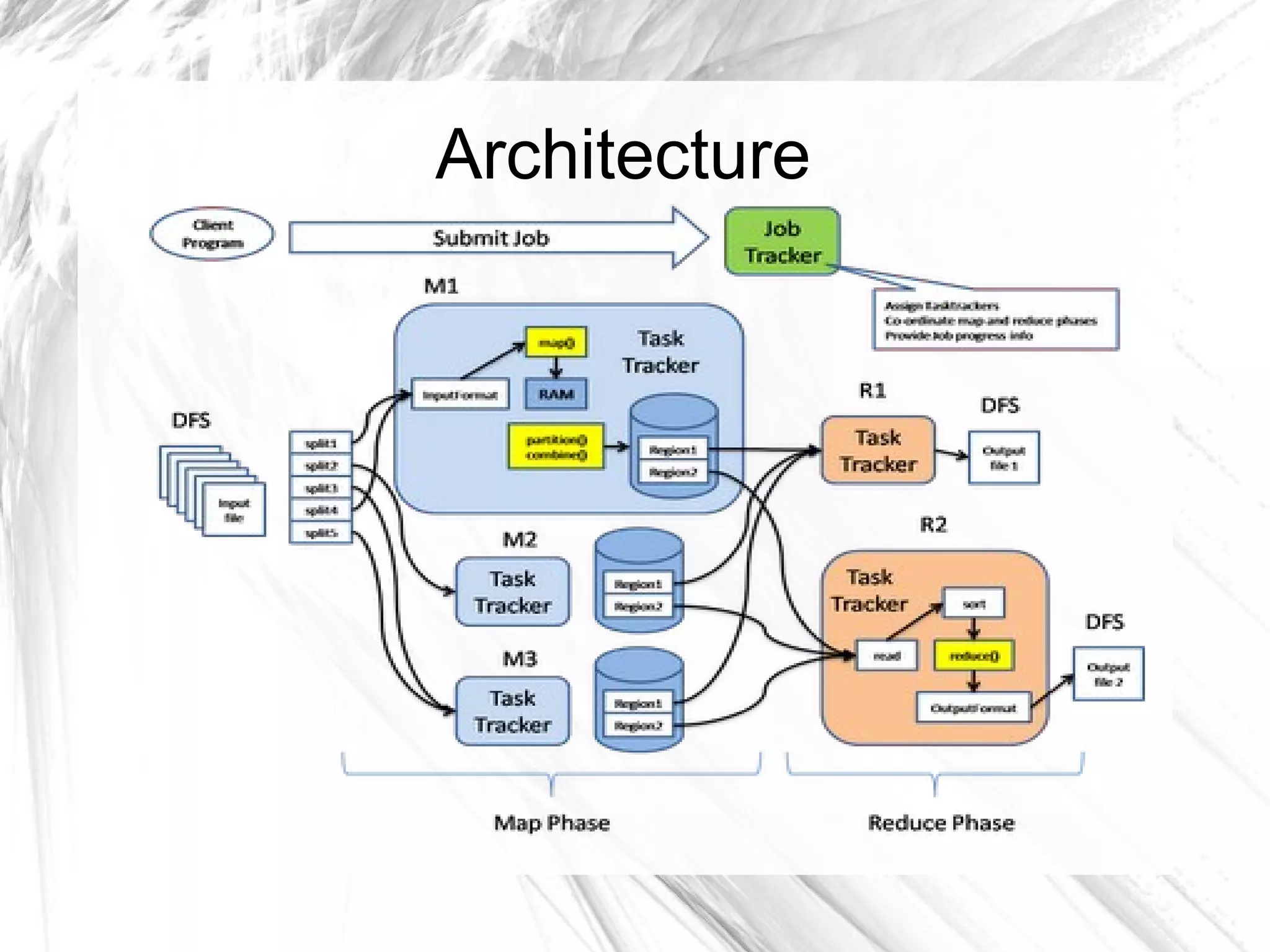
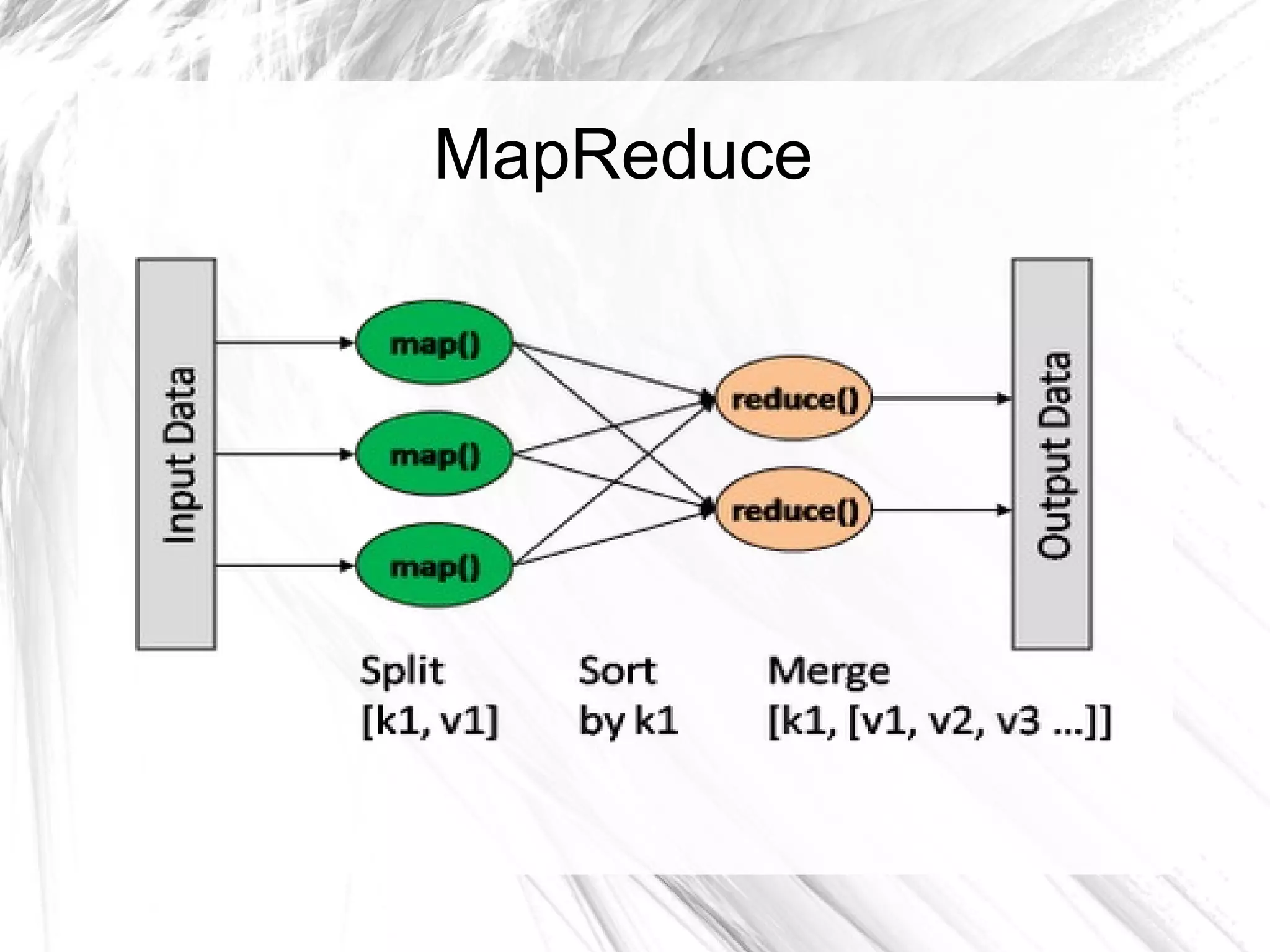
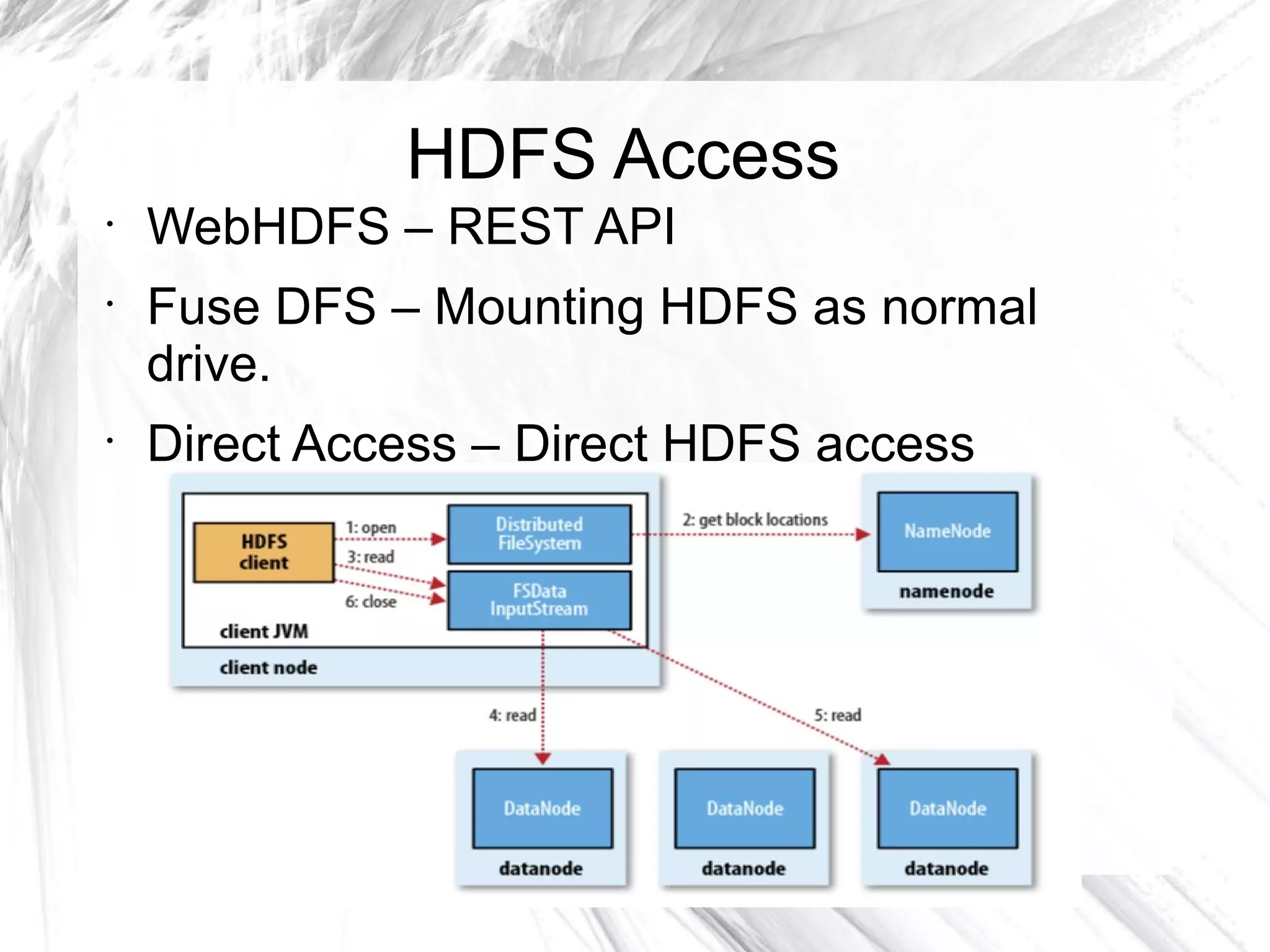
