This document provides an overview of important concepts for operating HBase, including:
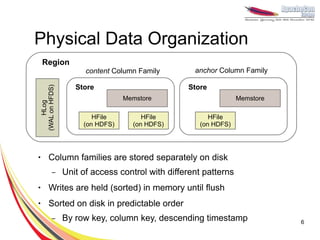
- HBase stores data in columns families stored as files on disk and writes to memory before flushing to disk.
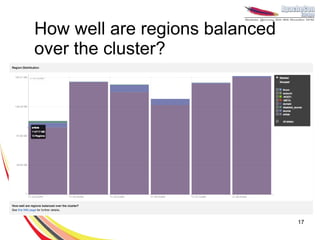
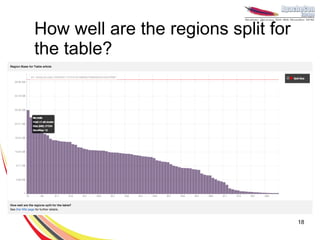
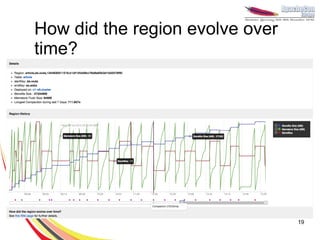
- Manual and automatic splitting of regions is covered, as well as challenges of improper splitting.
- Tools for monitoring, debugging, and visualizing HBase operations are discussed.
- Key lessons focus on proper data modeling, extensive monitoring, and understanding the whole Hadoop ecosystem.




![Data Model
● A sparse, multi-dimensional, sorted map
● Table consist of rows, each has a row key
● Each row may have any number of columns
● Rows are sorted lexicographically based on row key
● Column = Column Family : Column Qualifier
– Cell → {rowkey, column, timestamp}
[Bigtable: A Distributed Storage System for Structured Data]
● Region: contiguous set of sorted rows
● Region: unit of distribution and availability 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachecon-europe-operating-hbase-121106101235-phpapp02/85/Apachecon-Europe-2012-Operating-HBase-Things-you-need-to-know-5-320.jpg)

![System Architecture
HBase API
RegionServer
Master
HFile Memstore
Write-Ahead Log
HDFS ZooKeeper
[HBase: The Definitive Guide]
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachecon-europe-operating-hbase-121106101235-phpapp02/85/Apachecon-Europe-2012-Operating-HBase-Things-you-need-to-know-8-320.jpg)