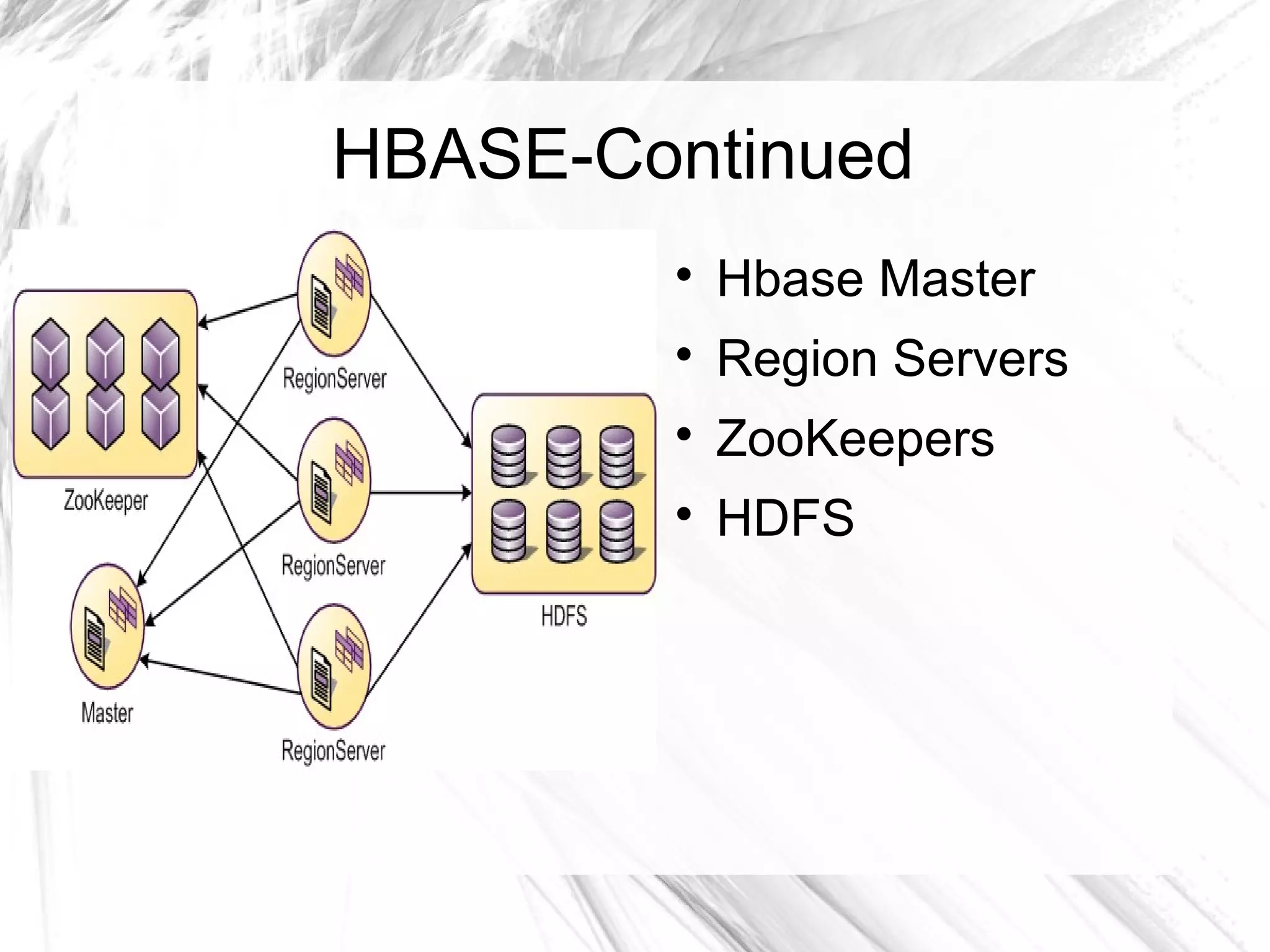
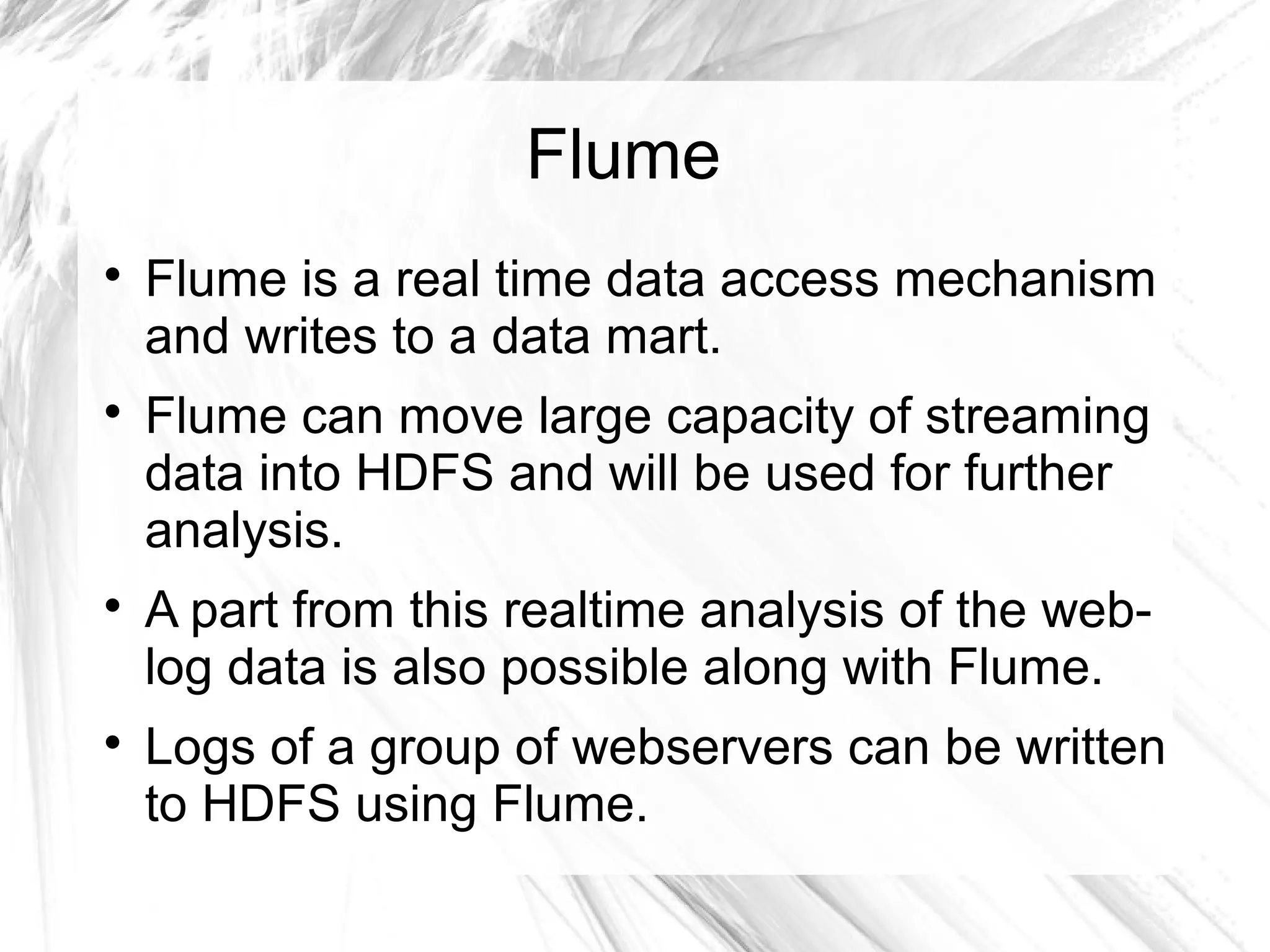
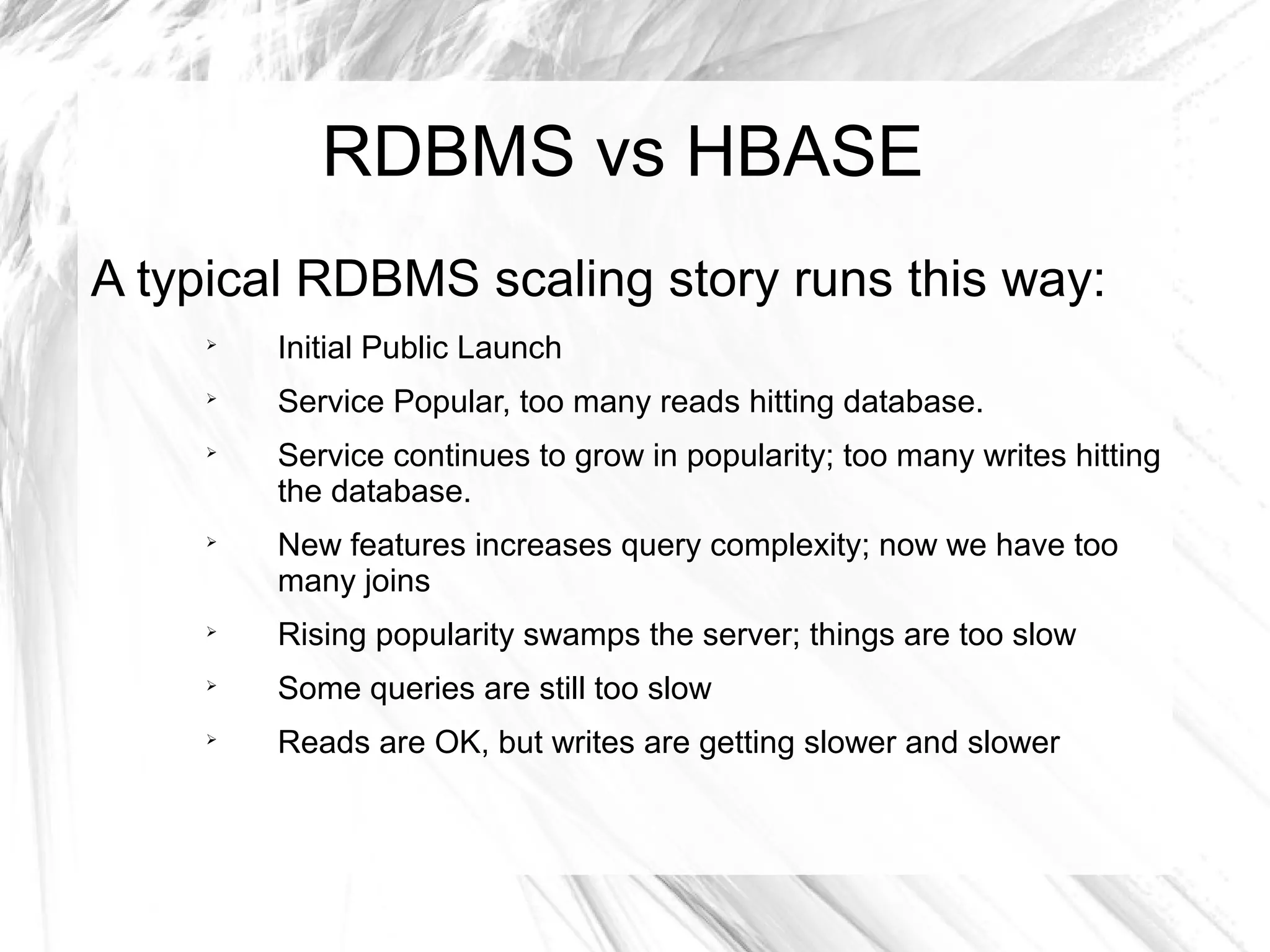
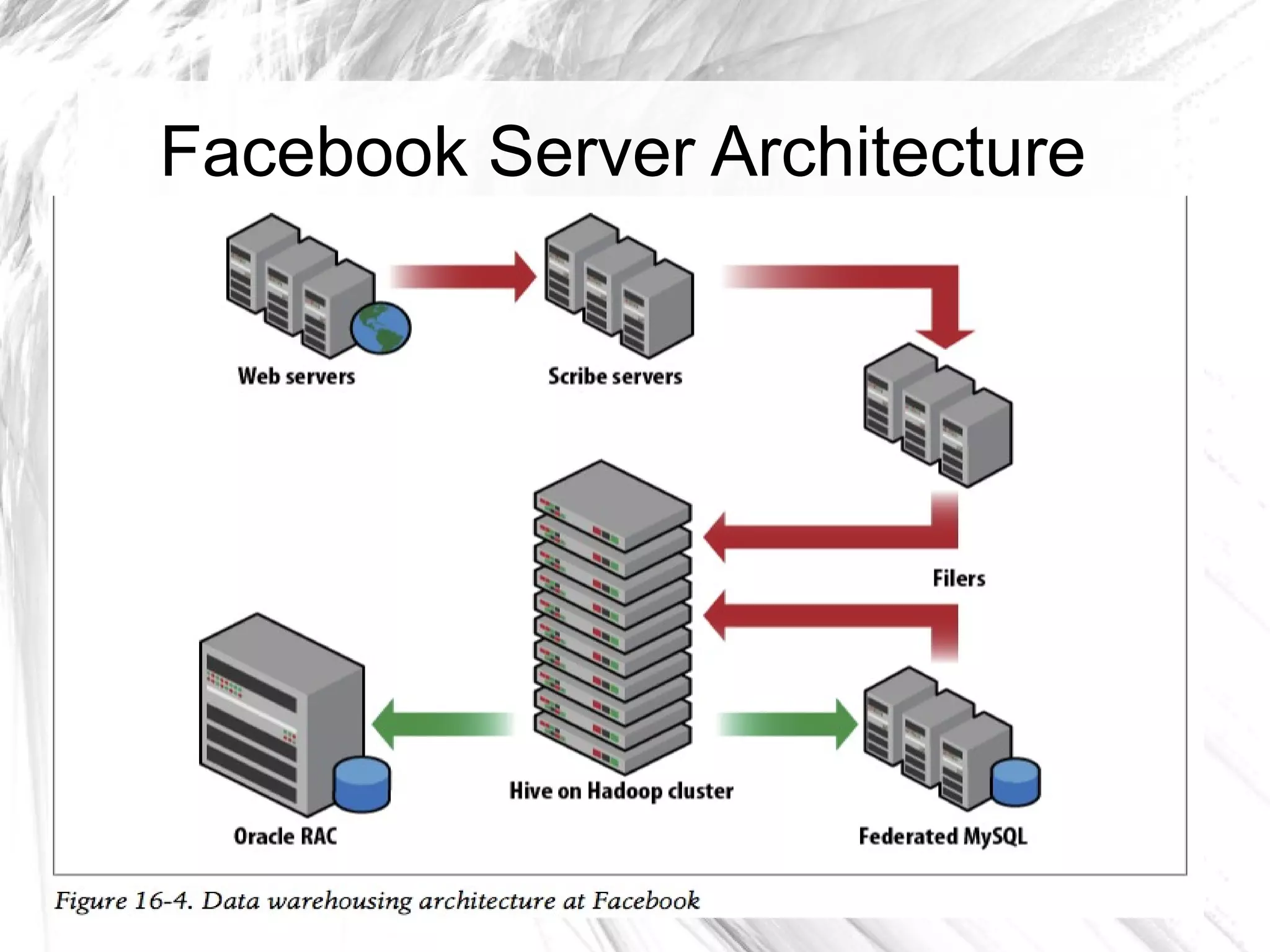
The document provides an overview of big data and Hadoop, detailing its architecture, components, and tools used for processing large datasets. It discusses the challenges of big data management and the advantages of using Hadoop alongside traditional RDBMS for efficient data processing. Key Hadoop components such as HDFS, MapReduce, Hive, Pig, and HBase are explained, highlighting their roles in distributed data operations and analytics.